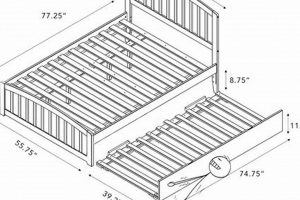
A portable sleeping solution constructed around a foldable frame and a compatible mattress is designed for ease of storage and transport. These units typically consist of a metal or wooden frame that can collapse into a compact form, coupled with a mattress, often made of foam or a similar flexible material, designed to bend and fold along with the frame. An example of such a system is a guest bed that can be easily stored in a closet when not in use, maximizing space in a smaller living environment.
The significance of this type of bed lies in its efficient use of space and convenience for accommodating temporary sleeping arrangements. Historically, such beds have been utilized in situations where space is limited, such as apartments, dormitories, or emergency shelters. The benefits include providing a comfortable sleeping surface without the commitment of a permanent bed, enabling flexibility in room configuration, and offering a cost-effective solution for occasional guests.
The subsequent sections will delve into various aspects, including different types of frame and mattress materials, size considerations, storage options, and factors to consider when selecting a suitable model to ensure comfort and durability.
Considerations for Optimal Use
Maximizing the utility and lifespan of portable sleeping solutions requires careful attention to several key factors. The following recommendations provide guidance for informed selection, proper maintenance, and safe operation.
Tip 1: Frame Material Evaluation: Prioritize frames constructed from durable materials such as steel or reinforced wood. Assess the load-bearing capacity to ensure compatibility with the intended user’s weight. Inspect for any signs of weakness or instability prior to use.
Tip 2: Mattress Density and Support: Evaluate the mattress density and firmness level to align with individual comfort preferences and support requirements. Thicker mattresses generally offer enhanced support and pressure relief. Memory foam or hybrid constructions provide conforming support.
Tip 3: Locking Mechanism Verification: Prior to each use, thoroughly inspect and engage all locking mechanisms designed to secure the frame in its open and closed positions. Failure to properly engage these mechanisms may result in instability or collapse.
Tip 4: Storage Environment: When not in use, store the unit in a dry, climate-controlled environment. Avoid exposure to excessive moisture, direct sunlight, or extreme temperatures, as these conditions can degrade the frame and mattress materials.
Tip 5: Regular Cleaning and Maintenance: Implement a regular cleaning schedule to prevent the accumulation of dust, allergens, and stains on the mattress surface. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for appropriate cleaning agents and methods.
Tip 6: Weight Distribution and Stability: Ensure even weight distribution across the mattress surface during use. Avoid concentrating excessive weight in a single area, as this can compromise the frame’s stability and potentially lead to structural damage.
These considerations aim to enhance the user experience and extend the functional life of the sleeping arrangement. Careful adherence to these tips will contribute to a more secure and comfortable experience.
The final section will provide insights into selecting the most appropriate model for specific needs, considering various configurations and budget constraints.
1. Frame Durability
Frame durability is a foundational characteristic directly impacting the overall lifespan, stability, and safety of portable sleeping systems. It dictates the unit’s capacity to withstand repeated use, storage, and transportation without compromising structural integrity, therefore playing a pivotal role in the long-term cost-effectiveness and user satisfaction of the product.
- Material Composition
The constituent materials of the frame, such as steel, aluminum, or reinforced wood, significantly influence its resistance to bending, breaking, and corrosion. Steel, particularly when powder-coated for rust prevention, provides a high degree of durability under stress. Aluminum offers a lightweight alternative with moderate durability, while wood frames require careful selection of hardwood species and protective finishes to prevent warping or insect damage.
- Joint Construction and Reinforcement
The method of joining frame components, including welding, bolting, and riveting, contributes critically to its overall strength. Welded joints, when properly executed, provide a seamless and robust connection. Bolted joints offer flexibility for disassembly and repair but necessitate periodic tightening to maintain stability. Reinforcement elements, such as gussets or cross-braces, can further enhance the frame’s resistance to torsional forces and prevent premature failure.
- Weight Capacity and Load Distribution
The specified weight capacity of the frame directly relates to its ability to support the intended user or users without experiencing deformation or collapse. Exceeding the weight limit can lead to structural fatigue and eventual breakage. Proper weight distribution across the mattress surface is also essential to prevent localized stress concentrations that can weaken the frame over time.
- Folding Mechanism Longevity
The hinges and locking mechanisms that enable the folding and unfolding functionality are subject to repeated stress and wear. High-quality hinges constructed from hardened steel with precision bearings are essential for smooth operation and long-term reliability. The locking mechanism must securely engage to prevent unintended collapse during use and should be resistant to wear or corrosion that could compromise its effectiveness.
The interplay of these facetsmaterial composition, joint construction, weight capacity, and mechanism longevitycollectively determines the durability of the frame, directly influencing its suitability for various applications and user needs. Selecting a model with a robust frame construction is essential for maximizing the return on investment and ensuring safe and reliable performance over an extended period of use. Moreover, frame durability is crucial in situations where the sleeping solution is regularly transported, as it ensures the bed withstands the rigors of travel and repeated handling.
