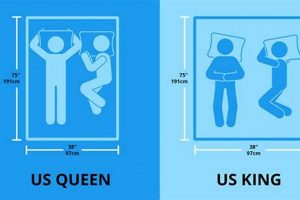
The specific bedding configuration under consideration refers to a mattress designed to fit a queen-sized bed frame, providing ample sleeping space for individuals or couples. Its construction incorporates materials and techniques that result in a balance between support and cushioning. This level of firmness aims to accommodate a wide range of sleeping positions and body types. Examples include models utilizing innerspring coils, memory foam, or hybrid constructions engineered for balanced support and pressure relief.
A mattress with these characteristics offers a compelling blend of advantages. It can promote proper spinal alignment, potentially reducing back pain and discomfort. The balanced support minimizes pressure points, contributing to a more restful sleep experience. Historically, mattresses of this type represent a compromise between overly soft surfaces that lack support and excessively rigid surfaces that can cause discomfort, embodying an evolution in sleep technology and design focused on optimizing sleep quality and comfort.
The following sections will delve deeper into the specific materials used in construction, the factors influencing the overall feel and performance, and the considerations relevant to selecting a suitable option based on individual needs and preferences. Further exploration will also cover aspects such as durability, maintenance, and the impact on sleep quality, providing a holistic understanding of this bedding type.
Guidance on Mattress Selection
The following recommendations offer practical guidance for individuals seeking a specific bedding solution that balances support and comfort, designed for a standard queen-sized bed frame.
Tip 1: Assess Individual Sleep Needs: Evaluate preferred sleeping positions and any specific physical considerations, such as back pain or pressure point sensitivity. This assessment will inform the suitability of the balanced firmness level.
Tip 2: Research Construction Materials: Investigate the internal components, including coil type, foam density, and layering, as these factors significantly impact durability, support, and temperature regulation. Compare models using innerspring, memory foam, latex, or hybrid designs.
Tip 3: Consider Edge Support: Evaluate the mattress’s edge support, especially if utilizing the full sleeping surface is a priority. Stronger edge support prevents sagging and enhances the usable area.
Tip 4: Investigate Trial Periods and Warranties: Seek manufacturers or retailers offering extended trial periods to thoroughly evaluate comfort and suitability. Review warranty terms to understand coverage for potential defects or premature wear.
Tip 5: Read Reviews from Verified Owners: Consult independent reviews from verified purchasers to gain insights into long-term performance, durability, and customer satisfaction. Focus on reviews addressing factors relevant to individual needs and preferences.
Tip 6: Prioritize Proper Bed Frame Support: Ensure the chosen bed frame provides adequate support to prevent sagging or damage. Confirm the frame’s compatibility with the chosen mattress type and weight.
Tip 7: Consider Partner Preferences: If sharing the bed, consider the preferences and needs of both individuals to ensure a mutually comfortable sleep experience. Factors such as motion isolation become particularly important.
Selecting a bedding solution tailored to individual needs promotes better sleep quality and overall well-being. Careful consideration of these factors will contribute to a more informed and satisfactory purchasing decision.
The subsequent sections will explore specific product recommendations and maintenance techniques to maximize the lifespan and performance of the selected mattress.
1. Balanced Support
Balanced support, in the context of a queen-size mattress with a medium-firm feel, refers to the mattress’s capacity to distribute body weight evenly across its surface. This characteristic directly impacts spinal alignment and pressure point reduction. Without balanced support, certain areas of the body, such as the hips or shoulders, may sink excessively, leading to spinal misalignment and discomfort. Conversely, insufficient give can result in pressure points and a restless sleep. The medium-firm specification seeks to mitigate these issues by providing adequate support for the lower back and hips while simultaneously allowing sufficient contouring to alleviate pressure. A mattress lacking balanced support may lead to conditions such as sciatica or exacerbate existing back pain issues, rendering it unsuitable for individuals requiring proper spinal alignment. In contrast, a well-constructed medium-firm queen mattress can promote healthier sleep posture and reduce instances of tossing and turning.
