The process of removing biological matter from porous bedding surfaces necessitates prompt and methodical action. Addressing such discoloration promptly minimizes the likelihood of permanent staining and prevents the potential growth of bacteria. Delaying intervention may lead to deeper penetration of the stain within the mattress fibers, rendering removal significantly more challenging.
Effective stain removal contributes to the longevity and hygiene of the sleeping environment. Maintaining a clean mattress is important for promoting healthy sleep and reducing potential allergens. Historically, various methods have been employed, from simple water and soap solutions to more sophisticated enzymatic cleaners, reflecting a continuous effort to preserve the integrity of mattresses.
The following sections will detail specific techniques for treating affected areas, encompassing readily available household remedies and commercially available products. These methods prioritize both efficacy and the preservation of the mattress material.
Strategies for Bloodstain Removal from Mattresses
The following strategies outline effective methods for addressing bloodstains on mattresses. Immediate action and the correct application of cleaning agents are crucial for optimal results.
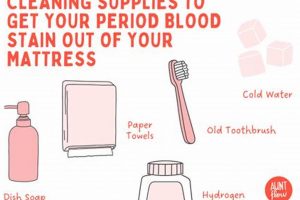
Tip 1: Cold Water Application: Initiate the cleaning process by applying cold water directly to the stained area. Avoid hot water, as it can cause the blood to coagulate and set the stain. Blot the area gently with a clean cloth or sponge, working from the outside of the stain inward.
Tip 2: Salt Paste Formulation: Create a paste using cold water and table salt. Apply the paste generously to the stain, ensuring complete coverage. Allow the paste to sit for approximately 30 minutes, enabling the salt to draw out the blood. Subsequently, blot the area with a damp cloth.
Tip 3: Hydrogen Peroxide Application: Exercise caution when utilizing hydrogen peroxide. Test a small, inconspicuous area of the mattress first to ensure colorfastness. If no discoloration occurs, apply a small amount of 3% hydrogen peroxide directly to the stain. Blot gently and allow to air dry. Note that hydrogen peroxide may lighten the fabric.
Tip 4: Baking Soda Solution: Prepare a solution of baking soda and cold water. Apply the solution to the affected area and allow it to sit for several hours, or preferably overnight. Baking soda acts as a natural deodorizer and absorbent. Vacuum the dried baking soda residue from the mattress.
Tip 5: Enzyme Cleaner Utilization: Consider using an enzyme-based cleaner specifically formulated for biological stains. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. Enzyme cleaners break down the proteins in the blood, facilitating removal. Allow the cleaner to penetrate the stain thoroughly before blotting.
Tip 6: Cornstarch Application: Combine cornstarch with cold water to form a paste. Apply the paste to the stain and allow it to dry completely. The cornstarch will absorb the blood. Vacuum the dried residue.
Tip 7: Ammonia Solution (Use with Caution): Dilute ammonia with cold water. Apply the solution to the stain and blot gently. Exercise extreme caution, as ammonia can be irritating and should never be mixed with bleach. Ensure adequate ventilation.
Prompt and appropriate application of these techniques can significantly improve the likelihood of successful bloodstain removal and contribute to the maintenance of a hygienic sleeping environment.
Following these specific treatments, the subsequent section will address preventative measures and long-term mattress care.
1. Prompt Action
The temporal element plays a decisive role in the efficacy of bloodstain removal from mattresses. Delay directly correlates with the degree of difficulty encountered during the cleaning process and the likelihood of residual discoloration. The longer blood remains on the mattress surface, the deeper it penetrates the fibers, forming a stronger bond that resists removal efforts.
Consider the scenario of a minor nosebleed occurring during sleep. If addressed immediately upon discovery, a simple application of cold water and gentle blotting may suffice to eliminate the stain entirely. Conversely, if the stain is left untreated for several days, the blood will dry and solidify, requiring more aggressive cleaning agents and techniques, potentially causing damage to the mattress material. The initial prompt intervention significantly reduces the need for extensive measures.
Therefore, immediate response is a critical component of effective mattress stain removal. Understanding this principle empowers individuals to minimize damage and maintain the integrity of their mattresses. The subsequent steps are rendered more effective when undertaken swiftly, reinforcing the importance of prompt action in the overall process.
