A bed designed for individual use, utilizing viscoelastic foam material and measuring ten inches in thickness. This type of bedding conforms to the body’s shape, distributing weight and potentially alleviating pressure points. The dimensions make it suitable for smaller spaces, such as guest rooms or children’s bedrooms.
These beds provide a balance of support and comfort. The foam construction offers cushioning while maintaining spinal alignment. Historically, memory foam was developed for NASA to improve aircraft cushions. Its application in mattresses has since grown due to its potential to enhance sleep quality and reduce discomfort.
The following sections will delve into the specific benefits, construction details, considerations for purchase, and maintenance guidelines of this type of bedding.
Guidance on Optimizing Sleep with a Properly Sized Viscoelastic Bed
The following guidelines provide valuable insights to maximize the benefits and longevity of a ten-inch viscoelastic foam bed designed for single occupancy.
Tip 1: Foundation Compatibility. Ensure the bed frame or foundation provides adequate support. Slatted frames with minimal spacing or a solid platform are recommended to prevent sagging and maintain proper foam distribution.
Tip 2: Proper Unpacking and Ventilation. Upon arrival, allow the bed to fully expand in a well-ventilated room. Viscoelastic foam may have a slight odor initially, which dissipates with exposure to air.
Tip 3: Use a Mattress Protector. A waterproof and breathable mattress protector is essential to shield the foam from spills, stains, and dust mites, extending its lifespan and maintaining hygiene.
Tip 4: Regular Rotation. Rotate the bed 180 degrees every 3-6 months to promote even wear and prevent body impressions from forming in specific areas.
Tip 5: Temperature Considerations. Viscoelastic foam can retain heat. Consider using breathable bedding materials such as cotton or linen to regulate temperature and improve sleep comfort.
Tip 6: Cleaning Protocols. Spot clean spills immediately with a mild detergent and water solution. Avoid harsh chemicals or excessive moisture, which can damage the foam.
Tip 7: Understanding Density. Be aware that different densities of viscoelastic foam offer varying levels of support and conformability. Research density options to align with individual preferences and needs.
Implementing these strategies will contribute to a more comfortable and supportive sleep environment, enhancing the overall performance and durability of the bed.
The subsequent section will provide information regarding common consumer concerns and frequently asked questions regarding this specific type of bedding.
1. Dimensions
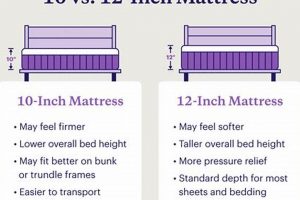
The term “Dimensions” in relation to a viscoelastic foam bed of this kind refers explicitly to its physical measurements, primarily its width, length, and thickness. For this specific type of bedding, the dimensions are standardized to fit a “twin” size frame, with a thickness of 10 inches. Deviations from these established measurements can impact its suitability for designated bed frames and potentially affect the overall comfort and support provided.
The 10-inch thickness is particularly crucial. A bed that is significantly thinner might lack adequate support, leading to discomfort or potential spinal misalignment. Conversely, an excessively thick bed may be too firm or difficult to maneuver. The standardized twin size, typically around 38 inches wide and 75 inches long, ensures compatibility with common bed frames and bedding accessories. Real-world examples include dorm rooms, guest rooms, and smaller bedrooms where space is a constraint. Accurate dimensions ensure a proper fit and optimal utilization of available space.
Understanding these dimensional characteristics is essential for both consumers and manufacturers. Manufacturers must adhere to these specifications to ensure product compatibility. Consumers, conversely, must consider room size and frame compatibility before purchase. In summary, the dimensions are not merely a descriptive feature but a defining characteristic that dictates functionality, comfort, and compatibility within the broader sleep environment. Failure to consider these dimensions can lead to improper fit, reduced comfort, and ultimately, a less-than-optimal sleep experience.
2. Density
Density is a critical attribute influencing the performance characteristics of a viscoelastic foam bed of this size. Expressed in pounds per cubic foot (PCF), density directly correlates with the support, durability, and overall feel of the material. Higher density foam provides greater resistance to compression, leading to enhanced support and a reduced likelihood of sagging over time. Conversely, lower density foam offers a softer feel but may exhibit diminished long-term support and a higher propensity for impressions to form. A practical example is the difference experienced between a bed with 5 PCF foam, which offers substantial support, and one with 3 PCF foam, which compresses more easily under body weight. Understanding density enables consumers to align their purchase with their individual comfort preferences and support needs.
