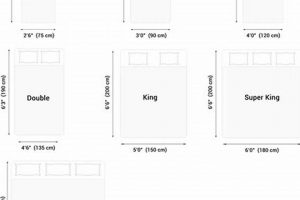
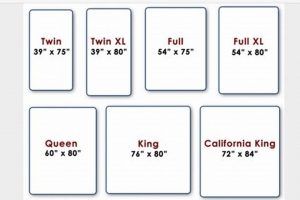
A futon designed to accommodate a queen-size mattress offers a sleeping and seating surface that corresponds to the dimensions of a standard queen bed. The specified dimensions typically measure around 60 inches wide and 80 inches long. This configuration provides ample space for two adults to sleep comfortably.
Utilizing this dimension allows for versatility in smaller living spaces. The furniture can function as a sofa during the day and be converted into a bed at night, maximizing the utility of the room. The availability of fitted sheets and mattress protectors designed for queen-size beds simplifies the process of maintaining the futon’s hygiene and extending its lifespan. Furthermore, this standard measurement ensures compatibility with a wide array of bedding accessories.
The following sections will delve into the specific considerations for selecting a suitable frame, the various mattress types available for such a futon, and the factors influencing overall comfort and support.
Considerations for Queen Futon Selection
Selecting components for a queen-size futon requires careful consideration to ensure optimal comfort and longevity. The following guidelines provide a framework for informed decision-making.
Tip 1: Frame Material Assessment: Evaluate the frame material based on intended usage. Solid hardwood frames offer greater durability for frequent conversion between seating and sleeping configurations. Metal frames provide a cost-effective alternative, suitable for less demanding applications.
Tip 2: Mattress Thickness Evaluation: A thicker mattress generally provides enhanced comfort. Consider the intended use; thicker options are advisable for primary sleeping arrangements, while thinner mattresses may suffice for occasional guest use.
Tip 3: Support System Examination: Inspect the support system beneath the mattress. Closely spaced slats or a solid platform provide more consistent support, minimizing sagging and maximizing mattress lifespan.
Tip 4: Cover Fabric Durability Analysis: Select a cover fabric that withstands anticipated wear and tear. Tightly woven fabrics resist abrasion and staining more effectively than loosely woven alternatives.
Tip 5: Assembly Process Comprehension: Review the assembly instructions thoroughly before purchase. Ensure the process is manageable, or consider professional assembly services to guarantee structural integrity.
Tip 6: Space Measurement Verification: Precisely measure the intended location. A queen-size futon requires adequate clearance, particularly when converted to the sleeping position, to avoid obstructing walkways or other furniture.
Adhering to these guidelines facilitates the selection of a queen-size futon that meets specific needs and provides lasting value.
The subsequent sections of this resource will explore maintenance protocols and potential issues associated with queen-size futons, enabling proactive care and problem-solving.
1. Overall Dimensions
The overall dimensions of a futon frame designed for a queen-size mattress are intrinsically linked to the designated mattress size, influencing functionality and spatial considerations. Understanding these dimensions is crucial for ensuring compatibility and optimizing the furniture’s placement within a given environment.
- Frame Width and Mattress Overhang
The frame width directly correlates with the intended mattress width, approximately 60 inches for a queen size. Accurate frame construction prevents excessive mattress overhang, which can compromise edge support and reduce sleeping surface area. Slight overhang may be present for aesthetic reasons or to accommodate thicker mattresses, but significant discrepancies can lead to instability and premature wear.
- Length in Sofa Configuration
When configured as a sofa, the futon’s length extends beyond the 60-inch mattress width due to the armrests and frame structure. This extended length must be factored into room layout planning. Failure to account for this additional space can result in obstructed walkways or limited maneuverability within the room.
- Length in Bed Configuration
Converting the futon to a bed requires sufficient clearance along its length, which will be approximately 80 inches, mirroring the queen mattress length. Obstructions such as walls or furniture can impede full extension and compromise the functionality of the sleeping surface. This dimension is paramount for comfortable use as a bed.
