A sleep surface, commonly used on a bed designed for individual use or small spaces, incorporates an additional layer of padding sewn onto the uppermost portion. This supplementary cushioning is intended to enhance comfort, creating a softer initial feel for the sleeper. Its dimensions are standardized to fit a common bed frame size, making it a popular choice for guest rooms and smaller bedrooms.
The addition of an integrated upper layer offers several advantages. It can provide pressure relief at key points of contact, contributing to a more restful experience. Furthermore, this design can prolong the lifespan of the core support structure by absorbing some of the initial wear and tear. Historically, similar features have been incorporated into bedding to emulate the feel of more luxurious sleeping arrangements at a more accessible price point.
The following sections will delve deeper into the construction materials, support mechanisms, and suitability considerations related to this particular type of bedding, enabling a more informed purchasing decision based on individual needs and preferences.
Selection and Maintenance Tips
This section provides essential guidance to ensure the selection and prolonged use of a bed with an integrated comfort layer, maximizing its value and lifespan.
Tip 1: Assess Core Support. Prioritize models with a robust underlying support system, such as innerspring coils or high-density foam. The core provides the necessary structural integrity, preventing premature sagging and ensuring proper spinal alignment.
Tip 2: Consider Material Composition. Evaluate the materials used in both the comfort layer and the support structure. Natural fibers offer breathability, while synthetic options often enhance durability and resistance to allergens.
Tip 3: Evaluate Edge Support. Examine the firmness of the edges. Strong edge support maximizes the usable sleep surface and enhances stability when sitting on the side.
Tip 4: Rotate Regularly. Implement a consistent rotation schedule (e.g., every three months) to distribute wear evenly across the entire surface. This practice helps prevent localized compression and prolongs its lifespan.
Tip 5: Use a Mattress Protector. Invest in a high-quality mattress protector to safeguard against spills, stains, and allergens. A protector is an essential barrier that maintains the cleanliness and hygiene of the sleep surface.
Tip 6: Consider Weight Capacity. Adhere to the specified weight capacity. Exceeding the recommended weight limits can compromise structural integrity and void warranties.
Adhering to these guidelines ensures optimal comfort, support, and longevity, maximizing the investment and contributing to improved sleep quality.
The subsequent sections will explore specific use-case scenarios and address common concerns associated with different sleeping positions and body types.
1. Comfort Layer Material
The selection of materials used in the uppermost comfort layer of a mattress significantly impacts the overall sleep experience. This layer is specifically designed to provide immediate cushioning and pressure relief, influencing factors such as temperature regulation, support contouring, and motion isolation.
- Memory Foam Density and Responsiveness
Memory foam, known for its viscoelastic properties, conforms closely to the body’s shape, distributing weight evenly and reducing pressure points. Higher density memory foam tends to offer greater support and durability, while lower density options provide a softer feel. The responsiveness of the foam, or how quickly it returns to its original shape, affects ease of movement and can influence temperature regulation. Higher responsiveness may lead to cooler sleep.
- Latex Foam Composition and Firmness
Latex foam, derived from either natural rubber or synthetic materials, offers a resilient and supportive alternative to memory foam. Natural latex is known for its breathability and hypoallergenic properties. The firmness of latex varies depending on the manufacturing process and density. Firmer latex provides enhanced support and is often preferred by back and stomach sleepers, while softer latex conforms more closely to the body, offering pressure relief.
- Fiberfill Material and Loft
Fiberfill, often composed of polyester or other synthetic materials, provides a plush, cushioned feel. The loft, or thickness, of the fiberfill layer influences the initial softness of the surface. While fiberfill offers immediate comfort, it may compress over time, potentially reducing its support and loft. Higher quality fiberfill is more resilient and resists compression, extending its lifespan.