The density of the foam directly affects its ability to distribute weight evenly, thus alleviating pressure points. A higher density allows for better contouring to the body’s shape, reducing localized stress on areas like the hips and shoulders. This is particularly relevant for side sleepers or individuals with joint pain. Moreover, the density influences the bed’s thermal properties. Denser foams tend to retain more heat, which can be a consideration for those who sleep hot. Manufacturers may incorporate cooling technologies, such as gel infusions or open-cell structures, to mitigate this effect. It is therefore vital to consider both the foam’s density and any incorporated cooling features when selecting this specific type of bedding.
In summary, density plays a pivotal role in determining the performance, longevity, and comfort characteristics. Choosing the appropriate density necessitates a careful evaluation of individual needs, considering body weight, sleeping position, and temperature preferences. The challenge lies in balancing desired comfort levels with the need for adequate support and durability. A thorough understanding of density empowers consumers to make informed decisions, ultimately leading to a more satisfactory sleep experience.
3. Support
In the context of a viscoelastic foam bed designed for individual use with a ten-inch profile, “support” refers to the capacity of the construction to maintain spinal alignment and distribute body weight evenly. The degree of support offered directly impacts the sleeper’s comfort, long-term musculoskeletal health, and overall sleep quality. Insufficient support can lead to pressure points, spinal misalignment, and subsequent discomfort or pain. Conversely, adequate support fosters a neutral spine position, promoting muscle relaxation and reducing the risk of sleep-related ailments. For example, an individual with scoliosis requires a higher degree of support to minimize spinal curvature during sleep. The ten-inch thickness contributes to support by providing sufficient material for both contouring and resistance to compression. Without adequate thickness, the bed may bottom out under the sleeper’s weight, negating any potential benefits of the viscoelastic foam.
The foam’s density also plays a crucial role in determining support levels. Higher-density foam offers greater resistance to compression, making it suitable for individuals who require firmer support or those with higher body weights. Lower-density foam conforms more readily to the body’s shape but may lack the necessary support for heavier individuals or those with specific orthopedic needs. The bed’s design should balance contouring comfort with underlying support to prevent sinking or sagging. Hybrid designs, which incorporate springs or other support layers beneath the viscoelastic foam, can enhance support while retaining the pressure-relieving properties of the foam. These designs cater to individuals seeking a balance between plushness and firm support. Furthermore, edge support is an often-overlooked aspect that contributes to overall support. Reinforced edges prevent the bed from collapsing when the sleeper sits or lies near the edge, maximizing the usable sleep surface and providing a more stable feel.
In conclusion, support is a fundamental attribute of a viscoelastic foam bed of this kind, impacting comfort, spinal health, and sleep quality. Factors such as the foam’s density, the bed’s thickness, and the presence of additional support layers influence the overall level of support provided. Selecting a bed that offers adequate support is crucial for maintaining proper spinal alignment and preventing discomfort. Consumers should carefully consider their individual needs and preferences when evaluating the support characteristics of various beds to ensure a comfortable and healthy sleep experience. The challenge lies in finding the optimal balance between contouring comfort and underlying support, a balance that varies depending on individual factors such as body weight, sleeping position, and pre-existing medical conditions.
4. Conformability
Conformability, in the context of a viscoelastic foam bed of the type described, represents the material’s capacity to adapt to the unique contours of a sleeper’s body. This characteristic differentiates viscoelastic foam from traditional innerspring beds, offering a more personalized sleep surface that minimizes pressure points and promotes spinal alignment.
- Pressure Point Relief
Viscoelastic foam’s conformability allows it to distribute weight more evenly across the sleep surface, reducing concentrated pressure on areas like the hips, shoulders, and knees. This can alleviate discomfort for individuals with arthritis, fibromyalgia, or other conditions causing joint pain. An example would be a side sleeper experiencing reduced shoulder compression compared to a traditional innerspring bed.
- Spinal Alignment
By contouring to the body’s natural curves, viscoelastic foam helps maintain proper spinal alignment throughout the night. This is particularly beneficial for back sleepers, as it supports the lumbar region and prevents excessive curvature of the spine. Improper alignment can lead to back pain and stiffness, which conformability aims to mitigate.
- Motion Isolation
The conforming nature of viscoelastic foam also contributes to motion isolation. When one individual moves on the bed, the disturbance is localized to that area, minimizing the impact on the other sleeper. This feature is advantageous for couples or individuals sharing a bed, as it reduces sleep disruptions caused by movement.
- Temperature Sensitivity
Traditional viscoelastic foam can exhibit temperature sensitivity, becoming softer in warmer conditions and firmer in cooler conditions. This variability can affect its conformability and overall feel. Newer formulations incorporating gel or open-cell structures aim to mitigate this effect, providing more consistent conformability regardless of ambient temperature.
