This arrangement comprises two or more bed frames stacked vertically, typically designed to conserve space. A sleeping surface consisting of supportive material, often foam or springs encased in fabric, complements each level to provide a place for rest. This setup is frequently found in shared living spaces or areas with limited square footage.
Such structures offer significant advantages in maximizing floor space, making them ideal for dormitories, children’s rooms, and hostels. Historically, these tiered sleeping solutions have been employed in environments where efficient use of space is paramount, such as military barracks and ships. Their enduring popularity stems from their practicality and ability to accommodate multiple individuals within a compact footprint.
The subsequent sections will delve into considerations regarding safety standards, material options, mattress selection criteria, and assembly procedures related to these space-saving sleeping solutions. Emphasis will be placed on ensuring a secure and comfortable experience for users of all ages.
Guidance on Bunk Beds and Mattresses
The following recommendations are designed to provide essential guidance for selecting and maintaining safe and comfortable sleeping arrangements using vertically stacked beds and their corresponding sleeping surfaces. Adherence to these principles will contribute to the well-being and security of the users.
Tip 1: Prioritize Safety Standards: Verify that the bunk bed adheres to current safety regulations and standards established by relevant governing bodies. Look for certifications indicating compliance with recognized safety protocols. This ensures that the structure has undergone rigorous testing for stability and structural integrity.
Tip 2: Mattress Thickness and Fit: Select a mattress with a thickness that complies with the bunk bed’s safety guidelines. Insufficient guardrail height due to an overly thick mattress can compromise safety. Ensure a snug fit within the bunk bed frame to prevent shifting or accidental dislodgement.
Tip 3: Ladder or Stairway Security: Regularly inspect the ladder or stairway for stability and secure attachment to the bunk bed frame. Ensure that steps are slip-resistant and that handrails are securely fastened. Address any looseness or damage immediately to prevent falls.
Tip 4: Weight Capacity Adherence: Strictly adhere to the manufacturer’s specified weight capacity for both the upper and lower bunks. Exceeding the weight limit can compromise the structural integrity of the bed and create a hazardous situation.
Tip 5: Regular Inspection and Maintenance: Conduct routine inspections of all components, including frames, slats, and fasteners. Tighten any loose screws or bolts promptly. Address any signs of wear or damage, such as cracks or splinters, to maintain the structural integrity of the unit.
Tip 6: Age Appropriateness: Exercise caution when allowing younger children to use the upper bunk. Consider the child’s maturity and ability to safely climb and descend the ladder or stairs. Restricting upper bunk access to older children can mitigate the risk of falls.
By implementing these recommendations, individuals can create a secure and comfortable sleeping environment using these tiered sleeping solutions. Diligence in adhering to safety guidelines and performing regular maintenance is paramount for ensuring the long-term well-being of all users.
The subsequent sections will provide information concerning the selection of appropriate mattress materials and bunk bed designs to further enhance the user experience and promote restful sleep.
1. Safety Compliance
Safety compliance constitutes a fundamental aspect in the design, manufacturing, and use of tiered sleeping arrangements and their corresponding sleeping surfaces. Adherence to established safety standards mitigates potential hazards and ensures the well-being of occupants, particularly in environments where space is limited and multiple users may share the structure.
- Guardrail Height and Placement
Minimum guardrail height requirements are specified by safety regulations to prevent falls from the upper bunk. The placement of guardrails must effectively enclose the sleeping area, leaving only necessary openings for access. Insufficient guardrail height or improper placement significantly increases the risk of accidental falls and injuries.
- Ladder Stability and Angle
The ladder’s design and construction must ensure stability and ease of use. The angle of the ladder should be conducive to safe climbing and descending, minimizing the potential for slips or loss of balance. Secure attachment to the bunk bed frame is essential to prevent detachment or instability during use.
- Mattress Thickness Restrictions
Safety standards often impose restrictions on mattress thickness to maintain adequate guardrail height. Using an excessively thick mattress reduces the effective height of the guardrail, compromising its ability to prevent falls. Compliance with specified thickness limits is critical for maintaining the intended safety features of the bed.
