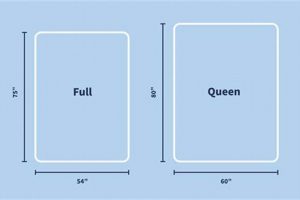
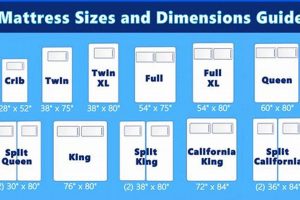
A bed designed to accommodate one or two sleepers comfortably, measuring approximately 54 inches wide and 75 inches long, and constructed with materials that promote air circulation is a common bedding choice. These materials facilitate the dissipation of body heat and moisture. An example would be a bed incorporating open-cell foam or a cover woven with breathable fibers.
The significance of such a sleeping surface lies in its capacity to enhance sleep quality. Improved airflow helps regulate body temperature, reducing the likelihood of overheating during the night. This can lead to fewer sleep disturbances and a more restful experience. Historically, advancements in material science have driven the development of increasingly effective methods for achieving this enhanced breathability, moving from traditional cotton and wool to sophisticated synthetic blends.
The following sections will delve into the specific materials and construction techniques used to create beds that offer superior ventilation, exploring how these features contribute to overall comfort and well-being. Further examination will be dedicated to care and maintenance, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Maximizing the Benefits
Optimizing the use of a sleep surface engineered for enhanced airflow requires consideration of several factors, from selection to maintenance. This section provides guidance on maximizing the benefits derived from such a product.
Tip 1: Select Appropriate Bedding: Opt for sheets and blankets made from natural, breathable fibers such as cotton, linen, or bamboo. Synthetic materials can impede airflow and diminish the breathability of the sleep surface itself.
Tip 2: Utilize a Supportive Foundation: Ensure the bed is placed on a foundation that allows for adequate ventilation. Slatted frames or breathable platforms are preferable to solid bases that can trap moisture.
Tip 3: Rotate Regularly: Periodically rotating the bed can help distribute wear evenly and prevent the accumulation of moisture in specific areas. Rotation frequency will depend on usage patterns.
Tip 4: Employ a Mattress Protector: A waterproof, yet breathable, mattress protector can shield the bed from spills and stains without compromising its airflow properties. Choose protectors specifically designed for breathability.
Tip 5: Maintain a Cool Bedroom Environment: A cooler room temperature facilitates better sleep and complements the breathability of the sleep surface. Optimal temperatures typically range from 60 to 67 degrees Fahrenheit.
Tip 6: Address Allergens: Regularly vacuum the sleep surface and surrounding areas to minimize dust mites and allergens that can accumulate and impede airflow. Consider using hypoallergenic bedding.
These strategies will enhance the performance and longevity of a bed designed for increased ventilation, promoting a more comfortable and restful sleep experience.
The subsequent section will explore the long-term advantages and considerations associated with this type of bedding, providing a comprehensive understanding of its potential impact on sleep quality and overall health.
1. Temperature regulation
Temperature regulation is a primary function in a sleep environment, influencing comfort and sleep quality. The interaction between the human body and the immediate surroundings during sleep significantly affects physiological processes. A bed designed for enhanced airflow directly addresses temperature management.
- Material Permeability
The construction materials’ inherent capacity to allow the passage of air is crucial. Open-cell foam structures, as opposed to closed-cell, facilitate greater airflow. Similarly, woven fabrics like cotton or linen offer superior breathability compared to synthetic alternatives such as polyester. The choice of materials directly impacts the rate at which heat dissipates from the sleeper’s body.
- Moisture Management
Evaporation of moisture from the skin is a key cooling mechanism. Materials that effectively wick away moisture, such as wool or certain synthetic fibers, promote this process. A bed incorporating these materials helps maintain a drier sleep surface, further contributing to temperature regulation. The absence of moisture accumulation reduces the likelihood of overheating.
- Convection Cooling
Air circulation around the sleeper’s body facilitates convective heat transfer. Beds designed with breathable materials allow for greater airflow between the body and the surrounding environment. This convection cooling effect helps regulate body temperature and prevents the build-up of heat, particularly in warmer climates or for individuals prone to night sweats.
- Heat Dissipation Rate
The rate at which heat is conducted away from the body is a critical factor. Materials with low thermal resistance, such as natural latex or specifically engineered cooling gels, enhance heat dissipation. A bed incorporating these elements provides a cooler sleeping surface, improving sleep quality and reducing the incidence of sleep disturbances caused by overheating.
The principles of material permeability, moisture management, convection cooling, and heat dissipation rate are integral to the effective design of a bed intended to regulate temperature. Combining these elements optimally creates a sleep environment that promotes thermal comfort and improves the quality of rest.