- Height Considerations
The overall height of the futon, both in sofa and bed configurations, dictates its ergonomic suitability. A height that is too low may cause discomfort when sitting or transitioning from a seated position. Conversely, a height that is too high may make it difficult to access the bed. Optimizing height in relation to mattress thickness and frame design is crucial for user comfort.
The precise overall dimensions of the futon frame, in both sofa and bed configurations, directly impact its usability and compatibility with the intended queen mattress. Therefore, careful attention to these measurements is essential during the selection process to ensure a functional and comfortable furnishing.
2. Folded Footprint
The folded footprint of a futon designed for a queen mattress dictates its space efficiency when configured for seating. This dimension is critical for individuals seeking a dual-purpose furniture piece in limited living areas. Precise measurement and understanding of this footprint are essential for informed purchasing decisions.
- Sofa Depth and Room Arrangement
The depth of the futon in sofa configuration, which contributes significantly to the folded footprint, determines the amount of floor space occupied. A greater depth restricts available room for movement and placement of other furnishings. Prior assessment of room dimensions is imperative to ensure harmonious integration of the futon within the space.
- Armrest Design and Width Contribution
The design and width of the armrests directly influence the overall folded footprint. Bulky or extended armrests increase the horizontal space required, potentially impacting walkway clearance and furniture arrangement options. Streamlined designs with minimal armrest protrusion contribute to a more compact footprint.
- Frame Style and Conversion Mechanism Influence
The style of the futon frame, particularly the conversion mechanism employed, affects the folded footprint. Frames with a “bi-fold” mechanism generally exhibit a deeper footprint compared to those using a “tri-fold” design. Understanding the mechanism’s spatial requirements is crucial for optimizing floor space utilization.
- Impact on Traffic Flow and Accessibility
The folded footprint directly impacts traffic flow within a room. A large footprint can obstruct pathways and limit accessibility to other areas. Careful consideration of the folded footprint in relation to doorways, hallways, and other access points is essential for ensuring a functional and comfortable living environment.
The characteristics of the folded footprint are inherently connected to a futon intended for a queen mattress, influencing usability within different spatial constraints. Analyzing each facet allows the selection of a frame that optimally balances seating space with overall room efficiency.
3. Mattress Thickness
Mattress thickness, when considered in conjunction with futon frames designed for queen-size mattresses, is a critical determinant of comfort, support, and overall suitability for intended use. The measurement directly influences the futon’s functionality, both as a seating surface and a sleeping platform. A thorough understanding of this relationship is essential for informed purchasing decisions.
- Support and Weight Distribution
Greater mattress thickness generally provides enhanced support and improved weight distribution, particularly for larger individuals or couples. Thicker mattresses often incorporate multiple layers of foam, innersprings, or other materials designed to contour to the body and alleviate pressure points. This enhanced support translates to a more comfortable sleeping experience and reduced risk of back pain or discomfort. Conversely, thinner mattresses may lack sufficient support, leading to sagging and uneven weight distribution.
- Frame Compatibility and Conversion Ease
Mattress thickness directly impacts the ease of converting the futon between its sofa and bed configurations. Excessively thick mattresses may hinder the conversion process, making it difficult to fold or unfold the frame. Additionally, a thicker mattress may not fit properly within the frame when in the sofa position, resulting in an aesthetically unappealing and potentially unstable seating surface. Careful consideration of frame design and maximum recommended mattress thickness is crucial for ensuring smooth and effortless conversion.
- Durability and Longevity
Mattress thickness can influence its overall durability and longevity. Thicker mattresses tend to withstand wear and tear more effectively than thinner counterparts, particularly when subjected to frequent use and weight. The increased material volume provides greater resistance to compression and deformation, extending the mattress’s lifespan. However, it’s important to note that material quality also plays a significant role in durability, and a thicker mattress made with inferior materials may not necessarily outlast a thinner mattress made with high-quality components.
- Seating Comfort and Ergonomics
While primarily intended for sleeping, a futon serves as a seating surface in its sofa configuration. Mattress thickness influences the comfort and ergonomics of this seating arrangement. Excessively thick mattresses can result in a seat height that is too high, causing discomfort for individuals with shorter legs. Conversely, very thin mattresses may provide inadequate cushioning and support, leading to discomfort during prolonged sitting. Finding an optimal balance between mattress thickness, seat height, and overall comfort is essential for maximizing the futon’s versatility and usability.