- Gel Infusion and Cooling Properties
Gel infusions within the comfort layer are designed to enhance temperature regulation by dissipating heat away from the body. Gel can be integrated into memory foam, latex, or fiberfill. The effectiveness of gel infusion varies depending on the concentration and distribution of the gel particles. Some gel-infused materials also incorporate phase change materials that absorb and release heat to maintain a consistent sleep temperature.
The interaction between these various comfort layer materials and the underlying support system dictates the overall performance and longevity of the sleep surface. The selection should align with individual sleep preferences, considering factors such as preferred sleeping position, body weight, and sensitivity to temperature variations.
2. Core Support System
The functionality and longevity of a sleep surface integrating a cushioned upper layer, referred to as a pillow top, are inextricably linked to the properties of its core support system. The core provides the foundational structure that determines the overall level of support, spinal alignment, and resistance to sagging. The addition of a comfort layer, while enhancing initial softness, does not negate the critical role of a robust and well-designed core. For example, an innerspring system with tempered steel coils will exhibit greater resistance to deformation under prolonged pressure compared to a less dense or poorly constructed coil system. Consequently, the lifespan of the sleep surface and the consistency of its support characteristics will be directly affected by the quality and design of the underlying core.
Consider the differences between various core support options. Individually wrapped pocket coils, for instance, minimize motion transfer, an important consideration for couples. A high-density foam core offers uniform support across the entire surface. The choice of core support system should be dictated by specific user needs and preferences. Individuals with back pain, for example, may benefit from a firmer core that promotes proper spinal alignment. Furthermore, the gauge of the steel used in innerspring systems and the density of the foam used in foam cores directly correlate with their ability to withstand weight and maintain their structural integrity over time. Ignoring these core characteristics can lead to premature wear and a compromised sleep experience.
In summary, while the enhanced cushioning of the upper layer provides immediate comfort, it is the core support system that fundamentally determines the performance and durability of the sleep product. A deficient core will negate the potential benefits of even the most luxurious comfort layer, leading to diminished support, premature sagging, and ultimately, a reduced lifespan. Selection should prioritize a core support system appropriate for the intended user’s weight, sleeping position, and specific support requirements, ensuring a long-term investment in sleep quality.
3. Edge Support Quality
The quality of edge support in a sleep surface incorporating a cushioned upper layer directly influences its overall usability and long-term durability. The perimeter of the bed is frequently subjected to concentrated weight, whether from sitting, entering, or exiting the bed. Inadequate edge support leads to premature sagging and compression along the perimeter, reducing the effective sleep surface and potentially impacting spinal alignment. A sleep surface lacking robust edge reinforcement will exhibit a noticeable slope towards the edge, making it uncomfortable and potentially unstable. This effect is exacerbated over time, as the edges become increasingly deformed under repeated stress.
Consider a scenario where an individual consistently sits on the edge of their bed to dress or read. Without sufficient edge support, the perimeter will gradually compress, leading to a localized dip. This not only reduces the usable surface area but also alters the overall support profile, potentially causing discomfort or even back pain. Conversely, a well-engineered edge support system, often employing reinforced coils or high-density foam, maintains its structural integrity, providing consistent support across the entire surface. This enhanced stability also facilitates easier movement and prevents the sensation of rolling off the bed, particularly beneficial for those who share the bed or tend to sleep near the edge. Therefore, the quality of edge support is not merely an aesthetic consideration but a functional attribute with significant implications for comfort, usability, and long-term product performance.
In conclusion, the integration of robust edge support mechanisms is critical for a bed with an integrated upper layer to deliver sustained comfort and support throughout its lifespan. Compromised edge support leads to decreased usability, accelerated wear, and potential musculoskeletal discomfort. Prioritizing models with reinforced edges ensures a more stable, comfortable, and durable sleep experience, maximizing the value and longevity of the investment. The ability of the edges to withstand consistent weight and pressure directly impacts its long-term performance, emphasizing the necessity of assessing this feature during the selection process.