2. Cold Water Only
The use of cold water is a fundamental principle in the effective removal of bloodstains from mattresses. This approach leverages the specific properties of blood and its interaction with temperature to facilitate stain removal without exacerbating the problem. Understanding the scientific rationale behind this practice is crucial for successful stain mitigation.
- Protein Coagulation Prevention
Heat causes the proteins in blood to coagulate, essentially cooking them and binding them more tightly to the mattress fibers. Cold water, conversely, helps to keep the proteins in a more soluble state, allowing them to be more easily lifted and removed. This principle is analogous to rinsing raw meat; cold water is used to prevent the proteins from hardening.
- Fiber Protection
Mattress fibers, particularly those made from natural materials, can be susceptible to damage from high temperatures. Using cold water minimizes the risk of shrinking, distortion, or other forms of degradation that can occur with heat exposure. This preservation of fiber integrity contributes to the longevity of the mattress.
- Stain Minimization
By preventing coagulation, cold water minimizes the staining effect. When proteins are not coagulated, they are less likely to set permanently into the fibers. This allows cleaning agents to penetrate more effectively and lift the blood molecules from the mattress, reducing the residual discoloration.
- Enhanced Solubility of Cleaning Agents
While some cleaning agents may benefit from warm water activation, the initial application of cold water to remove the bulk of the blood is critical. The subsequent use of specialized cleaners is made more effective when the initial blood mass has been addressed with cold water, as the remaining stain is less resistant to chemical action.
In summary, the exclusive use of cold water when addressing bloodstains on a mattress is not merely a conventional practice but a scientifically sound approach. It prevents protein coagulation, protects mattress fibers, minimizes staining, and enhances the solubility of cleaning agents, all contributing to more effective stain removal and the preservation of the mattress’s condition. Adherence to this principle is paramount for successful stain mitigation.
3. Blot, Never Rub
The admonition to “blot, never rub” when addressing biological stains on mattresses is not merely a suggestion, but a critical procedural element in effective stain management. When blood comes into contact with mattress fibers, rubbing the affected area forces the liquid deeper into the material. This action expands the surface area of the stain, embedding the blood within the intricate network of fibers and padding that constitute the mattress core. Consequently, stain removal becomes significantly more challenging, often resulting in permanent discoloration, or necessitating professional cleaning services. The immediate impact of rubbing is the increased saturation of the stain and an impediment to the efficacy of subsequent cleaning agents.
Consider a scenario where a small droplet of blood stains a mattress. If the immediate response is to rub the area vigorously with a cloth, the blood will spread laterally and vertically within the mattress structure. This distributes the stain across a larger area, making it more difficult to lift the blood from the fibers. In contrast, if blotting is employed, a clean cloth absorbs the blood, drawing it upwards and outwards without forcing it deeper. This approach minimizes the stain’s penetration and concentrates the residue on the surface, enabling more effective removal. The blotting technique maintains the stain’s localized presence, while the rubbing action diffuses it through the mattress.
Therefore, adhering to the “blot, never rub” principle is a prerequisite for successful mattress stain removal. The technique preserves the stain’s integrity and minimizes penetration, thereby maximizing the effectiveness of cleaning solutions and increasing the likelihood of complete stain eradication. Failure to implement this basic measure can render subsequent cleaning efforts less effective, potentially causing permanent damage to the mattress fabric and structural components. The awareness and application of the blotting technique is fundamental to maintaining a hygienic sleeping environment and prolonging the lifespan of the mattress.
4. Appropriate Solution
The selection of a suitable cleaning solution is paramount for the effective removal of bloodstains from a mattress. The efficacy of any stain removal method is directly contingent upon the correct choice of cleaning agent, tailored to the specific characteristics of both the stain and the mattress material. Inappropriate solutions may lead to ineffectual cleaning, permanent discoloration, or damage to the mattress fabric.
- Enzymatic Cleaners: Mechanism and Application
Enzymatic cleaners, specifically formulated for biological stains, contain enzymes that catalyze the breakdown of proteins, fats, and other organic components found in blood. These enzymes sever the bonds that hold the stain molecules together, facilitating their removal. For example, protease enzymes target and degrade protein-based stains, while lipase enzymes act on fatty components. These cleaners are particularly effective on older, set-in stains. Appropriate application involves saturating the stained area, allowing the cleaner to dwell for a specified period (as per the product instructions), and then blotting away the residue. Incorrect utilization or failure to follow manufacturer guidelines can reduce efficacy and potentially damage the mattress fabric.