The foregoing points illustrate the interconnectedness of mattress thickness and the suitability of a queen-size futon. Selecting a mattress thickness that aligns with individual needs, frame design, and intended use patterns is paramount for achieving optimal comfort, support, and long-term satisfaction.
4. Frame Strength
The structural integrity of a futon frame directly correlates with its ability to accommodate a queen-size mattress. The dimensions inherent to the designated mattress size impose significant load-bearing demands on the frame. Insufficient frame strength precipitates premature failure, manifested as sagging, breakage, or instability. For example, a frame constructed from lightweight materials, such as low-density particleboard, may exhibit structural weakness under the weight of a queen mattress, particularly when occupied. Conversely, a frame fabricated from solid hardwood or reinforced steel provides the necessary rigidity to support the mattress and occupants, ensuring long-term functionality.
The choice of frame material, joint construction, and support system architecture collectively determine the overall strength and durability. Mortise-and-tenon joints, commonly employed in hardwood frames, offer superior resistance to shear forces compared to simpler screw-based connections. Similarly, closely spaced support slats or a solid platform distribute weight more evenly, mitigating stress on individual frame components. The absence of adequate reinforcement, particularly in the center support region, can lead to pronounced sagging over time, compromising both comfort and structural integrity. Regular use, especially when the futon is frequently converted between seating and sleeping configurations, exacerbates the effects of inadequate frame strength.
In summary, frame strength is a foundational attribute of a futon designed for a queen-size mattress. Compromises in this area invariably result in diminished performance and reduced lifespan. Selecting a frame constructed from robust materials, incorporating durable joinery techniques, and featuring a well-designed support system is paramount for ensuring the safe and reliable operation of the futon. The long-term cost savings associated with a structurally sound frame outweigh the initial investment, making it a critical consideration in the purchasing decision.
5. Weight Capacity
Weight capacity is a critical specification for futons designed to accommodate queen-size mattresses. The dimensions of a queen mattress inherently dictate a larger surface area, which in turn necessitates a higher weight capacity to ensure structural integrity and user safety. Understanding this parameter is vital for preventing damage and maximizing the lifespan of the furniture.
- Frame Material and Load Distribution
The frame material dictates the futon’s ability to withstand static and dynamic loads. Hardwoods, such as oak or maple, offer superior weight-bearing capabilities compared to softwoods or composite materials. Poor load distribution, often resulting from inadequate frame design, concentrates stress on specific points, leading to premature failure. A well-engineered frame distributes weight evenly across its structure, maximizing its overall capacity.
- Slat System and Support Structure
The slat system directly supports the queen mattress and any occupants. The number, spacing, and material of the slats significantly influence weight capacity. Closely spaced, reinforced slats provide greater support and prevent sagging, while wider spacing or weaker materials compromise the structure’s ability to bear weight safely. The presence of a central support beam further enhances the system’s weight-bearing capabilities.
- Intended Use and Occupancy
Weight capacity must align with the intended use and typical occupancy. A futon primarily used for seating may require a lower weight capacity compared to one intended for regular sleeping. Exceeding the specified weight limit, either through excessive static load or dynamic forces during movement, can result in structural damage and potential injury. Manufacturers typically provide weight capacity ratings based on standardized testing protocols.
- Joint Construction and Fastener Strength
The method of joining frame components significantly impacts the overall weight capacity. Robust joinery techniques, such as mortise-and-tenon joints or bolted connections, provide greater strength compared to simpler screw-based assemblies. The quality and size of fasteners also play a crucial role in maintaining structural integrity under load. Weak or improperly installed fasteners can compromise the entire system’s ability to support weight effectively.
The interplay between frame material, support structure, intended use, and joint construction determines the overall weight capacity of a futon designed for a queen mattress. Careful consideration of these factors is essential for selecting a product that meets specific needs and ensures long-term durability and safety. Failure to adhere to specified weight limits can void warranties and lead to costly repairs or replacements.
