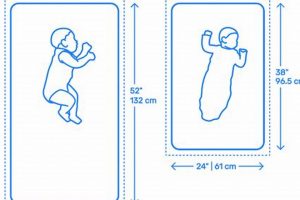
The measurement of a typical infant bed sleeping surface is approximately 28 inches wide and 52 inches long. This dimension is a crucial factor to consider when preparing a safe and comfortable environment for a baby. Meeting this specification ensures compatibility with most commercially available crib frames.
Adherence to this size offers significant advantages, primarily in terms of safety. A snug fit within the crib frame minimizes the risk of entrapment and potential injury to the infant. Historically, consistent dimensions have facilitated mass production and affordability, making suitable sleeping arrangements accessible to a wider range of families. The uniformity also simplifies the process of finding appropriately sized bedding and accessories.
Understanding the accepted dimensions for infant sleeping surfaces is the first step in selecting a safe and appropriate product. Subsequent articles will explore various aspects of materials, construction, safety certifications, and considerations for choosing the optimal sleeping surface for a baby.
Tips Regarding Infant Bed Sleeping Surface Dimensions
Selecting the correct infant bed sleeping surface involves careful consideration. The following guidelines assist in making informed decisions regarding product selection and usage.
Tip 1: Verify dimensions prior to purchase. Accurate measurements of the crib’s interior ensure a proper fit, minimizing gaps and potential hazards. Cross-reference the stated dimensions of the sleeping surface with the internal dimensions of the crib frame.
Tip 2: Prioritize a firm sleeping surface. Infant sleeping surfaces should be firm to reduce the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). Avoid overly soft or plush surfaces that may conform excessively to the infant’s face.
Tip 3: Inspect for gaps. Once the sleeping surface is placed within the crib, thoroughly inspect for any gaps exceeding two finger-widths between the edge and the crib frame. Excessive gaps pose a potential entrapment risk.
Tip 4: Consider sleeping surface weight. The sleeping surface should be sufficiently lightweight to facilitate easy removal for cleaning and sheet changes, but also possess enough heft to remain securely in place.
Tip 5: Research certifications. Look for certifications from reputable organizations that test for chemical emissions and structural integrity. Certifications indicate the product has undergone independent evaluation for safety and performance.
Tip 6: Check for appropriate sheet fit. Use only sheets specifically designed for a standard infant bed sleeping surface. Securely fitted sheets prevent bunching or loosening, which could pose a suffocation hazard.
Tip 7: Rotate the sleeping surface regularly. Periodic rotation helps distribute wear and tear evenly, extending the life of the product and preventing localized sagging or compression.
Adherence to these tips promotes a safer and more comfortable sleeping environment for infants, contributing to their well-being. Further discussion will address specific material options and long-term maintenance practices.
The subsequent sections will delve into detailed examinations of material choices and optimal care routines.
1. Length
The “Length: 52 inches” dimension is a definitive component of a typical infant bed sleeping surface. This measurement is not arbitrary; it is the product of careful consideration involving infant safety, developmental needs, and standardization efforts within the juvenile product industry. A 52-inch length, in conjunction with the standard width, allows adequate space for an infant to move and sleep comfortably within the confines of a crib, up to a certain age and developmental stage. Failure to adhere to this length risks creating a surface that is either too small, potentially causing discomfort and limiting movement, or too large, increasing the risk of gaps between the sleeping surface and the crib framea known safety hazard.
The practical implication of the 52-inch length is readily apparent in the design and manufacturing of cribs and related accessories. Crib manufacturers engineer their products to accommodate this specific dimension, ensuring a snug and secure fit. Bedding manufacturers create sheets and other linens specifically sized for this dimension. For instance, a fitted sheet designed for an infant bed sleeping surface will typically be sized to accommodate a 52-inch length, ensuring proper tension and preventing the sheet from becoming loose and posing a suffocation risk. Real-world examples also include scenarios where a sleeping surface shorter than 52 inches might lead to a child’s limbs becoming caught between the sleeping surface and the crib rails, resulting in injury.
In summary, the 52-inch length serves as a critical benchmark for infant bed sleeping surfaces. Deviation from this standard can compromise safety, comfort, and compatibility with other essential crib components. Understanding the significance of this dimension is crucial for both consumers selecting a sleeping surface and manufacturers adhering to safety standards. Consistent length aids in manufacturing predictability and reduces the likelihood of unsafe products reaching the market, fostering a safer environment for infants.
2. Width
The “Width: 28 inches” specification is inextricably linked to the notion of what constitutes a typical infant bed sleeping surface. This dimensional parameter, when combined with the length of 52 inches, establishes the rectangular footprint deemed safe and functional for infant sleeping environments. The 28-inch width is not arbitrary; it reflects considerations related to infant development, movement capabilities, and the structural design of cribs. A reduced width may restrict an infant’s ability to turn and reposition comfortably, while an excessive width introduces the risk of hazardous gaps between the sleeping surface and the crib’s side rails. The relationship is causal: the adherence to this 28-inch width is a direct determinant of whether a sleeping surface qualifies as “standard” and, consequently, whether it can be safely used in a typical crib.
