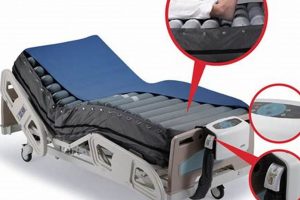
A support surface specifically engineered for use on medical beds in healthcare facilities. These surfaces are designed to provide comfort and pressure redistribution for patients, often with features like specialized foam, alternating air cells, or integrated sensors. They are a critical component of the patient’s environment within a hospital setting.
The utilization of these specialized supports is vital for preventing pressure ulcers, promoting proper spinal alignment, and enhancing overall patient comfort during extended periods of bed rest. Their development reflects a historical understanding of the relationship between prolonged immobility and skin breakdown, leading to innovations aimed at mitigating these risks and contributing to improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
The subsequent sections will explore the various types available, the factors influencing selection, cleaning and maintenance protocols, and emerging technologies impacting the future of patient support surfaces in medical settings.
Essential Considerations for Hospital Bed Support Surfaces
This section provides critical information for selecting, utilizing, and maintaining surfaces designed for patient support in a medical bed environment. Adherence to these guidelines contributes to improved patient outcomes and a reduction in healthcare-associated complications.
Tip 1: Material Selection: Prioritize materials that balance support and pressure redistribution. High-density foam or alternating air designs are commonly employed to minimize pressure points and promote circulation, which are vital for prevention of pressure injuries.
Tip 2: Weight Capacity Assessment: Always verify that the surface weight capacity meets or exceeds the patient’s weight. Exceeding the rated capacity compromises the support’s integrity and effectiveness, increasing the risk of patient injury and equipment damage.
Tip 3: Infection Control Protocols: Implement rigorous cleaning and disinfection procedures between patients. Select surfaces with fluid-resistant covers and follow manufacturer-recommended protocols to minimize the risk of cross-contamination and hospital-acquired infections. Regular inspection for tears or breaches in the cover is also vital.
Tip 4: Pressure Mapping Technology: Consider the use of pressure mapping technology during surface selection. This allows objective measurement of pressure distribution, ensuring the chosen surface effectively offloads pressure from vulnerable areas.
Tip 5: Patient-Specific Needs: Individual patient needs should dictate surface selection. Factors such as mobility, existing pressure injuries, and medical conditions should be considered when determining the optimal support surface.
Tip 6: Ongoing Monitoring and Adjustment: Regularly assess patients for signs of pressure injury development or discomfort. Adjust the surface type or pressure settings as needed to optimize patient comfort and prevent complications.
Tip 7: Proper Bed Frame Compatibility: Ensure that the surface is compatible with the hospital bed frame being used. Incompatible combinations can compromise both the patients safety and the functionality of the bed frame itself.
Adherence to these recommendations contributes to a safe and therapeutic environment for patients requiring medical bed support. Proper selection, utilization, and maintenance are crucial for minimizing risks and maximizing patient comfort and recovery.
The following sections will address specific types of support surfaces, including their features, benefits, and ideal applications.
1. Pressure Redistribution
Pressure redistribution is a fundamental property of specialized surfaces used in medical beds. It denotes the capacity of the support to evenly distribute the weight of a patient over a larger surface area, thereby reducing concentrated pressure on bony prominences and other vulnerable anatomical locations. This mechanism is vital for mitigating the risk of pressure injuries, which arise from prolonged or excessive pressure interrupting blood flow to the skin and underlying tissues. The effectiveness of pressure redistribution is directly influenced by the materials used in construction, such as viscoelastic foam, air cells, or gel, each offering distinct pressure-relieving characteristics. For example, in post-operative care of hip replacement patients, surfaces designed for pressure redistribution help minimize stress on the surgical site.
The relationship between specialized medical bed surfaces and pressure redistribution is causal. Inadequate pressure relief directly increases the probability of pressure injuries. Conversely, surfaces engineered for effective pressure redistribution demonstrably lower the incidence and severity of these injuries. The choice of the correct support, incorporating effective redistribution, is pivotal to preventative strategies in patients with limited mobility or compromised skin integrity. A practical demonstration of the importance of the right choice lies in selecting a bariatric medical bed surface for an overweight or obese patient, where standard surfaces would provide insufficient redistribution.