- Hydrogen Peroxide: Precautions and Limitations
Hydrogen peroxide (3% solution) possesses oxidizing properties that can effectively lift bloodstains from mattresses. However, its use requires caution due to its potential to bleach or discolor certain fabrics. Prior to application, a small, inconspicuous area should be tested to assess colorfastness. Hydrogen peroxide is most effective on fresh stains and may require repeated applications for older, more stubborn stains. Overuse or application on incompatible materials, such as dark-colored fabrics, can result in irreversible lightening or damage.
- Baking Soda Paste: Absorbent Properties and Application
A paste made from baking soda and water offers a gentle yet effective means of drawing out bloodstains. Baking soda acts as an absorbent agent, drawing moisture and stain molecules from the mattress fibers. The paste should be applied liberally to the affected area, allowed to dry completely, and then vacuumed away. This method is particularly suitable for delicate fabrics or when a less aggressive approach is desired. Incomplete removal of the baking soda residue may leave a powdery residue on the mattress surface.
- Ammonia Solution: Dilution and Safety Considerations
Diluted ammonia solution can be used to treat bloodstains; however, its use necessitates strict adherence to safety precautions. Ammonia is a harsh chemical that can irritate the skin and respiratory system. It should be diluted appropriately (typically a few drops in a cup of water) and used in a well-ventilated area. Moreover, ammonia should never be mixed with bleach, as this can produce toxic fumes. This solution is more effective on certain fabrics but carries a higher risk of damage or discoloration if not used correctly. Its application should be reserved for cases where other methods have proven ineffective, and only after careful testing and with full awareness of the potential hazards.
In conclusion, the strategic selection and application of a cleaning agent significantly impacts the success of bloodstain removal from a mattress. Consideration must be given to the nature of the stain, the composition of the mattress material, and the potential risks associated with each cleaning solution. Proper assessment and informed decision-making are essential to achieving optimal results while preserving the integrity of the mattress.
5. Thorough Drying
Following any method employed to address bloodstains on a mattress, adequate drying is critical. Residual moisture within the mattress core can foster microbial growth, leading to unpleasant odors and potential health hazards, thereby negating the benefits of stain removal efforts.
- Prevention of Mold and Mildew Growth
Damp environments provide ideal conditions for the proliferation of mold and mildew. Mattresses, with their porous structure and layered composition, are particularly susceptible. Lingering moisture, whether from cleaning solutions or residual blood, creates an environment conducive to fungal growth. Thorough drying inhibits this process, preventing the development of musty odors and safeguarding against allergenic or pathogenic organisms. Neglecting this step can result in long-term damage to the mattress and compromise indoor air quality.
- Odor Elimination
Residual moisture can trap and amplify odors associated with blood or cleaning agents. Even after a stain has been visually removed, lingering dampness can reactivate odor-causing molecules, leading to an unpleasant smell that permeates the sleeping environment. Thorough drying allows for the evaporation of these volatile compounds, ensuring a fresh and hygienic mattress.
- Restoration of Mattress Integrity
Mattress materials, such as foam and fibers, can lose their structural integrity when exposed to prolonged moisture. Over time, this can lead to sagging, compression, and reduced support. Complete drying helps to restore the mattress to its original shape and firmness, prolonging its lifespan and ensuring optimal comfort. Failure to dry thoroughly can result in irreversible damage and premature mattress degradation.
- Prevention of Stain Reappearance
In some cases, residual moisture can draw previously removed stain components back to the surface of the mattress, leading to the reappearance of discoloration. Capillary action can wick remaining blood particles from deeper within the mattress fibers, causing a faint but noticeable stain to reappear as the moisture evaporates unevenly. Thorough drying minimizes this risk by ensuring that all traces of blood and cleaning solution are completely removed from the mattress core.