6. Material Composition
The materials used in the construction of a futon frame and mattress designed for a queen-size configuration significantly influence its durability, comfort, and overall suitability for the intended use. The selection of appropriate materials directly affects the futon’s ability to withstand weight, resist wear, and provide a comfortable sleeping and seating surface.
- Frame Materials and Structural Integrity
Frame materials commonly include solid hardwoods, metal alloys, and engineered wood products. Solid hardwoods, such as oak or maple, offer superior strength and durability, making them suitable for frequent use and heavy loads. Metal frames, often constructed from steel, provide a cost-effective alternative with good structural support. Engineered wood products, such as plywood or particleboard, can reduce manufacturing costs but may compromise long-term durability. For example, a frame constructed from solid hardwood will typically outlast one made from particleboard, particularly under the weight of a queen mattress and multiple occupants. The choice of frame material directly impacts the futon’s ability to withstand stress and resist deformation over time.
- Mattress Core Materials and Comfort
The core of a futon mattress typically consists of various materials, including cotton batting, foam (polyurethane or memory foam), innersprings, or a combination thereof. Cotton batting provides a traditional feel but may compress over time, reducing support. Foam offers varying degrees of firmness and contouring, with memory foam conforming to the body’s shape for enhanced comfort. Innersprings provide resilient support and promote airflow. The selection of core materials influences the mattress’s comfort level, support characteristics, and ability to regulate temperature. A mattress with a high-density foam core, for instance, will generally provide greater support and durability than one composed primarily of cotton batting.
- Cover Fabrics and Durability
The outer covering of a futon mattress is typically made from durable fabrics, such as cotton, polyester, or a blend of both. The fabric’s weave, weight, and fiber composition influence its resistance to abrasion, staining, and fading. Tightly woven fabrics with a higher thread count generally offer greater durability and resistance to wear. Fabrics treated with stain-resistant finishes can simplify cleaning and maintenance. For example, a polyester blend fabric is more resistant to staining and fading compared to a natural cotton fabric. The selection of an appropriate cover fabric directly impacts the mattress’s appearance, longevity, and ease of care.
- Fill Materials and Flammability Standards
The filling materials used in a futon mattress, particularly those containing cotton or synthetic fibers, must comply with flammability standards to ensure user safety. Flame-retardant chemicals are often added to these materials to reduce their ignitability and slow the spread of fire. The specific flammability standards vary depending on the jurisdiction, but compliance is essential for legal sale and safe use. The presence of these chemicals can also affect the mattress’s comfort and breathability. Manufacturers must balance the need for fire safety with considerations for user comfort and environmental impact.
The material composition of a futon designed for a queen mattress is a multifaceted consideration that encompasses frame materials, mattress core components, cover fabrics, and compliance with flammability standards. Each of these elements contributes to the futon’s overall performance, durability, and safety. A careful assessment of these factors is essential for selecting a product that meets specific needs and provides long-term satisfaction.
7. Conversion Mechanism
The conversion mechanism of a futon frame designed for queen-size mattresses is a critical component determining ease of use, space optimization, and overall functionality. The mechanism dictates how the futon transitions between seating and sleeping configurations, directly impacting user experience and the practicality of the dual-purpose design.
- Bi-Fold Mechanisms and Spatial Requirements
Bi-fold mechanisms, a common design, fold the mattress in half along its width to transform the futon into a sofa. This design typically requires significant clearance in front of the futon to accommodate the unfolding action. For a queen-size futon, this clearance can be substantial, potentially limiting placement options in smaller rooms. The bi-fold mechanism is often simpler in construction, which can translate to lower cost but at the expense of increased spatial demands.
- Tri-Fold Mechanisms and Compact Footprint
Tri-fold mechanisms divide the mattress into three sections, allowing for a more compact sofa configuration. This design reduces the clearance needed for conversion compared to bi-fold mechanisms, making it suitable for tighter spaces. However, tri-fold mechanisms tend to be more complex in design, potentially increasing manufacturing costs and introducing more points of potential mechanical failure. The seating surface may also be less uniform due to the multiple folds.
