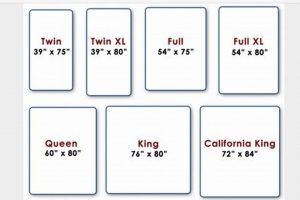
A standardized sleeping surface, typically measuring approximately 39 inches wide by 75 inches long, is frequently utilized in elevated bed frame configurations commonly found in shared living spaces or children’s rooms. This particular size is specifically designed to fit within the confines of the upper or lower levels of these structures. As an example, a child’s bedroom might feature two such surfaces stacked vertically to maximize floor space.
The selection of an appropriately sized sleeping surface for these elevated structures offers several advantages. These include space optimization, cost-effectiveness compared to larger alternatives, and suitability for individuals of smaller stature, especially children and adolescents. Historically, the implementation of such configurations has been driven by the need to accommodate multiple individuals within limited square footage, a practice seen in military barracks, dormitories, and residential homes.
Subsequent sections will address key considerations in the selection process, including mattress type, thickness, safety standards, and material composition, ensuring informed purchasing decisions for optimal comfort and safety in such sleeping arrangements.
Guidance for Bunk Bed Mattress Selection
Optimal selection necessitates careful consideration of several factors to ensure safety, comfort, and durability. The following guidelines provide a framework for informed decision-making.
Tip 1: Prioritize Safety Standards. Compliance with safety regulations, such as those established by the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC), is paramount. Verify that the selected item meets or exceeds these benchmarks to mitigate potential hazards.
Tip 2: Determine Appropriate Thickness. The mattress height should be carefully considered in relation to the bunk bed’s safety rails. Exceeding the recommended thickness can compromise the effectiveness of the rails, increasing the risk of falls. Consult the bed frame manufacturer’s specifications for guidance.
Tip 3: Evaluate Mattress Type. Options include innerspring, foam (memory foam, polyurethane foam), and hybrid designs. Innerspring models provide support and airflow, while foam options offer pressure relief and contouring. Hybrid constructions attempt to balance these characteristics. The choice depends on individual preferences and needs.
Tip 4: Assess Material Composition. Look for materials certified by reputable organizations such as CertiPUR-US. These certifications indicate that the foam has been tested for harmful substances and meets certain environmental standards. Hypoallergenic materials are advisable for individuals with sensitivities.
Tip 5: Consider Weight Capacity. Adherence to the manufacturer’s specified weight limit is crucial to prevent structural damage and ensure safe usage. This information is typically found on the mattress label or in the product documentation.
Tip 6: Evaluate Support and Comfort. Support is vital for spinal alignment and preventing back pain. Assess the firmness level to ensure it meets the user’s individual needs and sleeping style. Medium-firm options are often a good compromise for a variety of users.
Tip 7: Understand Warranty and Return Policies. Review the manufacturer’s warranty for coverage against defects in materials and workmanship. Understand the retailer’s return policy to facilitate a potential exchange or refund if the mattress does not meet expectations.
Adherence to these tips will promote informed selections, contributing to a safer and more comfortable sleeping experience in elevated bed configurations.
The subsequent section will address maintenance and care considerations for longevity.
1. Dimensions
The physical size of a sleeping surface intended for elevated bed frames is a primary consideration, directly influencing safety, stability, and user comfort. Precise dimensional conformity is essential to ensure compatibility and prevent potential hazards.
- Standard Size Compliance
The term ‘twin’ designates a specific set of measurements, typically 39 inches in width and 75 inches in length. Adherence to these standardized dimensions is crucial. Deviations can lead to improper fit, compromising the structural integrity of the bed frame and creating safety risks for the occupant. Real-world examples include gaps between the mattress and the frame, increasing the risk of entrapment, or instability leading to potential dislodgement.
- Height Restrictions and Safety Rail Clearance
Vertical thickness is a crucial dimension in the context of bunk beds. The combined height of the mattress and any bedding should not exceed the manufacturer’s specified limit, as this can reduce the effective height of the safety rails. This compromise negates the primary safety function, increasing the potential for falls. An example is a mattress that is too thick, causing the occupant to lie higher than the safety rail’s protective barrier.
