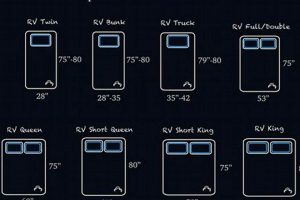
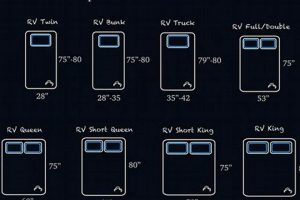
Dimensions of patient support surfaces in healthcare facilities are carefully considered aspects of medical equipment selection. These measurements directly impact patient comfort, safety, and the effectiveness of medical treatments. For instance, the dimensions must accommodate a diverse range of patient body types and allow for the use of specialized medical devices, such as pressure redistribution overlays.
Appropriate surface area dimensions in these settings are crucial for several reasons. Firstly, they contribute significantly to pressure ulcer prevention by providing adequate space for weight distribution. Secondly, they facilitate ease of movement and repositioning of patients by medical staff. Furthermore, standardization in dimensions simplifies inventory management and ensures compatibility with hospital beds and frames. Historical context reveals that specific surface area dimensions have evolved alongside advancements in medical technology and patient care protocols.
The following discussion will explore the key considerations involved in selecting appropriate patient support surface measurements for healthcare settings. This will include an examination of standard dimensions, regulatory guidelines, and the impact of size on patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
Considerations for Selecting Patient Support Surface Dimensions
The appropriate dimensions of patient support surfaces in healthcare environments are critical to patient care and operational efficiency. This section provides practical considerations for selecting surface area dimensions to meet these needs.
Tip 1: Compliance with Regulatory Standards: Adherence to relevant standards is paramount. Investigate local and national guidelines pertaining to patient support surface dimensions in healthcare facilities. These standards often dictate minimum or maximum surface area requirements to ensure patient safety and accessibility.
Tip 2: Patient Population Analysis: Assess the demographic characteristics of the patient population. Bariatric patients, for example, necessitate wider and more robust surfaces than standard populations. A comprehensive analysis informs dimension requirements.
Tip 3: Bed Frame Compatibility: Ensure that the selected surface area dimensions are compatible with existing or planned bed frames. Mismatched dimensions can lead to safety hazards and hinder proper functionality. Verify measurements prior to procurement.
Tip 4: Pressure Redistribution Properties: Evaluate the impact of surface area dimensions on pressure redistribution capabilities. Larger surface areas generally offer improved weight distribution, reducing the risk of pressure ulcer development, particularly for immobile patients.
Tip 5: Maneuverability and Access: Consider the impact of surface area dimensions on patient maneuverability and staff access. Excessively large surfaces can impede repositioning and other patient care activities. Balance surface area with practical considerations.
Tip 6: Infection Control Protocols: Smaller dimensions tend to be easier to clean, contributing to infection control efforts. Antimicrobial properties are equally valuable. Choose materials compatible with commonly used hospital-grade disinfectants.
The selection of appropriate patient support surface dimensions requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing regulatory compliance, patient population characteristics, and functional considerations. Thoughtful application of these considerations will optimize patient care and operational efficiency.
The subsequent section will delve into specific examples of optimal surface area dimensions for various patient care scenarios.
1. Width
Width, in the context of hospital support surfaces, is a critical dimension directly impacting patient comfort, safety, and the efficacy of medical interventions. Its selection demands careful consideration of patient demographics and intended applications.
- Patient Accommodation
The width must accommodate a diverse range of body types. Insufficient width restricts movement, contributes to discomfort, and elevates the risk of falls. Conversely, excessive width can impede maneuverability for both patient and medical staff. The goal is to strike a balance that maximizes patient comfort and minimizes potential hazards. Consideration of bariatric patient needs is essential, often requiring specialized surfaces with increased width to ensure adequate support and prevent off-loading.
- Pressure Redistribution
Width contributes to the overall surface area available for pressure redistribution. A wider surface facilitates greater dispersion of weight, thereby reducing localized pressure points and mitigating the risk of pressure ulcer development. This is particularly relevant for immobile patients who are unable to independently reposition themselves. The relationship between width and pressure redistribution highlights its role in preventative care.