The presence of balanced support is often achieved through a combination of core construction and comfort layer design. Innerspring mattresses may utilize zoned coil systems to provide targeted support to different areas of the body. Memory foam or latex models achieve balanced support through variations in density and thickness, ensuring that heavier body parts receive adequate resistance while lighter areas experience greater cushioning. For example, a hybrid mattress might combine a pocketed coil system for underlying support with a memory foam comfort layer to contour to the sleeper’s body. Regular rotation of this bedding can sustain even wear and ensure continual balanced support over its life cycle. However, neglecting to inspect the mattress for sagging or unevenness can lead to degradation of this essential element, reducing its benefits over time.
In summary, balanced support is an indispensable element of a queen-size mattress with a medium-firm feel. It directly influences sleep quality, spinal health, and overall comfort. While construction materials and design contribute to the realization of balanced support, consistent maintenance and careful assessment of individual needs are critical to ensuring its sustained efficacy. Recognizing and prioritizing this characteristic is vital for consumers seeking optimal sleep and long-term well-being.
2. Pressure Relief
Pressure relief, concerning bedding, pertains to the mattress’s capacity to minimize concentrated forces on specific areas of the body during sleep. A queen size mattress with a medium firm specification aims to strike a balance; it must provide adequate support to prevent spinal misalignment while simultaneously offering sufficient give to alleviate pressure on areas such as the shoulders, hips, and knees. Inadequate pressure relief can lead to discomfort, restlessness, and even exacerbate conditions like bursitis or arthritis. For example, an individual sleeping on a surface that is too firm may experience increased pressure on bony prominences, resulting in localized pain and compromised circulation. Conversely, a surface that lacks sufficient support can cause the body to sink excessively, creating pressure points due to unnatural spinal curvature. Therefore, the practical significance of understanding pressure relief stems from its direct impact on sleep quality and physical well-being.
The effectiveness of pressure relief in a mattress is largely determined by its construction materials and design. Memory foam, for instance, is known for its ability to conform to the body’s contours, distributing weight more evenly and reducing pressure points. Latex offers a similar, though often slightly firmer, pressure-relieving effect. Hybrid mattresses, which combine innerspring support with layers of memory foam or latex, attempt to leverage the benefits of both technologies. The density and thickness of the comfort layers, as well as the type of coil system used, all contribute to the overall pressure-relieving capabilities of the mattress. Consider an individual with chronic hip pain; a mattress with strategically placed pressure-relieving zones can significantly reduce discomfort and improve sleep quality. Similarly, side sleepers, who often experience pressure on their shoulders and hips, can benefit from a mattress that contours to their body’s curves and distributes weight effectively.
In summary, pressure relief is an indispensable component of a comfortable and supportive queen-size mattress. It directly affects sleep quality, joint health, and overall physical well-being. The challenge lies in finding a bedding solution that provides both adequate support and effective pressure relief, tailored to individual needs and preferences. Ultimately, an informed understanding of pressure relief, coupled with careful consideration of mattress construction and personal requirements, is crucial for making an informed purchasing decision and achieving restful, pain-free sleep.
3. Spinal Alignment
Spinal alignment is a foundational element of sleep health, directly influenced by the support characteristics of a mattress. A queen size mattress with a medium-firm specification is often recommended due to its purported ability to maintain the natural curvature of the spine during sleep. Proper spinal alignment minimizes stress on vertebral discs, ligaments, and muscles, thereby reducing the likelihood of back pain and stiffness. A mattress that is too soft may allow the spine to sag, while one that is too firm may create pressure points that force the spine out of alignment. The medium-firm designation seeks to strike a balance, offering sufficient support to prevent sagging while providing enough give to accommodate the body’s contours. For example, individuals who sleep on their back require support for the lumbar region to maintain the spine’s natural arch. Side sleepers, conversely, need a mattress that allows the shoulder and hip to sink slightly, keeping the spine aligned along its lateral axis.