The level of conformability provided by a ten-inch viscoelastic foam bed is influenced by factors such as the foam’s density, thickness, and any additional layers or technologies incorporated into the construction. A higher density foam generally offers greater support but may conform less readily, while lower density foam conforms more easily but may lack adequate support for some individuals. Choosing a bed with the appropriate level of conformability requires careful consideration of individual preferences, sleeping position, and any specific health concerns.
5. Heat Retention
Heat retention is a notable characteristic associated with viscoelastic foam beds, including the specified dimensions. The dense structure of viscoelastic foam, designed to conform closely to the body, inherently restricts airflow compared to traditional innerspring constructions. This reduced airflow impedes the dissipation of body heat, leading to a potential increase in sleeping temperature. Individuals who tend to sleep “hot” may find this a significant factor affecting comfort. The thickness of the ten-inch profile can exacerbate this issue, as the greater volume of foam provides more insulation, trapping heat within the sleeping surface. For example, a sleeper experiencing night sweats may find the heat retention properties of this material less desirable than a more breathable alternative, such as a latex or hybrid bed.
Manufacturers have attempted to mitigate heat retention through various design modifications. These include incorporating open-cell foam structures, which promote increased airflow, and infusing the foam with gel particles intended to absorb and dissipate heat. Breathable mattress covers made from materials like cotton or Tencel can further improve airflow and reduce heat buildup. The effectiveness of these modifications varies, and their impact on the overall performance and durability of the bed should be considered. Furthermore, the ambient room temperature and bedding materials used can also influence heat retention. Utilizing lightweight, breathable bedding can help to offset some of the heat-trapping tendencies of the viscoelastic foam.
In summary, heat retention represents a key consideration when evaluating the suitability of a viscoelastic foam bed. While the conforming properties of the material offer potential benefits for pressure relief and spinal alignment, the associated heat retention can detract from sleep comfort for some individuals. Awareness of this characteristic and the availability of mitigation strategies is crucial for making an informed purchasing decision. Consumers should carefully weigh their individual temperature preferences and explore options designed to minimize heat retention to ensure a comfortable and restful sleep experience.
6. Lifespan
The lifespan of a viscoelastic foam bed of this configuration is a critical consideration influencing its overall value proposition. Several factors directly impact the usable life of the material. Density of the foam is paramount; higher density foam typically exhibits greater resistance to compression and degradation, thus prolonging the bed’s structural integrity. Regular usage patterns contribute significantly. Daily use, especially by individuals with higher body weights, accelerates wear and tear. Conversely, occasional use, such as in a guest room, typically extends the lifespan. Manufacturing processes also play a crucial role. Foam produced with higher-quality materials and more rigorous quality control tends to exhibit greater durability. For example, a bed constructed with low-density foam and substandard manufacturing processes might exhibit sagging and a loss of support within a few years, while a higher-quality alternative could maintain its integrity for a decade or more. External factors such as humidity and temperature fluctuations can also affect the rate of foam degradation.
Maintenance practices directly correlate with the lifespan. Regular rotation of the bed, typically every three to six months, helps to distribute wear more evenly, preventing localized depressions from forming. The use of a mattress protector is essential for shielding the foam from spills, stains, and dust mites, which can contribute to material degradation. Avoidance of harsh chemicals or excessive moisture during cleaning is also critical. Compression testing provides a quantitative measure of lifespan potential. Manufacturers often conduct compression tests to assess the foam’s ability to recover its original shape after repeated compression cycles. The results of these tests can provide insights into the long-term durability of the material. Warranty terms offer an indirect indicator of expected lifespan. While a longer warranty does not guarantee extended durability, it reflects the manufacturer’s confidence in the product’s longevity. However, warranty coverage often excludes normal wear and tear, so it is essential to carefully review the terms and conditions.
In summary, the lifespan is a complex function of material quality, usage patterns, maintenance practices, and environmental conditions. While higher density foam and diligent maintenance can contribute to extended lifespan, no viscoelastic foam bed is immune to eventual degradation. Consumers should carefully consider these factors when evaluating the long-term value of this type of bedding. The challenge lies in balancing initial cost with expected durability, recognizing that a higher upfront investment in a higher-quality bed may result in lower long-term costs due to its extended lifespan and sustained performance.