- Side Rail Compatibility
Width must be compatible with hospital bed side rails. Insufficient clearance can compromise the functionality of the rails, increasing the risk of falls and hindering patient access. Conversely, excessive clearance can negate the protective benefits of the rails. Proper alignment between width and side rail dimensions is paramount to ensuring patient safety.
- Operational Efficiency
Width can impact operational efficiency within a healthcare setting. Surfaces with excessive width may pose challenges during transport and storage, while surfaces with insufficient width may require specialized handling procedures. Standardized width dimensions can streamline inventory management and facilitate seamless integration with existing hospital infrastructure.
In summation, width is a fundamental parameter in the specification of patient support surfaces. Its influence extends beyond mere dimensions, impacting patient comfort, safety, and operational efficiency. A comprehensive understanding of these facets is essential for optimizing patient care within the hospital environment.
2. Length
Length, as a dimension of hospital patient support surfaces, significantly dictates patient comfort and affects clinical outcomes. Insufficient surface length leads to compromised support for extremities, potentially increasing the risk of pressure injuries at the heels or sacrum. Inadequate length can also force patients into uncomfortable or unsafe postures, negating the benefits of pressure redistribution technologies embedded within the surface. For instance, a taller patient on a support surface of insufficient length may experience their feet extending beyond the edge, concentrating pressure and increasing the likelihood of skin breakdown.
Consideration of length is paramount in specialized care settings. In rehabilitation units, where patients often spend extended periods in bed, proper surface length is crucial to support therapeutic positioning and prevent contractures. Furthermore, in pediatric settings, length must be appropriately scaled to accommodate the anatomical needs of younger patients, avoiding the discomfort and potential for injury associated with inappropriately sized equipment. The precise specification of length therefore requires meticulous assessment of patient populations and clinical requirements. For example, extended-length support surfaces are available to meet the needs of taller individuals or those requiring specialized positioning.
Ultimately, appropriate length contributes to a holistic approach to patient care. Challenges related to surface length can lead to compromised comfort and potentially adverse medical outcomes. Adherence to recommended length guidelines, coupled with individual patient assessments, is essential to optimizing support surface functionality and fostering a healing environment. The careful selection of length is an integral component of comprehensive pressure injury prevention strategies and the overall quality of patient care.
3. Thickness
Thickness, a key dimension of hospital mattresses, dictates the pressure redistribution capabilities and overall support provided to patients. Insufficient thickness compromises pressure relief, concentrating body weight on bony prominences and increasing the risk of pressure injuries. Conversely, excessive thickness can hinder patient mobility and complicate transfers. The correlation between thickness and patient outcome necessitates a calibrated approach to mattress selection, tailored to specific patient needs and clinical environments. For example, a support surface designed for a low-acuity setting may require less thickness than one intended for an intensive care unit where patients are typically immobile for extended periods. The optimal thickness contributes significantly to preventive care and overall patient well-being.
The material composition of the mattress significantly influences the effectiveness of its thickness. A thicker mattress made of low-density foam may provide less pressure relief than a thinner mattress comprised of high-density viscoelastic foam. Understanding the interplay between thickness and material properties is critical in selecting appropriate surfaces. Consider a scenario where a patient recovering from surgery requires both pressure relief and ease of movement. A medium-thickness, high-density foam surface may offer the ideal balance, providing adequate support while allowing for comfortable repositioning. This highlights the practical significance of assessing both thickness and material composition when selecting hospital mattresses.
In conclusion, thickness is not merely a measurement, but a critical determinant of a hospital mattress’s functionality and its impact on patient safety. Effective utilization of thickness, in conjunction with material selection, contributes directly to improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs associated with pressure injury management. The challenge lies in identifying the optimal thickness for diverse patient populations and clinical contexts, emphasizing the need for comprehensive assessment and informed decision-making.
4. Weight Capacity
Weight capacity is a critical, yet often overlooked, component directly influencing the suitability of a hospital mattress. The dimensions of the mattress, length, width, and thickness, collectively define its ability to safely and effectively support a patient’s weight. A direct correlation exists: inadequate weight capacity relative to the patient’s weight can lead to mattress deformation, compromising pressure redistribution and potentially causing or exacerbating pressure injuries. For instance, a standard-size mattress with a 250-pound weight limit will perform sub-optimally, or even fail, when supporting a 350-pound patient, negating any therapeutic benefits intended by its design. Therefore, weight capacity is not merely a specification but an integral consideration in determining appropriate patient support, functioning as a safety threshold within the overall size parameters of the hospital mattress. This factor has implications for patient comfort and safety.
