This product represents a specific configuration within the broader sleep solutions market, typically involving a mattress designed to integrate with, or function as, part of a larger bedding system. Such systems often prioritize comfort and support. For instance, a mattress utilizing temperature-regulating materials, combined with specifically designed sheets and pillows, could exemplify this product category.
The significance of this type of bedding lies in its potential to improve sleep quality and overall well-being. Considerations such as spinal alignment, pressure point relief, and breathability contribute to a more restful and restorative sleep experience. Historically, the evolution of bedding has consistently aimed towards enhancing these comfort factors, with modern iterations focusing on material science and ergonomic design to optimize sleep conditions.
The following sections will delve into the key features and considerations associated with selecting such a mattress. This includes a review of materials, construction techniques, and the specific benefits these elements contribute to the overall sleep experience. Subsequent discussions will address factors like firmness, size options, and maintenance requirements, enabling informed decision-making.
Selection and Maintenance Guidance
The following guidelines provide key considerations for choosing and maintaining a mattress system designed to optimize sleep quality and longevity.
Tip 1: Prioritize Material Composition. Mattress materials directly impact comfort, support, and temperature regulation. Research specific material properties, such as latex’s responsiveness or memory foam’s conforming capabilities, to align with individual sleep preferences.
Tip 2: Evaluate Support Structure. Internal support systems, including coil count and design, influence spinal alignment and pressure relief. Consider the type of coils (e.g., pocketed, continuous) and their density to ensure adequate support based on body weight and sleeping position.
Tip 3: Assess Firmness Level. Mattress firmness is subjective but crucial for comfort. Consider body weight and preferred sleeping position when selecting a firmness level. Side sleepers often benefit from softer surfaces, while back and stomach sleepers generally require firmer support.
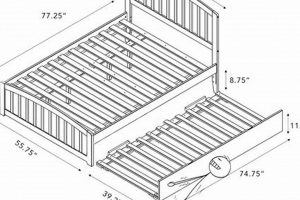
Tip 4: Consider Size Specifications. Choosing the appropriate mattress size is critical for undisturbed sleep. Factors to consider include individual size, sleeping habits (e.g., sprawling), and the number of sleepers sharing the bed. Standard sizes range from Twin to California King; measure the bedroom space accordingly.
Tip 5: Implement Protective Measures. Protect the mattress from spills, stains, and allergens by using a high-quality mattress protector. A waterproof protector is recommended, particularly for individuals with allergies or young children.
Tip 6: Rotate Regularly. Rotating the mattress periodically (e.g., every three to six months) helps to distribute wear evenly and prolong its lifespan. Check manufacturer guidelines for specific rotation recommendations.
Tip 7: Maintain Cleanliness. Regularly vacuum the mattress surface to remove dust mites, allergens, and debris. Follow manufacturer instructions for spot cleaning stains, avoiding harsh chemicals that could damage the materials.
These guidelines emphasize the importance of aligning mattress selection with individual needs and consistently practicing proper maintenance. Implementing these strategies contributes to a more comfortable and hygienic sleep environment, ultimately promoting restful sleep and overall well-being.
The concluding section will summarize the benefits of a suitable sleeping system and provide resources for further exploration.
1. Optimal Support
Optimal support, in the context of a mattress system, refers to the ability of the mattress to maintain proper spinal alignment and distribute body weight evenly. Within a specific mattress, this translates to a design that actively mitigates pressure points and prevents sinking or sagging, thereby reducing the potential for back pain and discomfort. The connection to this type of bedding is fundamental: a mattress lacking adequate support negates the purported benefits of the larger sleep system, rendering ancillary features like temperature regulation less effective.
The importance of optimal support manifests in several ways. For instance, a mattress designed for side sleepers should possess zoned support, allowing the shoulders and hips to sink slightly while maintaining spinal alignment. A real-life example can be seen in mattresses incorporating pocketed coil systems, where each coil operates independently to conform to the body’s contours. Without such design features, the mattress may fail to provide targeted support, leading to pressure buildup and compromised sleep quality. Similarly, inadequate support contributes to poor posture during sleep, potentially exacerbating existing musculoskeletal conditions.
In conclusion, the link between optimal support and a specific type of mattress system is inextricable. Achieving truly restorative sleep depends heavily on a mattress that prioritizes spinal alignment and even weight distribution. While other features contribute to a comfortable sleep experience, the foundation of effective bedding remains the provision of targeted and consistent support. Challenges lie in navigating the complexities of individual needs and ensuring that marketing claims align with demonstrable performance, underscoring the need for consumers to prioritize reliable information and verifiable product specifications when evaluating the suitability of mattress systems.