- Material Flammability Standards
Bunk beds and mattresses are subject to flammability standards to minimize the risk of fire-related injuries. Materials used in construction must meet specific requirements regarding flame resistance and the release of toxic fumes in the event of a fire. Compliance with these standards enhances the overall safety of the sleeping environment.
The comprehensive application of safety compliance measures is paramount in mitigating risks associated with tiered sleeping arrangements. By adhering to established standards and regulations, manufacturers and users contribute to a safer and more secure environment for all occupants. Failure to prioritize safety compliance can have severe consequences, underscoring the importance of vigilance and adherence to best practices.
2. Mattress Support
Mattress support constitutes a critical element within the context of tiered sleeping arrangements. The supportive characteristics of the sleeping surface directly influence user comfort, spinal alignment, and overall sleep quality, particularly given the space constraints and potential for multiple users inherent in these setups.
- Weight Distribution and Pressure Relief
Effective mattress support ensures even distribution of body weight, minimizing pressure points and promoting circulation. In the context of bunk beds, where users may range in size and weight, this becomes particularly important. Inadequate support can lead to discomfort, restless sleep, and potential musculoskeletal issues. For example, a memory foam mattress with high-density support lay
ers effectively contours to the body, relieving pressure on hips and shoulders. - Spinal Alignment and Posture
Proper mattress support facilitates optimal spinal alignment during sleep. A supportive mattress helps maintain the natural curvature of the spine, preventing postural distortions that can contribute to back pain and discomfort. Bunk beds, often used by growing children and adolescents, necessitate a mattress that promotes healthy spinal development. For instance, an innerspring mattress with targeted lumbar support can effectively maintain spinal alignment for individuals of various body types.
- Edge Support and Stability
Adequate edge support prevents mattress sagging and provides a stable sleeping surface along the perimeter. This is especially relevant for the upper bunk, where users may be closer to the edge. Insufficient edge support can lead to a feeling of instability and increase the risk of rolling off the bed. Reinforced edge coils or foam encasements can significantly improve edge support and stability.
- Durability and Longevity
A mattress with robust support systems tends to exhibit greater durability and longevity. Materials and construction techniques that enhance support also contribute to the mattress’s ability to withstand repeated use and maintain its shape over time. Given the potentially high usage of bunk beds, particularly in shared living spaces, selecting a durable and long-lasting mattress is crucial for cost-effectiveness and sustained comfort.
In summary, the supportive characteristics of a mattress are intrinsically linked to the comfort, health, and safety aspects of tiered sleeping arrangements. Selecting a mattress that adequately addresses weight distribution, spinal alignment, edge support, and durability is paramount for optimizing the sleeping experience and promoting the well-being of bunk bed users.
3. Space Optimization
Space optimization represents a primary driver in the adoption of tiered sleeping solutions and associated mattresses. In environments where square footage is limited, such as dormitories, small apartments, or shared bedrooms, maximizing available space is paramount. Bunk beds, in conjunction with appropriately sized mattresses, offer a strategic approach to achieving this objective.
- Vertical Space Utilization
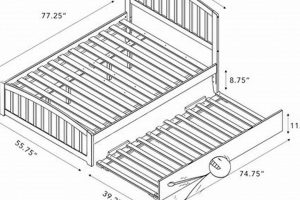
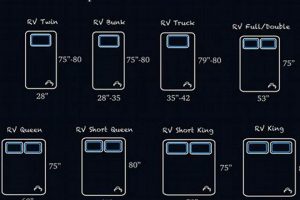
Bunk beds inherently exploit vertical space, effectively doubling the sleeping capacity within the footprint of a single bed. This configuration frees up valuable floor area that can be repurposed for other essential functions, such as studying, playing, or storage. For instance, a standard twin-sized bed occupies approximately 39 square feet of floor space. A bunk bed with two twin mattresses occupies the same area but provides sleeping surfaces for two individuals. This efficient use of vertical space is particularly beneficial in densely populated urban settings.