4. Material Breathability
Material breathability significantly influences the overall comfort and sleep quality experienced when using a sleep surface with an integrated upper layer. The construction of such a surface typically involves multiple layers, including a comfort layer and a core support system. Reduced breathability within these layers, particularly in the comfort layer closest to the sleeper, can lead to heat retention and elevated body temperature. This effect disrupts sleep cycles and results in discomfort. Materials like dense memory foam, if not engineered with open-cell structures or cooling infusions, restrict airflow and exacerbate heat buildup. Conversely, materials like natural latex or open-weave cotton promote ventilation, facilitating heat dissipation and maintaining a more consistent sleep temperature.
The choice of materials impacts practical aspects. For instance, a person prone to night sweats may find a sleep surface constructed with high-density, non-breathable materials particularly uncomfortable, leading to frequent awakenings. In contrast, a model incorporating breathable materials such as wool or Tencel in the cover, combined with a latex comfort layer, would mitigate heat retention and promote a more restful sleep. The design can also affect the breathability; a thicker, denser integrated layer will inherently trap more heat than a thinner, more porous layer. Therefore, the selection should prioritize materials known for their breathability, particularly in the uppermost layers, to minimize heat retention and optimize sleep quality.
In summary, material breathability is a critical consideration in sleep surfaces that feature a sewn-on comfort layer, with its effects significantly impacting the sleeper’s thermal comfort. The selection of breathable materials minimizes heat retention, promoting a more restful and undisturbed sleep cycle. The practical significance of understanding this lies in choosing a model that aligns with individual temperature regulation needs, ultimately enhancing sleep quality and overall well-being. Challenges remain in balancing breathability with other desirable characteristics like support and durability, requiring ongoing innovation in material science and design.
5. Durability Expectations
The lifespan of a bed with an integrated upper comfort layer is a crucial consideration for consumers. Expectations regarding its longevity directly influence purchasing decisions and overall satisfaction. Understanding the factors that contribute to, or detract from, its durability is essential for making informed choices.
- Material Quality and Density
The materials used in both the comfort layer and the support core directly impact the product’s ability to withstand prolonged use. Higher density foams and tightly coiled innerspring systems generally exhibit greater resistance to compression and deformation. Lower quality materials are prone to sagging and breakdown, shortening the lifespan of the mattress. For example, a comfort layer composed of low-density polyurethane foam will degrade more rapidly than one made of high-density memory foam or natural latex.
- Construction Techniques and Stitching
The method of construction and the quality of stitching influence the structural integrity of the sleep surface. Reinforced seams and secure attachment of the comfort layer to the support core prevent shifting and bunching, which can lead to uneven wear and tear. A poorly constructed surface may exhibit premature separation of the comfort layer, compromising its comfort and support characteristics. Examples include the quality of the quilting and the use of durable thread.
- Weight Capacity and Usage Patterns
Exceeding the specified weight capacity accelerates wear and tear on both the comfort layer and the support core. Consistent overloading can lead to sagging and reduced support. Furthermore, usage patterns such as frequent sitting on the edge of the bed or concentrated pressure in specific areas can contribute to localized compression and uneven wear. Regular rotation and flipping (if applicable) can distribute wear more evenly, extending the lifespan of the product.
- Maintenance and Protection
Proper maintenance and protection are crucial for preserving the condition of a bed with a comfort layer. The use of a mattress protector shields the surface from spills, stains, and allergens, preventing damage and promoting hygiene. Regular vacuuming removes dust and debris that can contribute to material degradation. Failure to protect the surface from moisture and contaminants can lead to premature breakdown of the comfort layer and the development of mold or mildew.
In conclusion, durability expectations for a bed with an integrated upper comfort layer are closely linked to material quality, construction techniques, usage patterns, and maintenance practices. Consumers should carefully evaluate these factors to make informed purchasing decisions and maximize the lifespan of their investment. The interplay of these elements determines the overall value and long-term performance of the sleep surface.