The connection between spinal alignment and a queen size mattress with a medium-firm specification can be illustrated through biomechanical analysis. When the spine is properly aligned, weight is distributed evenly across the vertebral discs, reducing the risk of disc compression and nerve impingement. In contrast, poor spinal alignment can lead to conditions such as sciatica, spinal stenosis, and degenerative disc disease. A mattress that promotes proper alignment can also improve breathing by allowing the rib cage to expand fully and reduce snoring by maintaining an open airway. Furthermore, proper alignment facilitates optimal blood circulation, which is essential for tissue repair and overall health. Consider the case of a truck driver, spending long hours on the road with a strain on his back; a mattress of this specification is likely to provide adequate sleep support for his spine.
In summary, spinal alignment is a crucial consideration when selecting a mattress, particularly for individuals seeking to minimize back pain and promote restful sleep. A queen size mattress with a medium-firm feel offers a potentially beneficial compromise between support and comfort, aimed at maintaining the natural curvature of the spine. While individual needs may vary, understanding the relationship between mattress characteristics and spinal alignment is essential for making an informed purchasing decision that supports long-term spinal health and overall well-being. This understanding can be challenged when consumers have varying pain conditions and individual comfort preferences.
4. Versatile Comfort
Versatile comfort, when considered in the context of a queen size mattress with a medium-firm specification, pertains to its ability to accommodate a range of sleeping positions and body types without compromising support or pressure relief. The medium-firm designation attempts to strike a balance, catering to individuals who sleep on their back, side, or stomach. This attribute is significant because a mattress that is not versatile may lead to discomfort, restlessness, or even exacerbate existing physical conditions. For example, a mattress that is too soft may be unsuitable for stomach sleepers, causing the spine to sag and potentially leading to back pain. Conversely, a mattress that is too firm may be uncomfortable for side sleepers, creating pressure points on the shoulders and hips. Thus, versatile comfort implies a mattress’s capacity to adapt to varying needs and preferences, promoting restful sleep for a broader spectrum of individuals. The practical consequence of choosing a mattress that lacks versatile comfort is that the user might struggle to find a comfortable sleeping position throughout the night.
The achievement of versatile comfort in a queen size mattress with a medium-firm specification is often the result of strategic material selection and construction. Manufacturers may employ a combination of high-density support cores and responsive comfort layers to create a surface that conforms to the body while maintaining adequate support. For example, a mattress might incorporate a pocketed coil system to provide targeted support to different areas of the body, coupled with a layer of memory foam or latex to offer pressure relief and contouring. The layering effect is crucial as it ensures support for spinal alignment regardless of sleeping position, whilst providing a comfortable give for key body points. Another example is a blended fiber mattress, which balances temperature regulation with firmness control, thereby supporting different sleeper types. Maintenance actions such as mattress rotation also play a crucial role in sustaining its versatile comfort over time.
In summary, versatile comfort is a vital characteristic of a queen size mattress with a medium-firm specification, directly influencing sleep quality and user satisfaction. It is achieved through a combination of thoughtful design, material selection, and construction techniques. The challenges associated with achieving versatile comfort stem from the inherent variability in individual needs and preferences; however, a well-designed medium-firm queen mattress represents a viable compromise for many sleepers. Prioritizing this characteristic is essential for individuals seeking a bedding solution that promotes restful sleep and accommodates a variety of sleeping positions without sacrificing support.
5. Durability Factors
Durability, in the context of a queen size mattress with a medium-firm specification, refers to the mattress’s ability to maintain its original support, comfort, and structural integrity over an extended period of use. The durability factors influencing this lifespan are critical, impacting overall value and user satisfaction. Understanding these factors allows for informed purchasing decisions and appropriate maintenance practices. Below are key elements impacting the durability of this mattress type.
- Material Quality
The inherent quality of materials, such as foam density, coil gauge, and fabric composition, significantly affects longevity. High-density foams resist compression and sagging, while thicker gauge coils maintain support over time. Premium fabrics withstand wear and tear. Conversely, lower quality materials degrade more rapidly, reducing the mattress’s lifespan and performance. For example, a mattress using low-density memory foam may develop body impressions within a year, whereas one with high-density foam could maintain its shape and support for several years longer.