- Weight Distribution and Support Area
The surface area of the mattress, defined by its length and width, directly relates to weight distribution and overall support. Insufficient surface area can lead to concentrated pressure points, reducing comfort and potentially impacting spinal alignment. A smaller individual on a properly sized surface will experience more even weight distribution compared to a larger individual on the same area.
- Frame Compatibility and Tolerances
Bunk bed frames are designed with specific dimensional tolerances to accommodate mattresses. Understanding these tolerances is critical to avoid issues such as excessive tightness, which can damage the mattress, or looseness, which can create instability. For example, attempting to force a slightly oversized sleeping surface into a frame can compress the materials and reduce its lifespan.
In summary, the physical size parameters of a sleeping surface destined for elevated frames necessitate meticulous attention. Standard size compliance, height restrictions, weight distribution, and frame compatibility are crucial elements in ensuring safety, comfort, and durability. Deviations from specified dimensions can result in compromised structural integrity and increase the risk of accidents.
2. Thickness
Thickness is a critical parameter in the context of a twin-sized sleeping surface intended for elevated bed frames, exerting a direct influence on both safety and comfort. Exceeding the manufacturer’s recommended thickness for the bed frame compromises the integrity of the safety rails. These rails are designed to prevent occupants from falling out of the top bunk. If the mattress is too thick, it reduces the effective height of the rails, rendering them less effective. This, in turn, elevates the risk of accidental f
alls, particularly for younger children or restless sleepers. Consequently, adherence to specified thickness guidelines is not merely a matter of preference; it is a fundamental safety imperative.
Beyond safety, thickness also affects the overall comfort and support provided. An excessively thin mattress may fail to provide adequate cushioning and support for the occupant’s body, potentially leading to pressure points and discomfort during sleep. Conversely, while a thicker mattress might seem inherently more comfortable, it may not be suitable if it compromises safety rail height. The selection process, therefore, involves a trade-off between comfort and safety. For example, a thinner memory foam mattress might provide adequate comfort without exceeding thickness limitations, while a thicker innerspring mattress could necessitate lowering the bunk’s height to maintain safety rail effectiveness. Real-world scenarios underscore the need to prioritize safety: a child falling from a bunk bed due to inadequate rail height illustrates the potentially severe consequences of neglecting thickness considerations.
Ultimately, the relationship between thickness and twin mattresses for bunk beds necessitates a balanced approach. Safety must take precedence, but comfort and support should also be considered within the allowable parameters. Manufacturers often provide specific guidance on acceptable thickness ranges for their bunk bed models. Consulting these guidelines and carefully evaluating the available options ensures that the selected sleeping surface promotes both a safe and comfortable sleeping environment. The challenges associated with balancing these factors are best addressed through informed decision-making and a thorough understanding of the bunk bed’s specific requirements.
3. Support
Adequate support is a fundamental attribute when considering a sleeping surface for elevated bed frames, directly influencing spinal alignment, pressure distribution, and overall sleep quality. Selecting a mattress that provides insufficient or inappropriate support can lead to discomfort, musculoskeletal issues, and compromised rest.
- Spinal Alignment and Posture
Proper support maintains the natural curvature of the spine, preventing undue stress on spinal discs and surrounding muscles. A mattress that is too soft may allow the spine to sag, while one that is too firm may create pressure points. The goal is neutral spinal alignment. For example, a memory foam mattress can conform to the body’s contours, providing targeted support to different areas of the spine. The implications of poor spinal alignment include back pain, stiffness, and potentially long-term musculoskeletal problems.
- Pressure Distribution and Circulation
Support contributes to the even distribution of body weight across the sleeping surface. This prevents excessive pressure on specific areas, such as the hips and shoulders, thereby promoting healthy blood circulation. A mattress with inadequate support may concentrate pressure, leading to discomfort and potential circulatory issues. For example, an innerspring mattress with individually wrapped coils can contour to the body, minimizing pressure points. The consequences of poor pressure distribution include numbness, tingling, and restless sleep.