6. Size Appropriateness
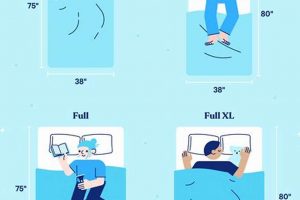
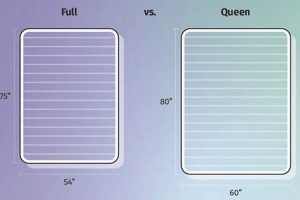
The dimensional congruity between a sleep surface featuring an integrated cushioned layer and the intended user or space is of paramount importance. Size appropriateness directly influences comfort, support, and the overall utility of the product. A sleep surface that is too small restricts movement and compromises spinal alignment, while one that is excessively large may overwhelm the available space, creating practical inconveniences. Therefore, careful consideration of room dimensions and user requirements is essential.
For instance, a full-size model, characterized by its specific width and length measurements, is typically suited for single sleepers or smaller rooms where space is limited. Selecting a larger queen-size model for an individual with limited space could hinder room functionality and accessibility. Conversely, placing a full-size version in a room intended for two adults would result in a cramped and uncomfortable sleeping arrangement. The inclusion of an attached upper layer can subtly alter the perceived dimensions and feel of the sleep surface. A thicker layer might reduce the usable surface area slightly, impacting the overall sensation of spaciousness. Size appropriateness is not solely about fitting the dimensions of a room; it encompasses the comfort and ergonomic needs of the individual or individuals using the surface.
In conclusion, the selection process must prioritize aligning the dimensions of the chosen sleep surface with the physical space and user requirements. A mismatch in size can negate the benefits of other features, such as enhanced cushioning or superior support. Therefore, a meticulous assessment of spatial constraints and individual comfort needs is paramount to ensuring optimal satisfaction and maximizing the functional utility of the sleep investment. Improper sizing leads to discomfort, restricts movement, and ultimately compromises the quality of sleep. The integration of a cushioning layer further emphasizes the importance of careful sizing to maintain equilibrium between comfort and space utilization.
7. Motion Isolation
The ability of a sleep surface to minimize the transfer of movement is a crucial factor influencing sleep quality, particularly for couples or individuals sharing a bed. In the context of a specific bed, the characteristics of the comfort layer and the underlying support system significantly impact the degree of motion isolation achieved. Understanding the mechanisms by which motion is dampened is essential for informed purchasing decisions.
- Comfort Layer Material and Dampening
The composition of the comfort layer directly affects its capacity to absorb and dissipate movement. Materials such as memory foam and latex exhibit inherent dampening properties, conforming to the body and reducing the propagation of motion across the surface. A thicker, denser comfort layer generally provides greater motion isolation compared to a thinner, less resilient layer. For example, a memory foam layer will contour to the shape of one sleeper, preventing the movement from disturbing the other. A thinner layer, however, transmits more motion.
- Core Support System and Independent Suspension
The underlying support system plays a critical role in minimizing motion transfer. Individually wrapped pocket coils, for instance, operate independently, isolating movement to the immediate area of compression. This design contrasts with traditional innerspring systems, where interconnected coils transmit motion across the entire surface. High-density foam cores can also provide effective motion isolation, particularly when combined with a responsive comfort layer. The independent suspension of pocket coils ensures that pressure applied to one area does not significantly affect adjacent areas.
- Construction Techniques and Layer Integration
The manner in which the comfort layer and support system are integrated influences motion isolation. A tightly bonded construction minimizes movement between layers, enhancing the overall dampening effect. Techniques such as foam encasement around the perimeter can further reduce motion transfer by providing a stable edge and preventing vibrations from propagating outwards. Poor construction techniques can create gaps or inconsistencies, allowing motion to transfer more readily between layers.
