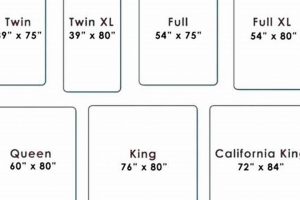
The standard measurements for a futon mattress designed to fit a full-size frame are generally 54 inches in width and 75 inches in length. This sizing allows it to be comfortably used in both the sofa and bed configurations of a full-size futon frame, offering a versatile sleeping and seating solution.
Adherence to these measurements is important for ensuring compatibility and proper function within the frame. Using a mattress outside of these specified proportions may lead to issues with folding mechanisms or an uneven sleeping surface. Historically, this standardized sizing has evolved to provide a convenient and space-saving option for smaller living spaces, combining seating and sleeping arrangements efficiently.
Further understanding involves considering factors such as thickness variations, material composition, and the relationship between these measurements and overall comfort or support provided by the futon mattress.
Essential Guidance
Understanding the specific measurements of a mattress intended for a full-size futon frame is vital for ensuring functionality and comfort. Consider the following points for optimal selection and use:
Tip 1: Accurate Measurement is Paramount: Always verify the stated dimensions of a mattress before purchase. Minor discrepancies can lead to fitting issues within the frame, potentially hindering its operation.
Tip 2: Prioritize Thickness Based on Intended Use: Thicker mattresses offer greater comfort for sleeping, but can make folding into the sofa position more challenging. Evaluate the balance between these two functions.
Tip 3: Account for Material Compression: Over time, futon mattresses may compress, slightly altering their dimensions. Selecting a higher-density material can mitigate this effect, ensuring long-term dimensional stability.
Tip 4: Factor in Frame Specifications: Different full-size futon frames may have slightly varying internal dimensions. Always consult the frame manufacturer’s specifications for recommended mattress sizes.
Tip 5: Inspect Mattress Edges: The edges should be uniformly straight and well-defined to ensure proper alignment within the frame. Rounded or uneven edges can cause instability and discomfort.
Tip 6: Consider the Weight Capacity: The mattress should be able to support the intended weight load without excessive sagging or deformation. Check the manufacturer’s specifications for weight capacity.
Tip 7: Measure Available Space: Before purchasing, measure the space where the futon will be placed when both in sofa and bed configurations to avoid space constraint issues.
By adhering to these guidelines, individuals can ensure they select a mattress that aligns with their needs, maximizing both the functionality and longevity of the futon arrangement.
The subsequent sections will delve into the relationship between mattress materials and overall durability, providing a more comprehensive overview of futon mattress selection.
1. Width
The specification of 54 inches as the width is an integral and defining component of dimensions suitable for a full-size futon mattress. This measurement directly dictates its compatibility with a corresponding full-size futon frame. A deviation from this width can lead to significant functional issues, preventing the mattress from properly fitting within the frame, thus hindering the futon’s ability to transition between seating and sleeping positions. For example, if a mattress were even slightly wider, it might bind within the frame, making conversion difficult or impossible. The practical significance lies in ensuring seamless operation and user convenience. Without adherence to this specified width, the essential functionality of the futon is compromised.
Considering real-world examples, furniture manufacturers precisely adhere to the 54-inch width standard when producing mattresses intended for full-size futon frames. This standardization allows consumers to purchase mattresses from various sources with the assurance that they will fit appropriately. This consistency facilitates interchangeability and provides options for consumers seeking different comfort levels or material compositions within the specified size constraints. Furthermore, this measurement impacts shipping and storage, as manufacturers can optimize packaging based on this consistent dimension. Without a standardized width, consumers would face significant challenges in finding compatible replacement mattresses, limiting the usability of their futon frames.
In summary, the 54-inch width dimension serves as a critical parameter within the full-size futon mattress specification, directly affecting compatibility, functionality, and ease of use. Its standardization streamlines manufacturing, distribution, and consumer purchasing decisions, ensuring a practical and user-friendly furniture solution. Ignoring or deviating from this width presents substantial challenges to the intended purpose of a full-size futon.