The selection process must also consider potential dynamic loading factors. A patient shifting position, sitting on the edge of the mattress, or undergoing certain medical procedures places increased, albeit temporary, stress on the support surface. Choosing a mattress with a weight capacity slightly exceeding the patient’s actual weight provides a safety margin, ensuring consistent performance under these variable conditions. Furthermore, this consideration is essential for long-term mattress durability. Consistently exceeding a weight capacity shortens the lifespan of the mattress, leading to premature wear and requiring more frequent replacements. Bariatric units within hospitals, therefore, require specialized mattresses with significantly higher weight capacities and reinforced construction to accommodate their patient population.
In conclusion, weight capacity is inextricably linked to hospital mattress dimensions, collectively shaping its functionality and safety profile. The appropriate selection requires careful assessment of patient-specific needs and potential dynamic loading factors. Failure to prioritize weight capacity undermines the therapeutic benefits of the mattress, increases the risk of patient injury, and contributes to avoidable healthcare costs. Comprehensive understanding and meticulous application of these principles are paramount to ensuring optimal patient care and resource management within healthcare facilities.
5. Bed Frame Compatibility
Bed frame compatibility is a fundamental consideration intimately linked to hospital mattress dimensions. The dimensions of a hospital mattress dictate whether it can be safely and effectively used with a given bed frame. Incompatible pairings can lead to several negative outcomes. A mattress too large for the frame may overhang the sides, creating a fall risk for patients and obstructing side rail functionality. Conversely, a mattress too small may shift during use, creating gaps between the mattress and frame that could entrap limbs. These scenarios highlight the direct impact of dimensional mismatches on patient safety and the importance of bed frame compatibility as an essential component of appropriate support surface selection.
Standardization in bed frame and mattress sizes aims to mitigate these risks. However, variations persist due to different manufacturers, specialized bed types (e.g., bariatric, low beds), and legacy equipment still in service. For instance, a bariatric bed frame, designed to accommodate wider and heavier mattresses, will be incompatible with a standard-sized mattress, leaving significant gaps and undermining the frame’s structural integrity. Similarly, a low bed frame requires a thinner mattress to maintain a safe patient egress height, preventing falls. Prior to procuring replacement mattresses, facilities must meticulously verify the internal dimensions of their existing bed frames, considering not only length and width but also depth to ensure a secure and functional fit. This process may involve consulting manufacturer specifications, performing physical measurements, or utilizing compatibility databases.
In conclusion, bed frame compatibility is inextricably linked to the proper dimensions of hospital mattresses. Failure to consider this relationship introduces significant risks to patient safety, compromises the functionality of the bed, and potentially increases maintenance costs. A proactive approach involving careful measurement, adherence to standards, and consideration of specialized bed types is essential for ensuring seamless integration and optimal performance, underscoring the critical importance of bed frame compatibility in the selection and utilization of hospital mattresses.
6. Pressure Distribution Area
The area over which a hospital mattress distributes a patient’s weight is a critical factor in pressure injury prevention. This distribution is directly affected by the mattress’s dimensions; therefore, understanding the relationship between size and pressure distribution area is essential for informed mattress selection.
- Surface Area and Immersion
A larger surface area generally provides a greater pressure distribution area, allowing the patient to “immerse” slightly into the mattress. This immersion increases contact area, lowering peak pressure points. However, excessive immersion can hinder movement and complicate repositioning, highlighting the need for balance between pressure reduction and functional considerations. Bariatric mattresses, for example, are wider to accommodate a larger body mass and provide adequate immersion without bottoming out.
- Mattress Material and Conformance
The material composition of a mattress influences its ability to conform to the patient’s body contours, thereby affecting pressure distribution. Viscoelastic foam, for example, conforms more readily than traditional innerspring mattresses, creating a larger contact area and more even pressure distribution. The dimensional characteristics, such as thickness and density, interact with the material to dictate the overall pressure redistribution performance. A thin viscoelastic mattress may not provide adequate pressure relief for heavier patients, emphasizing the importance of material properties in conjunction with size.