- Construction Methods
The methods used to assemble the mattress components influence its overall structural integrity. Reinforced edges prevent sagging and increase the usable sleeping surface, while robust stitching and bonding techniques minimize separation and material breakdown. Advanced construction methods, such as tufting or quilting, secure the layers and prevent shifting. Mattresses with weak seams or poorly attached components are more prone to failure. As an instance, a mattress constructed with weak edge support may experience premature sagging along the edges, diminishing comfort and support.
- Usage Patterns
The frequency and manner in which the mattress is used affects its durability. Higher weight loads, frequent movement, and improper care can accelerate wear and tear. Rotating and flipping the mattress (if applicable) can distribute weight evenly and extend its lifespan. Additionally, using a protective mattress encasement can shield against spills, stains, and allergens, preserving the mattress’s condition. For example, a mattress consistently subjected to excessive weight in one area will likely exhibit localized sagging, whereas one rotated regularly will experience more uniform wear.
- Environmental Conditions
Environmental factors, such as humidity, temperature, and exposure to sunlight, can impact the degradation of mattress materials. Excessive humidity promotes mold and mildew growth, while high temperatures can accelerate foam breakdown. Direct sunlight can fade fabrics and weaken structural components. Maintaining a controlled environment and using proper ventilation can help mitigate these effects. For example, a mattress stored in a damp basement is more susceptible to mold and mildew, leading to premature deterioration, compared to one kept in a dry, well-ventilated room.
These durability factors are interconnected and collectively determine the lifespan and performance of a queen size mattress with a medium-firm specification. Selecting a mattress with high-quality materials, robust construction, and adhering to proper care and maintenance practices can significantly extend its durability, ensuring a comfortable and supportive sleep surface for years to come. Comparisons between mattresses of different construction and material grades highlight the significance of focusing on long-term durability rather than short-term cost savings.
6. Motion Isolation
Motion isolation, concerning a queen size mattress with a medium firm specification, refers to the mattress’s capacity to minimize the transfer of movement across its surface. This characteristic is particularly relevant in shared sleeping environments, where one sleeper’s movements can disrupt the other’s rest. A mattress with effective motion isolation minimizes the propagation of these disturbances, contributing to a more restful and undisturbed sleep experience for both individuals. This contrasts with mattresses that readily transmit motion, leading to frequent awakenings and compromised sleep quality.
- Material Composition and Damping Properties
The type and density of materials used in a mattress significantly influence its ability to isolate motion. Memory foam and latex, for instance, are known for their damping properties, absorbing and dissipating movement rather than transmitting it across the surface. Mattresses with a high-density foam core or multiple layers of these materials generally exhibit superior motion isolation compared to those constructed primarily with innerspring coils. Consider a scenario where one partner frequently tosses and turns; a mattress with effective material-based damping will reduce the perceived disturbance for the other partner. Conversely, a mattress with minimal damping properties might amplify even minor movements, leading to frequent awakenings.
- Coil System Design and Encapsulation
The design of the coil system plays a crucial role in motion isolation, particularly in hybrid mattresses. Individually pocketed coils, where each coil is encased in fabric, reduce motion transfer by allowing each coil to respond independently to pressure. This contrasts with traditional interconnected coil systems, where movement in one area can affect the entire surface. A queen size mattress with individually pocketed coils will, to a great extent, isolate motion transfer across its surface. The implication is that even if one individual shifts positions on the bed, the vibrations are restricted and are not spread across the mattress surface, therefore reducing partner disturbance during sleep.
- Mattress Construction and Layering Techniques
The layering of different materials and the overall construction of the mattress can enhance motion isolation. Combining a supportive base layer with multiple layers of damping materials, such as memory foam or latex, creates a barrier that minimizes motion transfer. The order and thickness of these layers are critical; strategically placed layers of high-density foam can absorb and dissipate movement before it reaches the other side of the mattress. An example is a mattress with a high density base layer and pocketed coils, followed by a transition layer for comfort, with memory foam for absorbing vibrations.