- Edge Support and Stability
Edge support refers to the stability of the mattress perimeter. Adequate edge support prevents the mattress from sagging or collapsing when the occupant sits or lies near the edge. This is particularly important for upper bunks, where users may need to sit on the edge to get in or out of bed. For example, a hybrid mattress with reinforced edges can provide enhanced stability and prevent roll-off. The lack of edge support can lead to feelings of insecurity and increased risk of falls.
In conclusion, the level of support offered by a twin mattress significantly impacts both safety and comfort within the context of elevated bed frames. Ensuring proper spinal alignment, pressure distribution, and edge support contributes to a more restful and healthy sleep experience. Therefore, the selection process should prioritize mattresses designed to provide adequate and targeted support for the intended user.
4. Materials
The selection of materials in sleeping surfaces intended for elevated bed frames directly impacts safety, durability, comfort, and overall user well-being. Careful consideration of material properties is paramount to ensure suitability for this specific application.
- Foam Density and Composition
Foam, commonly polyurethane or memory foam, varies significantly in density and chemical composition. Higher-density foams offer increased support and durability but may retain more heat. Certifications such as CertiPUR-US indicate that the foam has been tested for harmful substances and meets certain environmental standards. For elevated bed frames, low-density foams may lack sufficient support, while uncertified foams could release volatile organic compounds (VOCs), affecting indoor air quality. An example is the off-gassing of cheaper, uncertified foams, which can be particularly problematic in smaller, enclosed sleeping areas.
- Innerspring Coil Gauge and Count
In innerspring mattresses, the coil gauge (thickness) and coil count influence support and longevity. Lower gauge numbers indicate thicker coils, providing firmer support. Higher coil counts generally improve contouring and reduce motion transfer. For bunk beds, especially upper bunks, robust coil systems are essential to prevent sagging and ensure consistent support across the surface. An example is a low-quality innerspring mattress with thin coils that quickly lose their shape, leading to discomfort and potential safety concerns.
- Fabric Cover and Fire Resistance
The fabric cover impacts breathability, moisture management, and fire resistance. Natural fibers, such as cotton or bamboo, promote airflow, while synthetic fabrics may be more durable and stain-resistant. All mattresses sold in the U.S. must meet federal fire safety standards, often achieved through the use of flame-retardant materials. However, the choice of flame retardants can impact the overall safety and environmental profile of the mattress. An example is the use of inherently flame-resistant materials like wool, which offer a safer alternative to chemical treatments.
- Adhesives and Binding Agents
Adhesives are used to bond different layers of the mattress together. The type of adhesive used can affect durability, comfort, and indoor air quality. Low-VOC adhesives are preferable to minimize off-gassing and potential health effects. Weak adhesives can lead to delamination and premature mattress failure. For bunk bed applications, where the mattress may experience more rigorous use, the quality of adhesives is particularly important. A common example is the breakdown of adhesives in poorly constructed mattresses, leading to shifting layers and uneven support.
These material considerations are critical to selecting a safe and appropriate sleeping surface for elevated bed frames. Prioritizing certified, durable, and low-VOC materials contributes to a healthier and more comfortable sleep environment, while also addressing the unique safety concerns associated with bunk bed use.
5. Weight Limit
The weight limit associated with a twin-sized sleeping surface intended for elevated bed frames is a critical safety parameter. This limitation, specified by both the mattress and bunk bed manufacturers, represents the maximum combined weight of the occupant and any associated bedding that the structure can safely support. Exceeding this limit can lead to structural failure of the bunk bed frame, compromising the safety of the user and potentially resulting in serious injury. The weight limit functions as a primary safety mechanism, preventing stress beyond the design capacity of the materials. For example, a bunk bed rated for 200 pounds per sleeping surface would be at risk of collapse if subjected to a load of 300 pounds, especially if the weight is unevenly distributed.