2. Length
The 75-inch measurement representing the length is a fundamental component of dimensions of full-size futon mattresses. It dictates the overall sleeping surface area when the futon is in its bed configuration. A direct correlation exists between this length and the suitability of the mattress for accommodating the average adult user. Any significant deviation from this standard length would demonstrably impact comfort and usability, potentially rendering the futon unsuitable for its intended purpose. For instance, a shorter mattress might leave a portion of the futon frame exposed, while a longer one could prevent proper folding and frame closure.
Consider the scenario of purchasing a futon mattress advertised as full-size, but with a length of only 70 inches. The resultant lack of support could lead to discomfort and inadequate spinal alignment, especially for taller individuals. Conversely, furniture manufacturers who adhere to the 75-inch standard ensure that the product aligns with common expectations and provides a functional sleeping space. Retailers emphasize this measurement in product descriptions to accurately represent the dimensions and avoid customer dissatisfaction. In practice, this length directly influences the overall value proposition of the full-size futon mattress.
In conclusion, the 75-inch length dimension is intrinsically linked to dimensions for full-size futon mattresses. It affects user comfort, frame compatibility, and ultimately, the practical value of the product. Upholding this standard ensures that the futon serves its dual purpose as both seating and sleeping accommodation effectively.
3. Thickness variations
The parameter of “thickness variations” represents a critical dimension within the broader context of standard full-size futon mattresses. These variations, typically ranging from approximately six to ten inches, directly impact the comfort, support, and overall functionality of the mattress within a standard frame. Thicker mattresses, while providing enhanced cushioning for sleeping, can present challenges in folding the futon into its sofa configuration. Conversely, thinner mattresses may fold more easily but offer reduced comfort and support for prolonged use. Thus, the chosen thickness profoundly influences the user experience and the futon’s dual-purpose capability.
For instance, consider a consumer selecting a ten-inch-thick futon mattress. The increased depth may provide superior comfort for nightly sleep, closely mimicking a conventional bed. However, the added bulk could strain the futon frame’s folding mechanism, potentially leading to premature wear or complete failure. Alternatively, a six-inch-thick mattress, while facilitating effortless folding, might prove inadequate for individuals seeking substantial support and pressure relief. Furniture manufacturers recognize this interplay, often providing guidance on optimal thickness levels compatible with their specific frame designs. Furthermore, retailers frequently offer mattresses in various thicknesses, allowing consumers to select the most appropriate option based on their individual needs and priorities. The material composition of the mattress, such as the density of foam or the type of fiber fill, further modulates the relationship between thickness and overall performance.
In summary, variations in mattress thickness constitute a significant dimensional aspect affecting both the comfort and functionality of a full-size futon. The selection process necessitates a careful evaluation of intended use, frame compatibility, and individual preferences. Compromises often become necessary to achieve a balance between comfortable sleep and ease of conversion between seating and sleeping modes, highlighting the practical importance of understanding dimensions.
4. Frame Compatibility
The concept of frame compatibility is intrinsically linked to the specifications of the full size futon mattress. Deviation from standard mattress dimensions directly impacts the ability of the mattress to properly integrate with the intended frame. Specifically, a mattress exceeding the specified width or length may not fit within the frame structure, precluding the futon’s ability to transition seamlessly between sofa and bed configurations. Conversely, a mattress significantly smaller than the frame could result in an unstable or uneven surface, undermining both seating and sleeping functionality. Therefore, adherence to precise dimensions is paramount for ensuring optimal frame compatibility and the intended utilization of the futon unit.
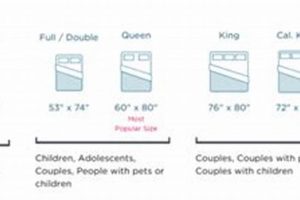
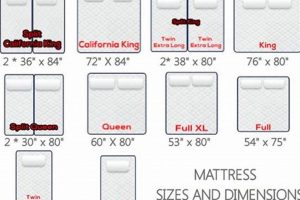
Real-world examples demonstrate the practical implications of mismatched dimensions. Consumers attempting to use a queen-size mattress on a full-size futon frame will encounter immediate difficulties in fitting the mattress. Similarly, utilizing a mattress designed for a bi-fold futon frame on a tri-fold frame can lead to structural instability and uneven weight distribution. Furniture manufacturers explicitly state the compatible mattress dimensions for each frame type to mitigate such issues. Retailers also emphasize this specification in product descriptions to facilitate informed purchasing decisions and prevent customer dissatisfaction. The economic consequences of incompatibility include the cost of returning ill-fitting mattresses and the potential need to purchase a new, appropriately sized mattress.