- Weight Distribution and Surface Tension
A mattress’s ability to distribute weight evenly and maintain a consistent surface tension can also affect motion isolation. Mattresses that conform closely to the body’s contours minimize the transfer of movement by distributing weight across a larger area. A queen size mattress with a medium-firm configuration may also offer better motion isolation as this type of mattress is specifically designed to distribute body weight evenly, in turn reducing motion transfer. For instance, if an individual tends to move a lot in their sleep, a mattress that evenly distributes weight can help restrict surface area vibration and hence partner disturbance.
In summary, motion isolation is a critical characteristic for queen size mattresses, especially for couples or individuals sharing a bed. The effectiveness of motion isolation is influenced by factors, such as, material composition, coil design, mattress construction, and weight distribution. Choosing a mattress with design that enhances motion isolation contributes significantly to a restful and undisturbed sleep environment for both partners, emphasizing the importance of this feature in mattress selection.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding queen-size mattresses with a medium-firm feel, providing detailed information to aid informed decision-making.
Question 1: What distinguishes a medium-firm mattress from firm or plush options?
A medium-firm mattress represents a balance between support and cushioning. Firm mattresses offer minimal give, while plush mattresses provide significant contouring. A medium-firm mattress aims to accommodate a broader range of sleeping positions and body types by offering a compromise between these extremes. Individuals seeking a blend of support and pressure relief often find this option suitable.
Question 2: Is a medium-firm mattress appropriate for individuals with back pain?
A medium-firm mattress can be beneficial for some individuals with back pain, as it can promote proper spinal alignment. However, the suitability depends on the specific cause and nature of the back pain. Individuals with more severe back pain should consult a medical professional to determine the most appropriate mattress firmness level.
Question 3: How does the material composition influence the performance of a medium-firm mattress?
Material composition significantly affects the support, comfort, and durability of a medium-firm mattress. Memory foam conforms to the body, providing pressure relief, while innerspring coils offer support and responsiveness. Hybrid mattresses combine these materials to offer a blend of benefits. The quality and density of the materials are crucial for long-term performance.
Question 4: What is the expected lifespan of a queen-size medium-firm mattress?
The lifespan varies depending on factors such as material quality, construction methods, usage patterns, and maintenance practices. Generally, a high-quality mattress can last between seven to ten years. Regular rotation and the use of a mattress protector can extend its lifespan. Signs of wear, such as sagging or body impressions, indicate the need for replacement.
Question 5: How does the size of a queen-size mattress compare to other standard mattress sizes?
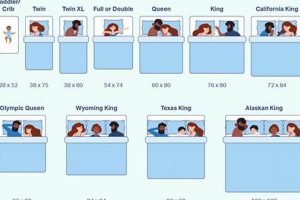
A queen-size mattress measures approximately 60 inches wide and 80 inches long. It is larger than a twin or full-size mattress, providing more sleeping space for individuals or couples. A king-size mattress is wider and longer, offering even more space. The appropriate size depends on individual needs, room dimensions, and sleeping arrangements.
Question 6: Are there specific maintenance requirements for a medium-firm mattress?
Yes, regular maintenance can extend the lifespan and maintain the performance of a medium-firm mattress. It is recommended to rotate the mattress every three to six months to distribute wear evenly. Using a mattress protector shields against spills, stains, and allergens. Spot cleaning stains promptly prevents permanent damage. Adhering to the manufacturer’s care instructions is essential.
Understanding these frequently asked questions allows consumers to have a holistic understanding when buying a “queen size mattress medium firm”. Individual research is vital for a great sleep.
The subsequent section will provide specific product recommendations and maintenance tips to optimize the lifespan and performance of this bedding type.
Conclusion
The preceding analysis has extensively explored the characteristics, benefits, and considerations associated with a queen size mattress medium firm. Key aspects include balanced support, pressure relief, spinal alignment, versatile comfort, durability factors, and motion isolation. A thorough understanding of these elements is crucial for making an informed purchasing decision.
The selection of a sleep surface represents a significant investment in long-term health and well-being. Careful evaluation of individual needs, coupled with diligent research, will maximize the potential for restful and restorative sleep. Consumers are encouraged to prioritize comprehensive assessment and informed decision-making in their pursuit of optimal sleep quality.