The practical significance of understanding and adhering to the weight limit is multifaceted. It ensures the longevity of the bunk bed structure, preventing premature wear and tear or catastrophic failure. It protects the user from the risk of falls and related injuries. Furthermore, it reinforces the importance of responsible usage and appropriate selection. For instance, in households with multiple children, it is essential to select bunk beds with weight limits that accommodate the size and growth potential of the occupants. Ignoring weight limits can have immediate and long-term consequences, including damaged property and, more importantly, physical harm.
In conclusion, the weight limit is an indispensable component of a twin mattress used within an elevated bed frame configuration. Its adherence guarantees user safety, structural integrity, and responsible product utilization. Challenges arise when users are unaware of the weight limit, underestimate the combined weight, or disregard the warning. Therefore, clear communication of weight limits and diligent compliance are paramount to safe and effective bunk bed operation. Failing to acknowledge this critical parameter introduces unnecessary risk and undermines the intended purpose of this space-saving furniture design.
6. Safety Rails
Safety rails are a fundamental safety component directly related to the selection and use of a twin mattress within a bunk bed configuration. The design and effectiveness of these rails are intrinsically linked to the dimensions of the mattress, impacting the overall safety profile of the elevated sleeping arrangement.
- Height and Protrusion
The height to which safety rails extend above the sleeping surface is paramount in preventing falls. This height must be sufficient to restrain a sleeping occupant, even with standard bedding in place. Insufficient rail height, often a consequence of an overly thick mattress, diminishes their protective function. Examples include instances where children roll off the top bunk due to inadequate rail protrusion above the mattress.
- Spacing and Entrapment
The spacing between the safety rails and the bed frame, as well as between individual rails, must adhere to established safety standards to prevent entrapment. Gaps that are too wide can pose a risk of a child’s head or limbs becoming lodged, leading to injury. Regulations typically specify maximum permissible spacing. A real-world scenario might involve a child becoming stuck between the rail and the frame, requiring adult intervention.
- Structural Integrity and Load-Bearing Capacity
Safety rails must possess adequate structural integrity to withstand the forces exerted by a leaning or falling occupant. The materials and construction must be robust enough to prevent breakage or deformation under load. Weak or poorly constructed rails can fail during an incident, negating their protective function. This is exemplified by rails that buckle or detach from the frame under pressure, providing a false sense of security.
- Secure Attachment and Stability
The manner in which safety rails are attached to the bunk bed frame is critical to their overall effectiveness. The attachment mechanism must be secure and prevent loosening or detachment over time. Unstable or poorly attached rails pose a significant safety hazard. Examples include rails that wobble or come loose, compromising their ability to prevent falls.
These facets highlight the essential role of safety rails in mitigating risks associated with elevated sleeping surfaces. The selection of a twin mattress must be considered in conjunction with the design and integrity of the safety rails to ensure a secure and protective sleeping environment within a bunk bed system. Proper installation and regular inspection are also necessary to maintain optimal safety performance.
7. Ventilation
Ventilation, regarding a twin mattress within a bunk bed configuration, assumes a critical role due to the confined nature of such sleeping arrangements. The restricted airflow surrounding the mattress can lead to moisture accumulation, promoting the growth of mold, mildew, and bacteria. These biological agents contribute to unpleasant odors, compromise air quality, and potentially trigger allergic reactions or respiratory issues in occupants. For instance, a twin mattress constructed of dense memory foam, placed on the upper bunk against a wall, restricts air circulation, thereby increasing the risk of moisture retention from perspiration and ambient humidity.
The material composition of the mattress significantly influences its ventilation characteristics. Open-cell foam structures and innerspring designs generally facilitate greater airflow compared to closed-cell foams or solid foam cores. Bunk beds often position the mattress close to walls and adjacent bed frames, further impeding ventilation. Practical implications include selecting mattresses with breathable covers, such as cotton or bamboo, and employing bed frames that allow for adequate airflow underneath the mattress. Regular rotation of the mattress can also help to distribute wear and prevent moisture buildup in specific areas. A practical example is noticing a musty odor emanating from a mattress that lacks proper ventilation, which necessitates immediate attention to mitigate further complications.