Pressure redistribution is an indispensable characteristic of any support surface used in medical beds. It directly affects patient outcomes, particularly concerning skin health and comfort. Understanding the principles and mechanisms of redistribution is paramount for healthcare providers to effectively select and utilize these surfaces, optimizing patient care and minimizing the occurrence of preventable complications. This understanding also facilitates informed procurement decisions for healthcare facilities, ensuring resources are allocated to surfaces that offer demonstrably superior pressure redistribution properties and align with the specific needs of the patient population.
2. Infection Control
Infection control is a critical consideration in the design, maintenance, and utilization of medical bed support surfaces. These surfaces, due to their proximity to patients, can serve as reservoirs for pathogens if not properly managed. Effective infection control practices are essential to prevent healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) and ensure patient safety.
- Fluid-Resistant Cover Materials
The outer covering of a medical bed support should be constructed from fluid-resistant and impermeable materials. These materials prevent bodily fluids, such as blood, urine, and wound exudate, from penetrating the interior of the support, where bacteria and viruses can proliferate. Vinyl and polyurethane coatings are commonly employed for this purpose. The integrity of this barrier is paramount; any tears or breaches compromise its effectiveness.
- Disinfection Protocols and Agents
Regular disinfection of th
e support surface is mandatory between patient uses. Healthcare facilities must establish and adhere to strict disinfection protocols using EPA-approved disinfectants. The selection of appropriate disinfectants is crucial; they should be effective against a broad spectrum of pathogens while remaining compatible with the cover material to prevent degradation or damage. Contact time, as specified by the disinfectant manufacturer, must be strictly observed to ensure adequate pathogen inactivation. - Seam Construction and Design
The design and construction of seams on the support surface contribute significantly to infection control. Sewn seams can create crevices that harbor microorganisms and are difficult to disinfect thoroughly. Welded or radio-frequency sealed seams minimize these crevices and provide a smoother, more easily cleaned surface. The location of seams should also be considered to minimize potential exposure to fluids.
- Internal Component Protection
In surfaces with internal components, such as air bladders or foam layers, protection against contamination is essential. If these components become contaminated, they are extremely difficult, if not impossible, to adequately disinfect. Design features that prevent fluid ingress, such as sealed compartments and waterproof barriers, are critical. In cases of contamination, these components may need to be replaced entirely.
The facets outlined above underscore the multifaceted nature of infection control in relation to medical bed supports. Neglecting any one of these aspects can significantly increase the risk of HAIs. Stringent adherence to established protocols, including the selection of appropriate materials, rigorous disinfection procedures, and careful attention to design details, is paramount to maintaining a safe and sanitary patient care environment.
3. Material Durability
Material durability is a critical attribute directly influencing the longevity, safety, and cost-effectiveness of hospital bed support surfaces. The constant use and rigorous cleaning protocols associated with these surfaces subject them to considerable wear and tear. Therefore, the selection of robust and resilient materials is paramount to ensure sustained performance and prevent premature degradation. A surface constructed with durable materials maintains its structural integrity and functional properties over time, providing consistent patient support and minimizing the risk of failure. Premature failure of the material can lead to discomfort, pressure injury development, and increased risk of contamination. For example, a support surface with a vinyl cover that cracks or tears easily compromises its fluid resistance, increasing the likelihood of pathogen proliferation and requiring costly and disruptive replacements.
The impact of material durability extends beyond simple longevity. It directly affects patient safety. A surface with weakened seams or compromised internal components, such as damaged air cells, may not provide adequate pressure redistribution, increasing the risk of pressure injuries. Furthermore, the durability of the material influences its resistance to cleaning agents. Hospital-grade disinfectants can be harsh and can degrade certain materials over time. Surfaces constructed with materials specifically designed to withstand repeated exposure to these chemicals maintain their integrity and fluid resistance for longer periods, reducing the risk of infection transmission. The initial investment in a more durable surface is often offset by reduced replacement costs, lower maintenance expenses, and improved infection control outcomes.
In conclusion, material durability is an indispensable characteristic of hospital bed support surfaces. It influences patient safety, infection control, and the overall cost of healthcare delivery. The selection of surfaces constructed with robust and resilient materials, capable of withstanding constant use and rigorous cleaning, is a critical decision with long-term implications for both patient well-being and facility financial stability. Recognizing this importance enables informed procurement choices, leading to improved patient outcomes and optimized resource allocation.