7. Flammability
Flammability standards are a critical aspect of a viscoelastic foam bed, dictating the material’s ignition resistance and burn rate. Regulations, such as those outlined in the 16 CFR Part 1633 standard in the United States, mandate specific performance criteria to minimize fire hazards. The inherent composition of viscoelastic foam renders it susceptible to ignition from open flames, such as those from candles or lighters. Untreated foam can rapidly ignite and release toxic fumes, posing a significant risk to occupants. Therefore, manufacturers employ various strategies to enhance fire resistance. These strategies typically involve the application of flame-retardant chemicals or the incorporation of inherently fire-resistant materials within the mattress construction. The ten-inch thickness does not inherently increase or decrease flammability but does affect the total amount of combustible material present, thereby influencing the potential fire load. A real-world example is a house fire where an improperly treated bed can contribute significantly to the spread of flames and the generation of smoke, exacerbating the consequences of the incident.
The effectiveness of flammability treatments is rigorously tested through standardized protocols. These tests simulate various ignition scenarios, such as exposure to an open flame or a smoldering cigarette. Mattresses that fail to meet the prescribed standards cannot be legally sold. However, it is important to note that flammability treatments are not a guarantee against ignition in all circumstances. Prolonged exposure to intense heat sources can still result in ignition and combustion. Furthermore, concerns exist regarding the potential health and environmental impacts of some flame-retardant chemicals. Consequently, manufacturers are increasingly exploring alternative, less toxic flame-retardant solutions. The practical significance of understanding flammability standards lies in the ability to make informed purchasing decisions. Consumers should seek out mattresses that demonstrably meet or exceed applicable regulations and, where possible, opt for products that utilize safer, more environmentally friendly flame-retardant technologies.
In conclusion, flammability is an unavoidable consideration. Compliance with established regulations is essential to minimize fire risks. Consumers should remain vigilant in preventing ignition sources and maintaining a fire-safe environment. The challenge lies in balancing fire safety with concerns regarding the potential health and environmental impacts of flame-retardant chemicals. Continued research and development are necessary to create beds that are both fire-resistant and safe for human health. The implementation of safer, more sustainable flammability solutions represents a key area for future innovation in the bedding industry, further emphasizing the importance of this crucial component.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding this specific type of bedding, providing factual and objective responses.
Question 1: What is the optimal weight capacity for this type of bed?
The suggested weight capacity varies based on foam density and construction. Typically, a well-constructed bed is designed to accommodate individuals weighing up to 250 pounds. Exceeding this limit may compromise support and shorten the lifespan.
Question 2: How frequently should this type of bed be rotated?
Rotation is recommended every 3-6 months to promote even wear and prevent impressions. A 180-degree rotation is generally sufficient. Flipping is not typically recommended, as the bed is often designed with a specific top layer.
Question 3: What is the expected lifespan of a viscoelastic foam bed of this type?
The expected lifespan is influenced by density, usage, and maintenance. On average, a well-maintained bed can last 7-10 years. Signs of degradation include sagging, loss of support, and persistent impressions.
Question 4: What type of foundation is most suitable?
A solid platform or slatted foundation with minimal spacing is recommended. Avoid foundations with wide gaps or springs, as these may compromise support and accelerate wear.
Question 5: How should spills be cleaned from this type of bed?
Spot clean spills immediately with a mild detergent and water solution. Avoid harsh chemicals or excessive moisture. Allow the area to air dry thoroughly before covering.
Question 6: Is it normal for a new bed to have an odor?
A slight odor is common with new viscoelastic foam due to off-gassing of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). This odor typically dissipates within a few days in a well-ventilated room. If the odor persists for more than a week, contact the manufacturer.
These responses offer clarity on prevalent concerns. Understanding these facets leads to informed decision-making and optimal bed maintenance.
The subsequent section will offer actionable strategies for prospective purchasers, aiding them in selecting a fitting model.
Conclusion
The preceding analysis clarifies multifaceted aspects of the `memory foam mattress twin 10 inch`. Dimensional suitability, foam density, support characteristics, conformability attributes, heat retention considerations, lifespan expectancy, and flammability standards were thoroughly explored. Addressing these considerations is paramount for informed consumer decision-making.
Proper evaluation, coupled with diligent maintenance, ensures optimal product utilization and longevity. Choosing the right model dictates user comfort, sleep quality, and long-term musculoskeletal well-being. Further research and technological advancements will likely refine and enhance the performance characteristics of this bedding type, impacting consumer satisfaction and sleep health in the foreseeable future.




![Best 11 Inch Mattress: Comfort & Support [Guide] Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Best 11 Inch Mattress: Comfort & Support [Guide] | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-3746-300x200.jpg)
![Best 4 Inch Twin Mattress [Guide] Review & Tips Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Best 4 Inch Twin Mattress [Guide] Review & Tips | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-3745-300x200.jpg)