In summary, frame compatibility represents a critical determinant of the overall functionality and usability of the full-size futon. Precise dimensions, encompassing width, length, and thickness, must align with the frame specifications to ensure seamless operation and user satisfaction. Challenges arising from dimensional discrepancies can lead to functional impairment, economic losses, and diminished product lifespan. A thorough understanding of these interdependencies is essential for both consumers and manufacturers in optimizing the performance and value of futon systems.
5. Folded profile
The folded profile of a full-size futon mattress is directly dictated by its inherent dimensions, specifically its width, length, and, crucially, its thickness. The thickness, when multiplied according to the number of folds inherent in the futon’s design (typically two or three), determines the overall height and depth of the unit when in its sofa configuration. A thicker mattress, conforming to standard width and length dimensions, will naturally result in a larger folded profile, potentially impacting the available space within a room. Conversely, a thinner mattress, while maintaining standard width and length dimensions, will produce a more compact folded profile, offering space-saving advantages. The folded profile, therefore, is a direct consequence of dimensions and directly affects the furniture’s practicality in smaller living spaces.
Consider two distinct scenarios: a full-size futon mattress with a thickness of ten inches, folded twice, will present a significantly more substantial profile than a similar mattress measuring only six inches in thickness. The former may dominate a small room, restricting movement and limiting additional furniture placement. The latter, however, could provide a more streamlined and unobtrusive seating arrangement. Furniture manufacturers often provide specifications regarding the folded profile dimensions to assist consumers in making informed decisions based on their spatial constraints. Retailers may also showcase the futon in both its open and folded configurations to visually represent the impact of the folded profile.
In conclusion, the folded profile represents a key consideration within the broader context of dimensions that define a full-size futon mattress. It is a direct consequence of the mattress’s width, length, and, most significantly, its thickness, influencing both spatial efficiency and aesthetic harmony within a given environment. Understanding the correlation between these dimensions and the resultant folded profile is therefore crucial for optimizing the practical value and usability of the futon unit. Challenges remain in balancing comfort and space-saving needs, requiring careful consideration of mattress thickness and its corresponding impact on the folded profile.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding mattress dimensions, providing clarity on their importance and implications.
Question 1: What constitutes dimensions for a full size futon mattress?
Dimensions generally measure 54 inches in width and 75 inches in length. Thickness may vary, typically ranging from 6 to 10 inches.
Question 2: How do standard dimensions impact frame compatibility?
Adherence to standard dimensions is crucial for ensuring proper fit within a full-size futon frame. Deviations may impede functionality.
Question 3: How does mattress thickness influence the folded profile?
Increased thickness contributes to a larger folded profile, potentially affecting space utilization within a room.
Question 4: Does material composition influence the effective dimensions?
Yes. Compressible materials may cause slight variations in dimensions over time, particularly in thickness. Denser materials resist compression.
Question 5: Where can consumers find reliable information on mattress dimensions?
Furniture manufacturers and retailers typically provide detailed dimensional specifications in product descriptions.
Question 6: What are the potential consequences of using an incorrectly sized mattress?
Incompatible dimensions may lead to functional impairment, instability, reduced comfort, and potential damage to the futon frame.
Understanding these dimensional considerations is essential for optimizing the performance and lifespan of a futon unit.
The next section explores the implications of material selection on durability and comfort.
Conclusion
The preceding discussion has elucidated the critical importance of dimensions in relation to full-size futon mattresses. Accurate adherence to standard dimensions, encompassing width, length, and thickness, is paramount for ensuring frame compatibility, functional efficacy, and user satisfaction. Deviations from these specifications can result in compromised performance, reduced lifespan, and potential structural damage. The influence of material composition on effective dimensions and the resultant folded profile was also examined.
Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of these dimensional factors is essential for both consumers and manufacturers. Precise measurement and specification remain crucial for realizing the full potential of futon systems as versatile and space-saving furniture solutions. Continued attention to dimensional integrity will ensure the ongoing relevance and utility of this furniture category.