4. Weight Capacity
Weight capacity is a fundamental specification dictating the maximum load a support surface is designed to safely and effectively bear. In the context of medical bed supports, this parameter is crucial for ensuring patient safety, maintaining surface integrity, and preventing premature equipment failure. Exceeding the stated weight capacity can compromise the support’s structural integrity, lead to inadequate pressure redistribution, and pose a significant risk of injury to both the patient and caregivers.
- Structural Integrity
Exceeding the specified limit on a medical bed support can cause structural damage. The internal components, such as foam layers or air bladders, may compress unevenly or rupture, leading to a loss of support and increasing the risk of pressure injury development. In extreme cases, the entire surface may collapse, potentially causing the patient to fall or suffer other injuries.
- Pressure Redistribution Efficacy
Weight capacity directly influences the ability to effectively redistribute pressure. Surfaces are engineered to evenly distribute a patient’s weight, minimizing pressure points. When the limit is exceeded, this redistribution mechanism is compromised, concentrating pressure on bony prominences and significantly elevating the risk of pressure ulcer formation. This is particularly important for patients with limited mobility who are unable to independently adjust their position.
- Equipment Longevity and Warranty
Consistent overloading of a medical bed support shortens its lifespan. Internal components experience accelerated wear and tear, leading to premature degradation and the need for replacement. Furthermore, exceeding the weight capacity may void the manufacturer’s warranty, resulting in unexpected financial burdens for the healthcare facility.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Healthcare facilities are legally and ethically obligated to provide a safe environment for patients. Utilizing supports beyond their specified parameters constitutes a breach of this obligation and could result in liability in the event of patient injury. Adherence to weight capacity specifications is an essential element of risk management and regulatory compliance.
These considerations underscore the critical importance of adhering to weight capacity specifications for medical bed supports. A thorough assessment of patient weight and proper selection of an appropriately rated surface are essential components of safe and effective patient care. Healthcare professionals must be trained to recognize the risks associated with overloading and to consistently follow protocols to ensure patient safety and equipment longevity.
5. Compatibility
The term “compatibility,” when applied to medical bed supports, denotes the degree to which the surface integrates effectively with the hospital bed frame and other related medi
cal equipment. This relationship is causal: incompatibility can negate the therapeutic benefits of a high-quality support, while a suitable fit ensures optimized performance and patient safety. A specific example involves a support designed with specialized pressure redistribution features that is placed on a bed frame with insufficient articulation. The result may be impaired support effectiveness due to frame limitations. A practical demonstration would also be a standard size support surface placed on a bariatric bed frame. It would result in unsafe gaps, rendering the equipment unsuitable and potentially hazardous. The surface must also allow for proper use of features like side rails and electric controls of the bed.
The impact of compatibility also extends to functionality. Features such as electric controls for adjusting bed positions are often integrated within the bed frame. A support that is too thick or improperly shaped can obstruct these controls, hindering the caregiver’s ability to provide appropriate patient positioning. Furthermore, some specialized medical equipment, such as scales or patient lifts, are designed to interface directly with the bed frame. An incompatible support can interfere with these interfaces, compromising the accuracy of measurements or preventing the safe operation of the equipment. The proper attachment and function of safety features like side rails is paramount and can be compromised by an improperly sized or designed support.
In summary, compatibility is not merely a matter of physical fit but a critical factor influencing the functionality, safety, and therapeutic effectiveness of a medical bed support. Prioritizing compatibility during the selection process ensures optimal patient outcomes, efficient use of medical equipment, and compliance with safety regulations. Challenges to compatibility can arise from variations in bed frame designs and the diverse range of support surfaces available; however, careful consideration and adherence to manufacturer specifications can mitigate these issues and foster a seamless integration of components within the patient care environment.
6. Patient Comfort
Patient comfort, in the context of medical bed surfaces, is more than a mere amenity; it is a critical component influencing physiological and psychological well-being. The surface directly impacts pressure distribution, temperature regulation, and support, all of which affect the patient’s perception of comfort. A support surface failing to adequately address these factors can lead to restlessness, agitation, and sleep deprivation. Compromised sleep and increased discomfort can hinder the healing process, exacerbate pain, and contribute to a decline in mental health. Surfaces designed with features like specialized foam layering, breathable fabrics, and adjustable firmness aim to minimize these negative impacts. For example, a patient recovering from major surgery may experience heightened sensitivity to pressure; a support surface offering enhanced pressure redistribution and a soft, conforming top layer can significantly alleviate discomfort and promote rest.