Therefore, thorough drying is an indispensable step in the comprehensive process. It not only prevents secondary issues such as mold growth and odor but also preserves the structural integrity of the mattress and reduces the likelihood of stain recurrence. Neglecting this aspect can undermine the effectiveness of stain removal efforts and compromise the overall hygiene and comfort of the sleeping environment.
6. Material Compatibility
The success of removing bloodstains from a mattress is significantly influenced by the compatibility between the cleaning agent employed and the mattress material itself. Selecting an incompatible cleaning solution can result in irreparable damage, discoloration, or degradation of the mattress fibers. Therefore, a thorough understanding of mattress composition and the properties of various cleaning agents is paramount.
Consider a mattress constructed with natural latex and organic cotton. Harsh chemicals, such as bleach or concentrated ammonia solutions, can degrade the latex, causing it to become brittle and lose its supportive properties. The organic cotton cover may also suffer discoloration or weakening of its fibers. Conversely, a mattress with a synthetic foam core and a polyester cover may be more resilient to certain chemicals, but still susceptible to damage from abrasive cleaners. Abrasive cleaners might cause the polyester fibers to pill or break down. The interaction between the cleaning agent and the mattress material directly dictates the final outcome, illustrating the critical link between material compatibility and stain removal success.
In conclusion, material compatibility is an indispensable consideration when attempting to remove bloodstains. Understanding the specific composition of the mattress and the potential effects of cleaning agents ensures effective stain removal without compromising the integrity and lifespan of the mattress. Prior testing of any cleaning solution on an inconspicuous area of the mattress is strongly advised to mitigate the risk of irreversible damage.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the effective and safe removal of bloodstains from mattresses. The provided information aims to clarify procedures and mitigate potential damage.
Question 1: Is immediate action truly necessary when addressing a bloodstain on a mattress?
Indeed, prompt intervention significantly enhances the likelihood of successful stain removal. Delay allows the blood to penetrate deeper into the mattress fibers, making subsequent cleaning efforts more difficult and potentially resulting in permanent discoloration.
Question 2: Why is cold water consistently recommended over warm or hot water for bloodstain removal?
Hot water coagulates the proteins present in blood, causing the stain to set more firmly into the mattress fibers. Cold water, conversely, helps to keep the proteins soluble, facilitating their removal.
Question 3: What is the rationale behind blotting a bloodstain instead of rubbing it?
Rubbing spreads the stain and forces it deeper into the mattress, making it more difficult to extract. Blotting, on the other hand, lifts the stain from the surface without driving it further into the material.
Question 4: Can hydrogen peroxide be used safely on all types of mattresses to remove bloodstains?
Hydrogen peroxide possesses bleaching properties and can cause discoloration on certain fabrics. A small, inconspicuous area should be tested prior to widespread application to ensure material compatibility.
Question 5: How can the complete drying of a mattress be ensured after stain removal?
After blotting away excess moisture, the mattress should be allowed to air dry in a well-ventilated area. The use of a fan or dehumidifier can expedite the drying process. Complete dryness is essential to prevent mold and mildew growth.
Question 6: Is professional mattress cleaning always necessary for bloodstain removal?
Professional cleaning may be warranted for extensive or deeply embedded stains, particularly if initial attempts at removal prove unsuccessful. Professional services possess specialized equipment and cleaning agents that can address stubborn stains without damaging the mattress.
The information provided above underscores the importance of prompt action, appropriate techniques, and careful selection of cleaning agents when addressing bloodstains. Adherence to these principles maximizes the chances of successful stain removal and preserves the integrity of the mattress.
The subsequent sections will address preventative measures and long-term mattress care strategies.
How to Get Blood Stains Out of a Mattress
The preceding exploration details effective methodologies for addressing bloodstains on mattresses. Key considerations include the imperative of immediate action, the exclusive utilization of cold water, the practice of blotting rather than rubbing, the selection of appropriate cleaning solutions contingent on mattress composition, and the necessity of thorough drying to prevent microbial growth. Understanding these factors is critical for successful stain removal and the preservation of mattress integrity.
Effective stain removal contributes to maintaining a hygienic sleep environment and extending the lifespan of the mattress. Diligent application of the outlined techniques provides a means of addressing bloodstains effectively and minimizing long-term damage. Continued awareness and adherence to these principles are essential for upholding the quality and cleanliness of sleeping surfaces.