- Integrated Storage Solutions
Many bunk bed designs incorporate integrated storage solutions, such as drawers, shelves, or built-in desks. These features further enhance space optimization by consolidating sleeping and storage functions into a single unit. For example, a bunk bed with under-bed drawers provides convenient storage for clothing, bedding, or personal belongings, eliminating the need for additional furniture that would otherwise occupy valuable floor space. Similarly, a bunk bed with an integrated desk offers a dedicated workspace, maximizing functionality within a compact footprint.
- Adaptability to Room Layout
Bunk beds are available in various configurations, including standard parallel designs, L-shaped arrangements, and loft beds with open space underneath. This versatility allows for adaptability to diverse room layouts and spatial constraints. For example, an L-shaped bunk bed can be strategically positioned in a corner to minimize intrusion into the central area of a room. A loft bed, which elevates a single sleeping surface and leaves the space below open, can accommodate a desk, seating area, or storage unit, effectively creating a multi-functional zone within a limited area.
- Reduction of Furniture Clutter
By combining multiple sleeping surfaces into a single structure, bunk beds inherently reduce furniture clutter and create a more streamlined and organized living environment. This simplification can contribute to a greater sense of spaciousness and improved functionality. For instance, replacing two separate twin beds with a single bunk bed eliminates the visual clutter associated with multiple pieces of furniture, making the room appear larger and more inviting. The reduced furniture footprint also facilitates easier movement and access within the space.
In conclusion, the strategic implementation of tiered sleeping arrangements and appropriately sized mattresses directly addresses the imperative of space optimization in constrained living environments. By leveraging vertical space, integrating storage solutions, adapting to room layouts, and reducing furniture clutter, these solutions provide a practical and efficient means of maximizing available area and enhancing the overall functionality and comfort of a room.
4. Material Durability
Material durability is a paramount consideration in the selection and maintenance of tiered sleeping arrangements and associated sleeping surfaces. The ability of these components to withstand prolonged use, resist wear and tear, and maintain structural integrity directly impacts safety, longevity, and overall value. In the context of bunk beds and mattresses, durability considerations extend beyond simple aesthetics to encompass critical safety and performance factors.
- Frame Construction Materials
The materials used in the construction of bunk bed frames, such as solid wood, engineered wood products, or metal, significantly influence the overall durability of the structure. Solid wood frames, particularly those crafted from hardwoods like oak or maple, offer superior strength and resistance to deformation under load. Metal frames, often constructed from steel or iron, provide robust support and are less susceptible to warping or cracking. Engineered wood products, such as plywood or particleboard, can offer a cost-effective alternative, but their durability depends on the quality of the materials and construction techniques employed. For example, a bunk bed frame constructed from solid hardwood with reinforced joints will exhibit significantly greater resistance to wear and tear compared to a frame made from lower-grade particleboard with simple screw connections.
- Mattress Core Composition
The composition of the mattress core, whether consisting of innerspring coils, memory foam, latex, or a hybrid combination, directly impacts the mattress’s ability to maintain its shape and support over time. Innerspring mattresses with high-gauge coils offer robust support and are less prone to sagging. Memory foam mattresses conform to the body’s contours, distributing weight evenly and reducing pressure points, but their long-term durability depends on the density and quality of the foam. Latex mattresses, derived from natural or synthetic rubber, provide excellent support, resilience, and resistance to compression. Hybrid mattresses combine the benefi
ts of innerspring and foam technologies, offering a balance of support and comfort. For instance, a memory foam mattress with a high-density foam core will retain its shape and supportive properties longer than a lower-density foam mattress that is more susceptible to compression and sagging. - Surface Fabric Resistance to Abrasion
The durability of the fabric covering the bunk bed frame and mattress is crucial for resisting abrasion, staining, and tearing. High-quality fabrics, such as tightly woven cotton blends, microfiber, or synthetic materials, offer superior resistance to wear and tear. The fabric’s ability to withstand repeated rubbing, scratching, and contact with bodily fluids directly impacts its aesthetic appeal and longevity. Furthermore, durable fabrics that are resistant to staining and easy to clean contribute to maintaining a hygienic sleeping environment. For example, a bunk bed frame upholstered in a durable microfiber fabric will resist abrasion and staining more effectively than a frame covered in a thin, loosely woven fabric.