2. Airflow Capacity
Airflow capacity represents a fundamental attribute of a bed designed for thermal regulation and sleep comfort. This characteristic denotes the extent to which air can circulate through the construction materials, influencing heat dissipation and moisture management.
- Material Porosity
The porosity of constituent materials, such as foam, batting, and ticking, directly affects airflow capacity. Open-cell foam structures exhibit higher porosity compared to closed-cell counterparts, allowing for greater air movement. The use of natural fibers, such as cotton or wool, in the ticking layer also contributes to enhanced porosity. High porosity facilitates effective heat dissipation and minimizes moisture accumulation within the bed.
- Construction Techniques
The manner in which the bed is assembled impacts overall airflow. Quilted patterns with sufficient spacing between stitching lines promote better air circulation than tightly packed designs. The inclusion of ventilation channels or strategically placed perforations can further enhance airflow capacity. These construction techniques aim to minimize obstructions to air movement throughout the bed’s layers.
- Density Gradient
The density gradient within the bed’s layers influences airflow patterns. A gradual transition from lower-density to higher-density materials can optimize air circulation. This gradient allows air to move more freely through the initial layers and gradually dissipate throughout the deeper sections. An abrupt change in density can impede airflow and compromise the bed’s breathability.
- Environmental Factors
External environmental factors, such as room temperature and humidity levels, can affect the airflow capacity. A cooler and drier environment promotes better air circulation within the bed. Conversely, high humidity can reduce airflow and increase moisture retention. Proper ventilation within the sleeping area is essential for maximizing the benefits of enhanced airflow capacity.
These interwoven aspects of material porosity, construction techniques, density gradient, and environmental factors collectively determine the overall airflow capacity. An optimal blend of these elements allows a bed to effectively regulate temperature, manage moisture, and contribute to a more comfortable sleep environment.
3. Material composition
The breathability of a full-size bed is intrinsically linked to its material composition. The selection of specific materials dictates the degree to which air can circulate, moisture can be wicked away, and heat can be dissipated. Synthetic foams, for example, generally retain more heat compared to natural latex or open-cell memory foam. Similarly, tightly woven fabrics, like some polyesters, impede airflow more significantly than loosely woven cotton or linen. A bed incorporating a combination of open-cell foam, natural latex, and a cotton cover will inherently exhibit greater breathability than one composed of closed-cell foam and synthetic materials.
The material composition influences not only breathability but also the longevity and sustainability of the product. Natural materials, such as latex derived from rubber trees or cotton grown without synthetic pesticides, often present a more environmentally sound option. Furthermore, these materials can possess inherent antimicrobial properties, contributing to a healthier sleep environment. Conversely, some synthetic materials may off-gas volatile organic compounds (VOCs), potentially impacting air quality. The choice of materials, therefore, necessitates a careful evaluation of breathability, durability, and environmental impact.
In summary, material composition is a pivotal determinant of the breathability of a full-size bed. An informed decision requires consideration of the thermal properties, moisture-wicking capabilities, and environmental implications of the constituent materials. While enhanced breathability can improve sleep quality, the selection should also align with broader concerns regarding sustainability and indoor air quality.
4. Moisture wicking
Moisture wicking is a critical property that significantly enhances the functionality of a bed designed for optimized breathability. The human body naturally releases moisture during sleep, primarily through perspiration. A bed lacking effective moisture-wicking capabilities can lead to a damp sleep environment, potentially disrupting sleep and fostering the growth of mold and bacteria. Therefore, materials with inherent moisture-wicking properties are essential components of a well-designed, breathable sleep surface. The ability to draw moisture away from the body helps regulate temperature and maintain a more hygienic sleep environment.
For instance, consider a bed constructed with a cover made from merino wool. This material excels at wicking moisture away from the sleeper’s skin, distributing it across the fabric’s surface where it can evaporate more readily. This contrasts with synthetic materials like polyester, which tend to trap moisture, creating a less comfortable and potentially unhygienic sleeping environment. Similarly, the inner layers of a breathable bed might incorporate open-cell foam or natural latex, both of which possess better moisture-wicking characteristics than traditional memory foam. The practical significance of this lies in the improved sleep quality and reduced risk of allergen or microbial accumulation within the sleep surface.
In conclusion, moisture wicking is not merely a desirable feature but a fundamental requirement for a bed engineered for optimal breathability. The selection of materials with effective moisture-wicking properties directly impacts sleep quality, hygiene, and overall comfort. While breathability focuses on airflow, moisture wicking ensures a dry and comfortable sleep environment, complementing the temperature regulation provided by enhanced ventilation. The integration of these properties results in a sleep surface that promotes restorative rest and long-term well-being.
5. Sleep quality
The relationship between sleep quality and the characteristics of a bed, particularly one designed for enhanced breathability, is substantial. Sleep quality, defined as the depth, continuity, and restorative nature of sleep, is influenced by environmental factors, including the sleeping surface. A full size bed engineered to promote airflow directly addresses certain environmental factors that can impede sleep quality.