The importance of the 28-inch width becomes evident in practical applications. Crib manufacturers design their products with an internal width to accommodate a sleeping surface of this size. Bedding manufacturers produce sheets tailored for these dimensions, ensuring a snug fit that minimizes the risk of entanglement. Failure to maintain this width could lead to complications such as ill-fitting bedding, potentially creating unsafe sleeping conditions. For instance, if the sleeping surface is narrower than 28 inches, larger gaps will appear at the sides, posing a potential entrapment hazard for infants. This dimension is also crucial for regulatory compliance; products deviating from these measurements may not meet safety standards.
In summary, the 28-inch width serves as an indispensable characteristic of a standard infant bed sleeping surface. Its contribution to overall safety, usability, and regulatory compliance is substantial. The dimension provides a basis for the design and manufacturing of both cribs and accessories, and its adherence is essential for minimizing risks associated with infant sleeping environments. Consequently, this understanding is vital for consumers, manufacturers, and regulatory bodies alike.
3. Thickness Variability
Thickness variability in infant bed sleeping surfaces, while seemingly a minor detail compared to standard length and width, introduces essential considerations concerning safety, support, and compatibility. Understanding how thickness can vary and its implications is paramount when evaluating the suitability of a sleeping surface.
- Support and Firmness
Thickness directly influences the firmness and support offered. A thicker surface does not automatically equate to greater support; the materials and construction techniques employed are crucial. However, thickness often correlates with the ability to incorporate multiple layers of supportive materials. Conversely, overly thick surfaces might compromise the crib’s safety railing height regulations, posing a risk if the railing becomes too low relative to the sleeping surface.
- Crib Compatibility
Although length and width are standardized, thickness variability can affect how well the sleeping surface fits within a particular crib. A sleeping surface that is too thick may be difficult to insert or remove, potentially damaging the crib frame or causing uneven pressure distribution. This misfit can also affect the performance of drop-side mechanisms, if present. Measurements should be checked to ensure adherence to manufacturer specifications.
- Material Composition and Comfort
Thickness often dictates the range of materials that can be incorporated. Thicker surfaces can accommodate multiple layers, such as a core support layer, a comfort layer, and a protective covering. This layering allows for a combination of firmness and cushioning. However, improper material selection can lead to discomfort or safety issues. For example, overly thick surfaces filled with low-density foam may compress excessively, reducing support and potentially increasing the risk of suffocation.
- Safety Standards and Certifications
Thickness is indirectly related to safety standards. Safety certifications often specify testing protocols that account for the sleeping surface’s dimensions, including thickness. Some standards mandate minimum or maximum thickness values to ensure adequate support and minimize the risk of entrapment or suffocation. Therefore, selecting a sleeping surface with recognized safety certifications provides assurance that its thickness has been vetted against relevant benchmarks.
In summary, thickness variability in infant bed sleeping surfaces presents nuanced considerations. While standard length and width provide a baseline, thickness impacts support, compatibility, material selection, and adherence to safety standards. A judicious assessment of thickness, in conjunction with other factors, helps ensure the selection of a safe and appropriate sleeping environment for the infant.
4. Corner Radius
Corner radius, though often overlooked, plays a critical role in ensuring a proper fit and minimizing safety risks associated with infant bed sleeping surfaces. It directly impacts how well the sleeping surface conforms to the crib frame, affecting both security and potential hazards.
- Fit and Compatibility
The corner radius of an infant bed sleeping surface dictates how smoothly the corners integrate with the crib’s frame. A correctly sized radius ensures a snug fit, preventing gaps where an infant could become entrapped. An incorrect radius, either too large or too small, can lead to instability and compromise the overall safety of the crib setup. Real-world examples include surfaces with excessively sharp corners that may damage the crib frame or pose a cutting hazard, or overly rounded corners that leave significant gaps, violating safety standards.
- Manufacturing Precision
Consistent corner radius is indicative of precise manufacturing. Deviation suggests a lack of quality control, potentially signaling other inconsistencies in the sleeping surface’s dimensions or materials. Corner radius tolerances are typically specified in manufacturing blueprints, and adherence to these tolerances is a measure of the manufacturer’s commitment to safety and quality. Non-compliant radius measurements may suggest shortcuts in production, potentially compromising the integrity of the product.
- Regulatory Compliance
Safety standards often implicitly address corner radius by specifying maximum allowable gaps between the sleeping surface and the crib frame. These gap requirements necessitate a carefully controlled corner radius. Failure to adhere to these regulations may result in product recalls or legal liabilities. Independent testing laboratories often assess corner radius dimensions as part of their certification process, ensuring compliance with established safety benchmarks.
- Aesthetic and Design Considerations
While primarily functional, corner radius also contributes to the aesthetic appeal of the sleeping surface and its integration with the overall crib design. A well-proportioned corner radius can enhance the visual harmony of the sleeping area. Sharp, abrupt corners may appear aesthetically jarring, while overly rounded corners can seem disproportionate. The design choice should balance safety requirements with visual appeal to provide a pleasant and secure environment.