2. Mattress Comfort
Mattress comfort is paramount in the context of foldable sleeping arrangements, functioning as a primary determinant of sleep quality and overall user satisfaction. The inherent design constraints of foldable beds, which prioritize portability and storage efficiency, often necessitate compromises in mattress thickness and material composition. This can directly affect the level of support, pr
essure relief, and temperature regulation provided, leading to potential discomfort or inadequate rest. For example, a thin foam mattress on a foldable bed might be suitable for short-term use but could cause back pain or stiffness if used regularly. The practical significance of understanding this connection lies in the ability to make informed purchasing decisions, balancing the need for portability with the requirement for adequate sleep support.
Addressing the comfort challenges associated with portable mattresses involves several strategies. Manufacturers often employ advanced foam technologies, such as memory foam or gel-infused foam, to enhance contouring and temperature control within a reduced thickness profile. The choice of materials directly impacts the sleeping experience. Another consideration involves the bed’s base support; a slatted or sprung base can augment the mattress’s inherent properties, improving weight distribution and ventilation. Real-world examples, such as high-end foldable guest beds featuring multi-layered foam constructions, demonstrate the potential for achieving a reasonable level of comfort, even within the limitations of the format.
In conclusion, mattress comfort is not merely a desirable attribute but an essential component of any functional portable bed solution. Achieving an adequate level of comfort presents unique challenges that necessitate careful consideration of mattress materials, support structure, and intended use. While compromises are often inevitable, a thorough understanding of the factors influencing comfort allows for informed decisions that mitigate potential drawbacks. The ability to prioritize and balance comfort with space-saving benefits is key to ensuring user satisfaction.
3. Storage Footprint
The defining characteristic of a “fold up mattress bed” is its ability to minimize its storage footprint when not in use. The bed’s utility is directly proportional to the degree to which it reduces spatial occupancy during periods of inactivity. The storage footprint dictates its applicability in space-constrained environments, such as apartments, dormitories, or temporary living quarters. The design of the folding mechanism, dimensions when folded, and the availability of integrated storage solutions all contribute to determining the overall storage footprint. A smaller storage footprint provides enhanced flexibility in room configuration and efficient utilization of available space. An example is a guest bed designed to fold into a compact cabinet, effectively reducing its footprint to that of a small piece of furniture. The practical significance of minimizing the storage footprint is clear: it enables temporary sleeping solutions without permanently sacrificing valuable living space.
Several factors influence the achievable storage footprint. The type of folding mechanism employed significantly affects the final dimensions. Bi-fold or tri-fold designs are common, each offering different trade-offs between complexity and compactness. The mattress material and thickness also play a role; thinner, more flexible mattresses, like those made of foam, allow for tighter folding. Some models incorporate features such as straps or clips to secure the folded unit and prevent unwanted expansion, further reducing the footprint. Furthermore, integrated storage compartments within the folded unit can provide space for bedding or pillows, consolidating the storage requirements. Consider, for example, a portable bed with an integrated cover that transforms into a storage bag, offering both protection during storage and a convenient way to carry the unit.
In summary, the storage footprint is a critical design parameter of a “fold up mattress bed,” determining its suitability for environments with limited space. Effective minimization of the storage footprint requires careful consideration of the folding mechanism, mattress material, and integration of storage solutions. The ability to efficiently store these beds enhances their practicality and utility, making them a valuable asset in situations where space is at a premium. Meeting the challenge of minimizing the storage footprint while maintaining comfort and durability is key to the continued innovation and adoption of this type of sleeping solution.
4. Portability Weight
The weight of a portable sleeping solution directly dictates its ease of transport, which is an essential attribute for a “fold up mattress bed.” Increased weight diminishes maneuverability and limits the ability to relocate the unit frequently or carry it over longer distances. This is particularly relevant in situations where the bed is intended for temporary use in various locations, such as guest accommodations, camping, or emergency shelters. A heavier unit imposes physical strain on the user during setup, takedown, and storage, potentially negating the intended convenience of a portable design. The practical significance of minimizing weight lies in enhancing user-friendliness and broadening the range of applicable scenarios. For example, a lightweight model constructed from aluminum framing and a compact foam mattress would be considerably more suitable for individuals with limited physical strength or those who require frequent relocation of the bed.
Efforts to mitigate weight are often balanced against the need for structural integrity and mattress comfort. Frame materials such as lightweight alloys and high-strength polymers are commonly employed, although these may compromise durability or load-bearing capacity compared to heavier alternatives like steel. Mattress composition also influences the overall weight; thinner mattresses made of lightweight foam reduce the burden, but potentially at the expense of sleep quality. Furthermore, design considerations such as the folding mechanism and the inclusion of features like wheels or handles impact the overall portability. For instance, incorporating a set of integrated wheels significantly eases transport, even if the unit remains relatively heavy. Careful engineering and material selection are essential to optimizing the balance between weight, durability, and comfort.