- Patient Positioning and Support
Hospital mattress size impacts the ability to effectively position patients. A mattress of insufficient width or length may limit the range of positioning options, hindering the ability to offload pressure from vulnerable areas. For example, side-lying positioning requires adequate width to prevent pressure on the greater trochanter. Similarly, proper heel offloading requires sufficient length. Proper sizing promotes better pressure distribution through effective positioning strategies.
- Bed Frame Articulation and Adjustment
The articulation capabilities of the hospital bed frame interact with mattress dimensions to influence pressure distribution. When the head of the bed is elevated, shear forces increase, concentrating pressure on the sacrum and ischial tuberosities. A mattress with appropriate dimensions and pressure redistribution properties can help mitigate these forces, maintaining a more even pressure distribution across the body. The dimensions of the mattress must also allow for full articulation of the bed frame without compromising its intended support characteristics.
These considerations underscore that the selection of an appropriate hospital mattress size is intimately connected to the effective management of pressure distribution. Understanding these interconnected factors is essential for healthcare providers to select mattresses that promote patient comfort, prevent pressure injuries, and optimize clinical outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the dimensions of patient support surfaces within healthcare facilities. The information provided aims to clarify standards, considerations, and implications associated with hospital mattress size.
Question 1: What are the standard dimensions for hospital mattresses?
Standard dimensions typically range around 36 inches in width, 80 inches in length, and 6 inches in thickness. However, variations exist depending on the specific type of bed (e.g., bariatric, pediatric) and the manufacturer. Facilities should consult specific equipment specifications for precise measurements.
Question 2: How does hospital mattress size impact pressure injury prevention?
Appropriate surface area facilitates effective pressure redistribution. A larger surface area, provided the material is appropriate, can reduce concentrated pressure points, thereby decreasing the risk of pressure injury development, particularly for immobile patients. Insufficient surface area concentrates pressure, negating preventative efforts.
Question 3: What considerations apply when selecting a hospital mattress size for bariatric patients?
Bariatric patients require wider and more robust mattresses with increased weight capacity. These mattresses must accommodate larger body mass, providing adequate support and preventing bottoming out, which compromises pressure redistribution. Standard-sized mattresses are inadequate for this patient population.
Question 4: How does mattress thickness relate to its pressure redistribution capabilities?
Thickness contributes to pressure redistribution, but material composition is equally important. A thicker mattress made of low-density foam may offer less pressure relief than a thinner mattress comprised of high-density viscoelastic foam. The interplay between thickness and material properties determines effectiveness.
Question 5: How does hospital mattress size affect bed frame compatibility?
Mattress dimensions must align with bed frame dimensions to ensure patient safety and proper functionality. Mismatched sizes can create fall hazards, obstruct side rail operation, or compromise the structural integrity of the bed. Facilities must verify compatibility prior to procurement.
Question 6: Are there regulatory guidelines regarding hospital mattress size?
While specific dimensional requirements may vary by jurisdiction, regulatory standards often address overall patient safety and pressure injury prevention. Compliance typically involves adhering to manufacturer guidelines and implementing comprehensive patient assessment protocols to ensure appropriate mattress selection. Consult local and national healthcare regulations for details.
In summary, hospital mattress size is a multifaceted consideration encompassing patient safety, clinical efficacy, and regulatory compliance. Thoughtful assessment of these factors is essential for optimizing patient care.
The following section will explore the selection process for hospital mattresses.
Conclusion
This exploration of hospital mattress size underscores its significance in patient care and operational efficiency. Dimensions are not arbitrary; they directly impact patient safety, pressure injury prevention, and bed functionality. Selecting appropriate dimensions necessitates careful consideration of patient demographics, regulatory standards, and bed frame compatibility.
Failure to prioritize hospital mattress size compromises patient well-being and increases healthcare costs. Healthcare facilities must implement rigorous assessment protocols and adhere to evidence-based practices to optimize mattress selection. A continued focus on research and innovation is essential to advancing patient support surface technology and improving outcomes.




![Best Queen Size Mattress Foundation [Guide + Deals] Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Best Queen Size Mattress Foundation [Guide + Deals] | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-2313-300x200.jpg)