- Joint Strength and Fastener Integrity
The strength and integrity of the joints and fasteners used to assemble the bunk bed frame are critical for ensuring structural stability and preventing premature failure. High-quality fasteners, such as bolts, screws, and dowels, provide secure connections between frame components and resist loosening or breakage under load. Reinforced joints, often incorporating metal brackets or corner blocks, enhance the overall strength and stability of the structure. Regular inspection and maintenance of joints and fasteners are essential for identifying and addressing any signs of wear or damage. For instance, a bunk bed frame with reinforced joints secured by high-strength bolts will be less prone to wobbling or collapsing compared to a frame with simple screw connections that can loosen over time.
In summary, the material durability of bunk beds and mattresses is a multifaceted consideration that encompasses frame construction materials, mattress core composition, surface fabric resistance, and joint strength. Selecting components constructed from high-quality, durable materials and implementing a program of regular inspection and maintenance are essential for ensuring the safety, longevity, and overall value of these sleeping arrangements. Failure to prioritize material durability can result in premature failure, compromised safety, and increased costs over the long term.
5. Ladder Design
Ladder design is intrinsically linked to the overall safety and functionality of tiered sleeping arrangements. Serving as the primary means of access to the upper bunk, the ladder’s design significantly impacts user experience and the potential for accidents. Considerations related to ladder design extend beyond mere aesthetics, encompassing ergonomic factors, structural integrity, and adherence to safety standards.
- Angle and Inclination
The angle of inclination directly influences the ease and safety of climbing. Steeper angles require greater upper body strength and increase the risk of falling backward, while shallower angles consume more floor space and may impede movement within the room. Ergonomic design principles dictate an optimal angle range that balances ease of climbing with space efficiency. For example, ladders with angles between 65 and 75 degrees from the horizontal offer a reasonable compromise between these competing factors. Ladders exceeding 75 degrees are inherently more precarious, particularly for younger children or individuals with mobility limitations.
- Step Dimensions and Spacing
Step dimensions and spacing significantly impact foot placement and stability. Narrow steps can be difficult to grip and may cause discomfort or fatigue, while excessively wide steps can impede the climbing motion. The spacing between steps should be consistent and appropriate for the intended user population. Industry best practices suggest step widths of at least 1.5 inches and consistent spacing of no more than 12 inches between steps. Inconsistent spacing or inadequate step widths can lead to missteps and increase the risk of falls.
- Material and Construction
The materials used in ladder construction and the methods employed in its assembly directly influence its strength, stability, and longevity. Ladders constructed from solid wood or metal offer greater resistance to bending, flexing, or breaking under load. The joints connecting the steps to the side rails must be robust and securely fastened to prevent loosening or detachment. Welded joints, bolted connections, or mortise-and-tenon joinery provide superior strength compared to simple screw connections. The ladder’s surface should be free of sharp edges, splinters, or other hazards that could cause injury.
- Attachment and Security
The method by which the ladder is attached to the bunk bed frame is critical for ensuring stability and preventing accidental dislodgement. Ladders should be securely fastened to the frame using bolts, screws, or other reliable fasteners. Locking mechanisms or brackets can further enhance the ladder’s stability and prevent it from shifting or detaching during use. The attachment points should be regularly inspected for looseness or damage, and any necessary repairs should be promptly addressed. A ladder that is not securely attached to the frame poses a significant safety hazard and increases the risk of falls.
In conclusion, ladder design is an integral component of the overall safety and functionality of tiered sleeping solutions. By carefully considering the angle and inclination, step dimensions and spacing, material and construction, and attachment security, manufacturers and consumers can mitigate potential hazards and create a more comfortable and user-friendly sleeping environment. Failure to address these critical design considerations can compromise user safety and diminish the overall value of the bunk bed system.
6. Weight Limit
The weight limit associated with tiered sleeping arrangements, and more specifically with each bunk and the mattress it supports, is a critical safety parameter. Exceeding this limit can initiate a cascade of adverse effects. It can induce structural stress within the frame, potentially leading to deformation, component failure, or complete collapse of the structure. Real-world examples include instances where overloaded bunk beds have exhibited bent or fractured frame members, compromised support slats, and detached ladder connections, resulting in occupant injuries. The weight limit, therefore, is not merely a suggestion, but a design constraint integral to the safe operation of the system.