In summary, adequate ventilation is a non-negotiable aspect of twin mattress selection for bunk bed applications. It mitigates the risks associated with moisture retention, promotes hygiene, and contributes to a healthier sleep environment. Overlooking this factor can lead to compromised air quality, potential health issues, and reduced mattress lifespan. Addressing ventilation considerations through careful material selection, appropriate bed frame design, and proactive maintenance practices is essential for ensuring occupant well-being and maintaining the longevity of the twin mattress within a bunk bed setting.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the selection, use, and maintenance of twin mattresses specifically intended for bunk bed applications. The responses provided aim to offer clear, concise, and factually accurate information.
Question 1: What are the standard dimensions of a twin mattress suitable for bunk beds?
A twin mattress typically measures approximately 39 inches in width and 75 inches in l
ength. However, it is imperative to consult the bunk bed manufacturer’s specifications to confirm compatibility and ensure a proper fit within the designated frame.
Question 2: How does mattress thickness affect the safety of a bunk bed?
Mattress thickness directly impacts the effectiveness of the safety rails. Exceeding the recommended maximum thickness reduces the rail’s protective height, increasing the risk of falls. It is critical to adhere to the bunk bed manufacturer’s thickness guidelines.
Question 3: What type of mattress is best suited for a bunk bed application?
The optimal mattress type depends on individual preferences and needs. However, options such as innerspring, foam, or hybrid designs should be evaluated based on support, comfort, durability, and weight. Safety considerations, particularly thickness and weight capacity, should take precedence.
Question 4: How important is ventilation for a bunk bed mattress?
Ventilation is crucial due to the confined nature of bunk beds. Adequate airflow prevents moisture accumulation, which can lead to mold, mildew, and unpleasant odors. Selecting mattresses with breathable materials and ensuring proper bed frame design can enhance ventilation.
Question 5: What weight limit should be considered when selecting a twin mattress for a bunk bed?
The weight limit, specified by both the mattress and bunk bed manufacturers, must be strictly observed. Exceeding this limit can compromise the structural integrity of the bed, potentially leading to collapse and injury. The combined weight of the occupant and all bedding must be within the specified limit.
Question 6: How frequently should a twin mattress be rotated or flipped within a bunk bed?
Regular rotation, ideally every three to six months, helps distribute wear and prevent the formation of body impressions. Flipping the mattress, if the design allows, further enhances longevity and maintains support. Consult the manufacturer’s recommendations for specific rotation and flipping guidelines.
The information provided above highlights critical aspects to consider when choosing a twin mattress for a bunk bed, emphasizing safety, comfort, and longevity.
The subsequent section will summarize the key points discussed in this article.
Twin Mattress for Bunk Bed
This exposition has underscored the multifaceted aspects requiring diligent consideration when selecting a twin mattress for bunk bed applications. Emphasis has been placed on adherence to safety standards, appropriate thickness relative to safety rail height, material composition ensuring both comfort and hygiene, adequate support for spinal alignment, and strict compliance with weight limitations. Moreover, the importance of ventilation to mitigate moisture accumulation and the role of robust safety rail design have been thoroughly examined. These elements collectively contribute to a secure and healthful sleeping environment.
The responsible selection of a twin mattress for bunk bed represents a commitment to user safety and well-being. Continued adherence to these principles will foster a more informed consumer base and promote the development of safer, more durable, and more comfortable sleeping solutions within elevated bed frame configurations. Prioritizing these key factors is essential for maximizing the benefits and minimizing the risks associated with bunk bed usage.



![Best Twin Mattress Platform [Deals!] - Beds & More Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Best Twin Mattress Platform [Deals!] - Beds & More | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-5168-300x200.jpg)