- Weight Distribution and Surface Tension
The manner in which weight is distributed across the sleep surface affects the propagation of motion. A surface that evenly distributes weight minimizes localized pressure points, reducing the likelihood of motion transfer. High surface tension, characteristic of some materials, can also contribute to motion isolation by dampening vibrations. Uneven weight distribution, conversely, exacerbates motion transfer. The ability of the surface to maintain its shape under pressure prevents disturbances to the other sleeper.
The facets discussed, comfort layer material, core support system, construction techniques, and weight distribution, are interdependent factors that determine the effectiveness of motion isolation. A well-designed integrates these elements to minimize sleep disturbances for couples, resulting in a more restful experience. The selection of materials and construction methods should prioritize motion isolation to maximize the benefits of individual sleeping space and reduce sleep interruptions.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the characteristics, performance, and maintenance of beds with integrated cushioned layers, designed to provide clarity and informed decision-making.
Question 1: How does the lifespan of a mattress with a sewn-on upper layer compare to that of a conventional mattress?
The longevity depends on the quality of materials used in both the comfort layer and the support core. Models constructed with high-density foam and robust innerspring systems tend to exhibit greater durability than those made with lower-grade materials. Proper maintenance, including regular rotation and the use of a protector, significantly extends its lifespan. Generally, expect a lifespan comparable to that of a traditional mattress, ranging from seven to ten years with appropriate care.
Question 2: What are the primary advantages of a sleep surface incorporating a quilted upper layer compared to a firm surface?
The main benefit is enhanced initial comfort and pressure relief. The extra layer of padding contours to the body, reducing pressure points and promoting a more restful sleep. This feature is particularly beneficial for side sleepers who often experience pressure on their shoulders and hips.
Question 3: Does the addition of an integrated upper layer impact the level of support provided?
While the uppermost layer enhances initial comfort, the level of support is primarily determined by the underlying core structure. A robust core, whether innerspring or high-density foam, is essential for maintaining proper spinal alignment. The comfort layer should complement, not compromise, the support provided by the core.
Question 4: How should I properly maintain a model with an attached padded surface to maximize its lifespan?
Regular rotation, ideally every three months, is crucial for distributing wear evenly across the surface. Additionally, the use of a quality protector shields the surface from spills, stains, and allergens. Vacuuming the surface periodically helps remove dust and debris that can contribute to material degradation.
Question 5: Is a good choice for individuals with back pain?
The suitability depends on the firmness of the underlying support core and individual preferences. A model with a firm support core and a moderately plush comfort layer can provide both pressure relief and adequate spinal support. Individuals with severe back pain should consult with a medical professional to determine the most appropriate type.
Question 6: What are the key differences between memory foam and latex foam in the context of a mattress featuring a upper layer?
Memory foam conforms closely to the body, providing excellent pressure relief but potentially retaining heat. Latex foam offers a more resilient and breathable alternative, providing good support and temperature regulation. The choice depends on individual preferences regarding feel, support, and temperature sensitivity.
These responses provide a foundational understanding of considerations related to this sleep surface. Selecting a model that aligns with individual needs and preferences is key to optimizing sleep quality and overall satisfaction.
The following sections will delve into comparisons with alternative bedding options and discuss emerging trends in sleep technology.
Conclusion
This exploration has provided a comprehensive overview of the characteristics, benefits, and considerations associated with a bed featuring an integrated upper layer and dimensions suited for a single occupant. The discussions have encompassed construction materials, support systems, maintenance practices, and suitability for various sleep preferences. The importance of carefully evaluating these factors to align with individual needs has been consistently emphasized.
Ultimately, the selection of bedding is a personal decision that significantly impacts sleep quality and overall well-being. Continued advancements in sleep technology and material science will undoubtedly lead to further innovations, enhancing the performance and longevity of such surfaces. Individuals are encouraged to apply the knowledge gained to make informed choices that optimize their sleep environment.


![Best Size Full Mattress [Guide] Comfort & Value! Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Best Size Full Mattress [Guide] Comfort & Value! | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-2874-300x200.jpg)