The practical significance of understanding and adhering to this parameter extends to both manufacturers and consumers. Manufacturers have a responsibility to clearly specify the weight limit for each bunk and to design the structure to withstand these loads with an adequate safety margin. Consumers must exercise due diligence by verifying the specified weight limits before purchase and by strictly adhering to these limits during use. This may necessitate carefully selecting mattresses that, in combination with the occupant, do not exceed the stipulated weight. For example, a family with growing children should periodically reassess whether the current bunk bed configuration continues to meet t
he weight requirements, considering the increased mass of the occupants.
The challenges associated with enforcing weight limits include the difficulty in accurately assessing the combined weight of occupants and bedding and the potential for users to underestimate the cumulative load. Furthermore, variations in manufacturing tolerances and material properties may introduce some degree of uncertainty in the actual weight-bearing capacity of a specific bunk bed. Despite these challenges, strict adherence to the manufacturer’s specified weight limits remains the most effective means of mitigating the risk of structural failure and ensuring the safety of occupants. This understanding links directly to the broader theme of responsible product design, informed consumer behavior, and the prioritization of safety in the domestic environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding bunk beds and mattresses, providing information to guide safe and informed decision-making.
Question 1: What safety standards should be considered when purchasing a bunk bed?
Bunk beds should meet safety standards established by organizations such as ASTM International. Verify compliance with ASTM F1427, the standard consumer safety specification for bunk beds. This ensures adherence to requirements for structural integrity, guardrail height, and ladder design.
Question 2: How is the appropriate mattress thickness determined for a bunk bed?
Mattress thickness must comply with the bunk bed manufacturer’s specifications. An overly thick mattress can reduce the effectiveness of the guardrails, increasing the risk of falls. Consult the bunk bed’s documentation to determine the maximum permissible mattress thickness.
Question 3: What is the recommended age for children using the upper bunk?
The Consumer Product Safety Commission recommends that children under the age of six should not use the upper bunk. Maturity and the ability to safely climb and descend the ladder are critical factors to consider.
Question 4: How often should a bunk bed be inspected for safety?
Bunk beds should be inspected regularly, ideally at least monthly, to ensure that all components are secure and in good working order. Pay particular attention to the ladder, guardrails, and fasteners.
Question 5: What type of mattress provides the best support for a bunk bed?
The optimal mattress type depends on individual preferences and needs. However, mattresses with adequate support, such as innerspring or hybrid models, are generally recommended. Ensure that the chosen mattress meets the weight requirements of the bunk bed.
Question 6: How does the weight limit of a bunk bed affect mattress selection?
The combined weight of the mattress and the occupant must not exceed the bunk bed’s specified weight limit. Select a mattress that is lightweight yet supportive to remain within the allowable weight range.
Adherence to these guidelines promotes a safer and more comfortable environment for bunk bed users. Prioritizing safety and informed decision-making is essential for mitigating potential risks.
The subsequent section will explore the legal and ethical considerations surrounding the manufacturing and sale of these tiered sleeping arrangements.
Conclusion
This exposition has systematically addressed the critical aspects surrounding tiered sleeping structures and their corresponding sleeping surfaces. Key elements explored include safety compliance, mattress support, space optimization, material durability, ladder design, and adherence to weight limits. Each factor contributes to the overall functionality, safety, and longevity of these arrangements, influencing the well-being and comfort of users.
The responsible manufacturing, informed selection, and diligent maintenance of bunk beds and mattresses are paramount for mitigating potential hazards and maximizing the benefits of these space-saving solutions. Continued adherence to established safety standards, combined with a commitment to user education, will foster safer and more comfortable environments for all individuals utilizing tiered sleeping structures.



![Best Folding Mattress & Sofa Bed [Space Saver] Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Best Folding Mattress & Sofa Bed [Space Saver] | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-7182-300x200.jpg)