Effective promotion of patient comfort is not only ethically sound but also demonstrably beneficial from a clinical and economic perspective. Reduced discomfort levels often translate to decreased reliance on pain medication, lowering the risk of adverse drug effects and associated costs. Improved sleep quality can enhance the patient’s immune function, potentially shortening hospital stays and reducing the likelihood of complications. Furthermore, a comfortable patient is more likely to be compliant with treatment plans and rehabilitation protocols, leading to better overall outcomes. The practical application of this understanding involves implementing standardized protocols for assessing patient comfort levels and adjusting surface features accordingly. It also requires ongoing education and training for healthcare staff on the proper selection and utilization of different surface types to meet individual patient needs. For instance, a patient with a fever may benefit from a support with enhanced breathability to help regulate body temperature.
In summary, patient comfort is an integral factor in the design and implementation of medical bed supports. Its impact extends beyond mere subjective experience, influencing physiological processes, treatment adherence, and overall healthcare costs. While challenges persist in objectively measuring and optimizing patient comfort, a proactive approach that prioritizes individual needs, utilizes evidence-based practices, and integrates feedback from patients and caregivers can significantly enhance the therapeutic environment and promote better health outcomes. The understanding of this relationship can also be expanded to the use of additional comfort measures, such as pillows and blankets, tailored to individual requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries and misconceptions pertaining to medical bed surfaces. It provides concise, fact-based answers to enhance understanding and inform decision-making.
Question 1: What is the expected lifespan of a standard medical bed support?
The lifespan varies based on material composition, usage frequency, and maintenance protocols. High-quality supports, when properly maintained, can typically last between five to seven years. Regular inspection for damage is essential for extending its life and preventing unsafe conditions.
Question 2: How does support type influence pressure injury prevention?
Different surface types redistribute pressure in varying degrees. Alternating air surfaces actively cycle pressure, while foam surfaces rely on material properties. The appropriate support type is dependent on the patient’s risk factors, mobility, and existing skin integrity. Consult with a healthcare professional for optimal surface selection.
Question 3: What are the recommended cleaning protocols for disinfecting a medical bed support?
Strict adherence to manufacturer-recommended cleaning protocols is essential. Typically, this involves using an EPA-approved disinfectant and observing the specified contact time. Ensure the selected disinfectant is compatible with the surface material to prevent damage or degradation.
Question 4: Can a standard surface be used for bariatric patients?
Standard surfaces are not suitable for bariatric patients due to inadequate weight capacity and pressure redistribution capabilities. Bariatric-specific surfaces are engineered to accommodate higher weights and provide enhanced support, thereby reducing the risk of pressure-related complications.
Question 5: How does surface material affect infection control?
Impermeable, fluid-resistant materials are critical for infection control. These materials prevent the ingress of bodily fluids and facilitate effective disinfection. Surfaces with tears or breaches in the cover compromise infection control and should be replaced immediately.
Question 6: Are all medical bed supports compatible with any bed frame?
No. Compatibility between the surface and bed frame is paramount. Incompatible combinations can compromise safety and functionality. Verify dimensions, attachment mechanisms, and articulation capabilities before use.
The information provided here serves as a general guideline. Consultation with healthcare professionals and adherence to manufacturer specifications are essential for informed decision-making regarding medical bed surface selection and utilization.
The subsequent secti
on will address emerging trends and technological advancements in medical bed support surface design and functionality.
Conclusion
This exploration has underscored the critical importance of the hospital bed mattress as a central component of patient care within healthcare facilities. The selection, maintenance, and appropriate utilization directly impact patient safety, comfort, and clinical outcomes. A thorough understanding of pressure redistribution, infection control, material durability, weight capacity, compatibility, and patient comfort is essential for informed decision-making.
Continued research and technological advancements will undoubtedly lead to further refinements in surface design and functionality. Healthcare providers must remain vigilant in staying abreast of these developments to ensure optimal patient care and minimize the risk of preventable complications. The hospital bed mattress, therefore, remains an area demanding diligent attention and rigorous assessment to guarantee its efficacy in supporting the well-being of individuals requiring medical care.



![Best Toyota Tacoma Bed Air Mattress [Guide] Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Best Toyota Tacoma Bed Air Mattress [Guide] | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-7271-300x200.jpg)