In conclusion, portability weight is a pivotal factor influencing the practicality and versatility of a “fold up mattress bed.” Optimizing this parameter requires a nuanced understanding of the trade-offs between weight, structural integrity, and comfort. Lightweight construction enables broader applicability and enhanced user convenience, particularly in situations involving frequent transport or limited physical capacity. Ultimately, the ideal balance depends on the intended use case and the priorities of the user, necessitating careful consideration of these interlinked factors when selecting a suitable model.
5. Locking Security
The operational safety of a folding bed is inextricably linked to the integrity of its locking mechanism. This mechanism, responsible for maintaining the bed’s structural configuration during use, mitigates the risk of unintended collapse. A compromised locking system can lead to sudden closure, potentially resulting in injury to the occupant. Real-world instances of structural failure in furniture underscore the importance of robust locking security; malfunctions during use have caused severe harm. The prese
nce of a reliable locking mechanism is therefore not merely a convenience, but a critical safety component of any portable sleeping solution of this type.
Contemporary models often employ multiple locking points and safety latches to enhance redundancy. These may include spring-loaded pins, cam locks, or lever systems. Testing protocols should simulate extended use, subjecting the locking mechanism to repetitive stress and weight loads to ensure sustained performance. Furthermore, the ease of engaging and disengaging the locking system is an important ergonomic consideration; overly complex or difficult-to-operate mechanisms increase the likelihood of improper use or deliberate circumvention, thereby compromising safety. Consider, for example, a design featuring color-coded indicators to visually confirm secure locking.
In conclusion, the secure locking of a folding bed represents a non-negotiable safety requirement. Adequate design, rigorous testing, and user-friendly operation are essential to mitigate the risk of collapse and ensure occupant well-being. Challenges persist in balancing locking security with ease of use, but ongoing advancements in materials and engineering continue to drive improvements in both areas. The effectiveness of the locking system directly impacts the overall practicality and safety profile of this category of sleeping solutions, solidifying its significance for both manufacturers and end-users.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries and misconceptions concerning portable sleeping solutions, providing concise and factual answers to facilitate informed decision-making.
Question 1: What is the typical lifespan one can expect from a fold up mattress bed?
The longevity of a folding bed depends heavily on its construction quality and usage frequency. Models with steel frames and higher-density mattresses can last upwards of five years with regular use, while those with lighter materials and occasional use may only last two to three years. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning and tightening hardware, also extends the lifespan.
Question 2: Are fold up mattress beds suitable for individuals with back problems?
Suitability for individuals with back problems depends on the mattress quality and support provided. Thin, low-density mattresses may exacerbate existing back pain. Opting for models with thicker, memory foam or hybrid mattresses can offer better spinal alignment and pressure relief. Consulting a physician or physical therapist is advisable for personalized recommendations.
Question 3: How does one properly store a fold up mattress bed to prevent damage?
Proper storage involves ensuring the unit is clean and dry before folding. Store in a dry, climate-controlled environment to prevent mold or mildew growth. Using a protective cover can shield the mattress from dust and pests. Avoid stacking heavy objects on top of the folded bed, as this can damage the frame or mattress.
Question 4: What are the primary differences between various fold up mattress bed frame materials?
Frame materials commonly include steel, aluminum, and wood. Steel frames offer superior durability and weight capacity but are heavier. Aluminum provides a lighter alternative but may be less robust. Wood frames can offer aesthetic appeal but require careful selection of hardwoods and protective finishes to prevent warping or insect damage.
Question 5: How does one assess the stability of a fold up mattress bed before use?
Prior to each use, inspect all locking mechanisms to ensure they are properly engaged. Check for any signs of loose hardware, bent frames, or wobbly joints. Apply pressure to different areas of the mattress to assess stability and weight distribution. If any instability is detected, discontinue use until the issue is resolved.
Question 6: What is the recommended weight limit for a standard fold up mattress bed?
The recommended weight limit varies depending on the specific model. Consult the manufacturer’s specifications for the stated weight capacity. Exceeding the weight limit can compromise the frame’s structural integrity and potentially lead to collapse or injury. Typically, single-sized models support up to 250 pounds, while larger models may accommodate up to 300 pounds.
The information presented above aims to address common concerns, aiding in responsible purchase and utilization decisions for fold up mattress beds. Understanding these factors is essential for ensuring both comfort and safety.
The subsequent section will provide information regarding common material usage of the bed.
Fold up mattress bed Conclusion
This exploration has elucidated the multifaceted nature of the portable sleeping solution, addressing key aspects from frame durability to locking security. Factors such as mattress comfort, storage footprint, and portability weight have been examined to provide a comprehensive understanding of this type of beds utility. The significance of informed decision-making regarding material selection, maintenance, and usage practices has been emphasized throughout.
Ultimately, the effective utilization of a “fold up mattress bed” hinges on a clear comprehension of its inherent limitations and capabilities. Continued innovation in materials and design will likely drive further improvements in comfort, durability, and safety. Responsible selection and attentive maintenance are crucial for maximizing the benefits and ensuring the longevity of these space-saving sleeping solutions.