- Click-Clack Mechanisms and Simplified Operation
Click-clack mechanisms utilize a ratcheting system to adjust the backrest angle, allowing for quick and easy conversion between seating, lounging, and sleeping positions. These mechanisms often require minimal clearance and offer a straightforward user experience. However, click-clack mechanisms may not provide the same level of support and stability as more robust bi-fold or tri-fold designs, particularly when supporting the weight of a queen-size mattress and multiple occupants.
- Wall-Hugger Mechanisms and Space Efficiency
Wall-hugger mechanisms are designed to minimize the distance required between the futon and the wall during conversion. These mechanisms typically slide the seating surface forward as the backrest is lowered, allowing the futon to convert to a bed without requiring significant forward clearance. This design is particularly advantageous in smaller rooms where space is at a premium. However, wall-hugger mechanisms can be more complex and expensive to manufacture, potentially increasing the overall cost of the futon.
The choice of conversion mechanism for a queen-size futon directly impacts its functionality, spatial efficiency, and ease of use. Careful consideration of the available space, budget constraints, and desired level of convenience is essential for selecting a mechanism that meets individual needs and preferences. The mechanical robustness of the chosen design also affects the longevity of the futon, requiring a balance between ease of use and structural integrity.
Frequently Asked Questions About Futon Queen Mattress Size
The following section addresses common inquiries and misconceptions regarding futons designed to accommodate queen-size mattresses. The information provided aims to clarify essential aspects for prospective buyers and current owners.
Question 1: Is a standard queen-size mattress compatible with any queen-size futon frame?
While futon frames are designed to accommodate standard queen mattresses, slight variations in dimensions may exist between manufacturers. It is advisable to verify compatibility by consulting the product specifications or contacting the manufacturer directly.
Question 2: What is the typical weight capacity for a futon frame designed for a queen-size mattress?
The weight capacity varies depending on the frame material and construction. However, a well-constructed frame should typically support a minimum of 500 pounds. Always consult the manufacturer’s specifications for accurate weight limits.
Question 3: Does the thickness of the futon mattress affect the ease of converting between sofa and bed configurations?
Yes, a thicker mattress can make the conversion process more difficult, particularly with certain frame designs. Thicker mattresses may also place additional stress on the frame’s conversion mechanism. Consider the mattress thickness in relation to the frame’s design.
Question 4: What are the primary benefits of using a futon with a queen-size mattress compared to a traditional bed?
The primary benefit is space optimization. A futon functions as both a sofa and a bed, making it suitable for smaller living spaces. It also provides a cost-effective alternative to purchasing separate furniture pieces.
Question 5: How does the material composition of the futon frame affect its durability and longevity?
Solid hardwood frames offer the greatest durability and longevity. Metal frames provide a more economical option, while engineered wood products may be less durable and prone to damage over time. The material composition directly influences the frame’s ability to withstand weight and resist wear.
Question 6: Are there specific maintenance requirements for futons with queen-size mattresses?
Regular cleaning of the mattress and frame is essential. Rotate the mattress periodically to promote even wear. Inspect the frame’s hardware and joints for looseness and tighten as needed. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for specific cleaning and maintenance procedures.
These FAQs provide a foundational understanding of key considerations related to queen-size futons. Further research and careful evaluation of individual needs are recommended before making a purchase.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific recommendations for selecting futon mattresses and frames, offering practical guidance for optimizing comfort and durability.
futon queen mattress size
This article has meticulously examined the various facets of a futon configured to accommodate a queen mattress. The exploration encompassed dimensions, frame strength, mattress composition, conversion mechanisms, and critical specifications. An understanding of these elements is paramount to ensuring functionality, comfort, and longevity of the furniture.
As the demand for multi-functional furniture solutions grows, a comprehensive understanding of the inherent characteristics of futon frame dimensions and quality provides a basis for informed purchasing choices and optimized space utilization. Continued awareness of the nuances associated with the specific sleeping platform will provide a baseline to ensure a functional purchase as user requirements evolve.


![Best Queen Size Mattress Storage Bag [Easy Move] Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Best Queen Size Mattress Storage Bag [Easy Move] | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-2296-300x200.jpg)