- Temperature Regulation and Sleep Disruption
Body temperature fluctuates during sleep, and maintaining a stable thermal environment is crucial for uninterrupted rest. Overheating can lead to awakenings and lighter sleep stages. A breathable bed facilitates temperature regulation by dissipating body heat, reducing the likelihood of overheating and promoting deeper, more continuous sleep. For instance, an individual prone to night sweats may experience significant improvements in sleep quality when transitioning to a bed with enhanced breathability.
- Moisture Management and Comfort
The accumulation of moisture from perspiration can create a damp and uncomfortable sleep environment. This discomfort can lead to restlessness and frequent changes in position, disrupting sleep. A breathable bed that wicks away moisture helps maintain a drier surface, enhancing comfort and promoting more restful sleep. Individuals residing in humid climates may particularly benefit from the moisture-managing properties of such a bed.
- Airflow and Allergen Reduction
Improved airflow within the bed can reduce the accumulation of allergens, such as dust mites and mold spores, which can trigger allergic reactions and respiratory issues. These reactions can disrupt sleep and negatively impact sleep quality. A breathable bed facilitates ventilation, minimizing the build-up of allergens and creating a healthier sleep environment. Individuals with allergies or asthma may experience a reduction in nighttime symptoms and improved sleep as a result.
- Material Comfort and Restlessness
The materials used in the construction of a bed influence its overall comfort level. Stiff, unyielding materials can create pressure points and lead to discomfort, causing restlessness and disrupted sleep. Breathable beds often incorporate materials designed for both airflow and comfort, such as open-cell foam or natural latex. These materials conform to the body, reduce pressure points, and promote a more comfortable sleep experience, contributing to improved sleep quality.
These factorstemperature regulation, moisture management, allergen reduction, and material comfortcollectively demonstrate the significance of a full size bed with enhanced breathability in fostering improved sleep quality. While other factors, such as sleep hygiene practices and underlying health conditions, also play a role, the selection of a breathable bed can directly address certain environmental impediments to restful sleep. The benefits are realized in the form of deeper, more continuous, and more restorative rest.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common inquiries and concerns regarding the selection, use, and maintenance of a full size bed designed for enhanced breathability.
Question 1: What constitutes a breathable mattress?
A breathable bed is constructed with materials and designs that promote air circulation, facilitating the dissipation of heat and moisture. This typically involves the use of open-cell foams, breathable fabrics, and strategically placed ventilation channels.
Question 2: How does a breathable mattress improve sleep quality?
Improved airflow regulates body temperature, reducing the likelihood of overheating and promoting deeper, more continuous sleep. Effective moisture wicking maintains a drier sleep surface, enhancing comfort and reducing the potential for microbial growth.
Question 3: What materials are commonly used in breathable mattresses?
Common materials include open-cell memory foam, natural latex, cotton, linen, bamboo, and wool. These materials exhibit varying degrees of breathability and moisture-wicking properties.
Question 4: How should a breathable mattress be maintained?
Regular rotation, vacuuming, and the use of a breathable mattress protector are recommended. Avoid using harsh cleaning chemicals, which can damage the materials and compromise breathability.
Question 5: Is a breathable mattress suitable for all sleepers?
While generally beneficial, a breathable bed may be particularly advantageous for individuals who tend to overheat during sleep, experience night sweats, or reside in warm climates.
Question 6: Are there any potential drawbacks to consider?
Breathable beds may have a higher initial cost compared to conventional mattresses. The specific materials used can also affect the level of support and firmness provided, requiring careful consideration of individual preferences.
These frequently asked questions offer a basic understanding of beds designed for enhanced breathability. Individual requirements and preferences should be carefully considered before making a purchase.
The subsequent section will delve into a comparative analysis of different materials used in bed construction, focusing on their respective breathability characteristics.
Full Size Breathable Mattress
The foregoing exploration has examined the multifaceted aspects of the full size breathable mattress, from its constituent materials and construction techniques to its influence on sleep quality and overall well-being. The importance of temperature regulation, moisture wicking, and airflow capacity has been underscored, highlighting the significance of selecting a product that aligns with individual needs and environmental considerations.
The understanding of these principles facilitates informed decision-making in the pursuit of restorative sleep. Continued research and development in material science and bed design will undoubtedly yield further advancements in sleep technology, enhancing the potential for improved rest and optimized health outcomes.


![Tempur-Pedic Full Mattress: Best [Full] Sleep Ever! Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Tempur-Pedic Full Mattress: Best [Full] Sleep Ever! | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-2892-300x200.jpg)


![Best Full Intex Air Mattress: Reviews & Guide [Year] Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Best Full Intex Air Mattress: Reviews & Guide [Year] | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-2888-300x200.jpg)