In conclusion, the corner radius of an infant bed sleeping surface, though a seemingly subtle feature, exerts a significant influence on safety, fit, and manufacturing quality. A proper corner radius ensures a secure and aesthetically pleasing integration with the crib frame, minimizes entrapment risks, and reflects a commitment to quality and safety standards. Ignoring this dimensional aspect can compromise the overall safety and functionality of the sleeping environment.
5. Weight considerations
Weight considerations are integrally linked to the concept of a standard infant bed sleeping surface. The mass of the sleeping surface affects several critical aspects, including ease of handling, structural integrity, and overall safety. A sleeping surface that is excessively heavy poses challenges for caregivers when changing sheets or cleaning the crib. Conversely, a sleeping surface that is too light may compromise stability within the crib frame, increasing the risk of displacement and potential hazards. Therefore, the weight of the sleeping surface must strike a balance between manageability and security. The materials and construction methods employed directly influence this balance. For instance, a surface constructed with high-density foam will typically weigh more than one made with lighter, less dense materials. This mass disparity can impact both the ease with which caregivers can manipulate the product and its capacity to remain securely positioned within the crib.
The practical implications of weight become apparent in various scenarios. During routine sheet changes, a caregiver must lift and maneuver the sleeping surface. A heavier surface increases the physical strain associated with this task. In emergency situations, such as needing to quickly access a distressed infant, a lighter sleeping surface allows for faster removal. Furthermore, the weight distribution impacts the stability of the crib. An uneven weight distribution, particularly in a lighter surface, could lead to tilting or shifting, creating an unsafe sleeping environment. Regulatory standards often indirectly address weight considerations by specifying requirements for stability and gap limitations. Real-world examples of improperly weighted sleeping surfaces include situations where light surfaces were easily dislodged by active infants, leading to entrapment incidents.
In conclusion, weight is a crucial, though often understated, component of a standard infant bed sleeping surface. It affects both the practical usability of the product for caregivers and its inherent safety characteristics. Balancing weight with material selection and structural design is essential to creating a sleeping surface that is both manageable and secure. A thorough understanding of weight considerations contributes to a safer and more convenient environment for infants and their caregivers. Addressing weight-related challenges involves rigorous testing and adherence to safety standards to ensure the optimal balance between usability and security.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Standard Infant Bed Sleeping Surfaces
This section addresses common inquiries concerning the dimensions and characteristics of typical infant bed sleeping surfaces, aiming to provide clarity and informed guidance.
Question 1: Are all infant bed sleeping surfaces the same size?
While considerable uniformity exists, minor variations may occur. The generally accepted dimensions are approximately 28 inches in width and 52 inches in length. Discrepancies exceeding established tolerances should prompt careful evaluation to ensure compatibility and safety.
Question 2: What is the acceptable thickness range for an infant bed sleeping surface?
Thickness can vary depending on the material composition and construction. However, excessively thick surfaces may compromise the crib’s safety rail height, while overly thin surfaces may lack adequate support. Consult crib manufacturer specifications for recommended thickness guidelines.
Question 3: Why is maintaining the correct sleeping surface size important?
Adherence to established dimensions is critical for preventing entrapment hazards. Gaps between the sleeping surface and the crib frame pose a significant risk to infants. A properly sized surface minimizes these risks, promoting a safer sleeping environment.
Question 4: What should be done if the infant bed sleeping surface does not fit the crib properly?
If significant gaps or fitting issues exist, the sleeping surface should not be used. Contact the manufacturer or retailer to explore potential solutions, such as exchanging the product for one with appropriate dimensions. Prioritizing safety necessitates a proper fit.
Question 5: Do all infant bed sleeping surfaces adhere to safety standards?
While many surfaces meet or exceed safety standards, not all products are created equal. Look for certifications from recognized organizations, such as the Juvenile Products Manufacturers Association (JPMA), to ensure the product has undergone independent testing and meets established safety benchmarks.
Question 6: How often should an infant bed sleeping surface be replaced?
The lifespan of a sleeping surface depends on various factors, including material quality and usage. Regular inspection for signs of wear and tear is essential. Replacing the surface may be necessary if it exhibits significant sagging, damage, or compromised structural integrity.
In summary, careful attention to the dimensions, safety certifications, and condition of an infant bed sleeping surface is paramount. A proactive approach to selecting and maintaining a suitable sleeping surface contributes to a safer and more comfortable environment for the infant.
The following section will address specific material options and their respective advantages and disadvantages.
Conclusion
This article has addressed “what is standard size crib mattress,” detailing the essential dimensions and related considerations for ensuring infant safety and proper fit within a crib frame. The established measurements, specifically the length, width, thickness, corner radius, and weight, each contribute critically to the overall safety and functionality of the sleeping environment. Deviations from these standards can pose significant risks, emphasizing the importance of precise manufacturing and rigorous quality control.
Understanding these specifications empowers informed decision-making when selecting a sleeping surface. By prioritizing adherence to established dimensional standards, manufacturers and consumers alike contribute to a safer environment for infants. Continuous vigilance and adherence to safety guidelines are paramount in mitigating potential hazards and fostering optimal infant well-being. Future investigations should explore the long-term performance and material degradation of infant bed sleeping surfaces to further enhance product safety and longevity.