2. Breathable Materials
Breathable materials within this bedding context are defined as textiles and foams engineered to facilitate air circulation and moisture wicking, thereby regulating temperature and minimizing humidity buildup during sleep. The inclusion of these materials directly impacts the microclimate surrounding the sleeper, affecting comfort and sleep quality. The cause-and-effect relationship is evident: less breathable materials trap heat and moisture, creating an environment conducive to discomfort and potential sleep disruption. Conversely, breathable materials promote airflow, dissipating heat and moisture to maintain a more consistent and comfortable temperature.
The importance of breathable materials as a component is multifaceted. Firstly, temperature regulation is crucial for achieving and maintaining restful sleep. When the body overheats, the natural sleep cycle can be interrupted. Breathable materials mitigate this risk. Secondly, moisture management contributes to hygiene. By wicking away sweat, these materials reduce the likelihood of bacterial growth and odor accumulation, promoting a cleaner sleep environment. Real-life examples include mattresses incorporating op
en-cell foam structures or natural fibers like cotton or wool, which allow for increased airflow compared to closed-cell foams or synthetic materials with tighter weaves. For instance, a latex mattress with pinhole ventilation exemplifies enhanced breathability, facilitating air exchange and reducing heat retention. The practical significance of understanding this connection lies in informed consumer choices. Selecting a product with breathable materials addresses a fundamental aspect of sleep physiology and hygiene.
In summary, the incorporation of breathable materials is an integral factor influencing the effectiveness. These materials actively contribute to a more comfortable and hygienic sleep environment by regulating temperature and managing moisture. Challenges persist in accurately assessing breathability through marketing claims alone. Consumers must prioritize transparency in material specifications and seek independent verification to ensure the advertised benefits align with demonstrable performance.
3. Proper Alignment
Proper alignment, in the context of a mattress, signifies the maintenance of the spine’s natural curvature during sleep. It is a critical determinant of sleep quality and musculoskeletal health, directly influencing comfort and minimizing the risk of pain or injury. The design and materials of the mattress substantially affect its ability to facilitate proper alignment, which consequently determines the effectiveness of the sleep environment.
- Spinal Curvature Support
This facet involves the degree to which the mattress conforms to and supports the natural curves of the spine, particularly the lumbar region. Mattresses designed to promote proper alignment often incorporate zoned support systems or specialized materials that provide targeted firmness in specific areas. For example, a mattress with enhanced lumbar support will help maintain the natural inward curve of the lower back, preventing overextension or compression. Without adequate spinal curvature support, individuals may experience back pain, stiffness, and discomfort, which can disrupt sleep and lead to long-term musculoskeletal issues.
- Pressure Distribution
Proper alignment is closely linked to even pressure distribution across the body. A mattress that effectively distributes weight minimizes concentrated pressure on specific areas, such as the shoulders and hips. This is particularly important for side sleepers, who are more prone to pressure point discomfort. Memory foam and latex mattresses are often lauded for their pressure-relieving properties, as they contour to the body and evenly disperse weight. If pressure points are not adequately addressed, individuals may toss and turn frequently during the night in search of a more comfortable position, disrupting their sleep cycle.
- Sleeping Position Adaptation
Different sleeping positions require varying degrees of support and alignment. For instance, back sleepers generally benefit from a firmer mattress that prevents the hips from sinking too deeply, while side sleepers typically require a softer surface to accommodate the contours of their shoulders and hips. Stomach sleepers often need a firmer mattress to prevent excessive arching of the back. Mattresses designed to accommodate multiple sleeping positions may incorporate hybrid designs, combining features such as responsive coils with pressure-relieving foam layers. The ability of the mattress to adapt to different sleeping positions ensures that proper alignment is maintained regardless of individual preferences.
- Long-Term Spinal Health
Consistent proper alignment during sleep has significant implications for long-term spinal health. By preventing chronic misalignment and reducing stress on the spine, a supportive mattress can help mitigate the risk of developing conditions such as herniated discs, sciatica, and other musculoskeletal disorders. Conversely, sleeping on a mattress that fails to provide adequate support can exacerbate existing spinal problems and contribute to the development of new ones. Investing in a mattress that promotes proper alignment is therefore an investment in long-term physical well-being.
In conclusion, proper alignment represents a critical determinant of sleep quality and musculoskeletal health. A mattress’s ability to support spinal curvature, distribute pressure evenly, adapt to different sleeping positions, and promote long-term spinal health directly influences its overall effectiveness.
4. Pressure Relief
Pressure relief, in the context of sleep surfaces, refers to the reduction of concentrated forces exerted on specific areas of the body during sleep. This characteristic is a critical factor in determining sleep quality and comfort. A product’s ability to mitigate pressure points directly impacts the likelihood of tossing and turning, and the potential for pain or discomfort that disrupts the sleep cycle.
- Conforming Materials
Conforming materials, such as memory foam and latex, are integral to pressure relief. These materials adapt to the contours of the body, distributing weight more evenly and reducing localized pressure. For example, a memory foam layer responds to body heat and weight, molding to the individual’s shape and minimizing pressure on prominent areas like the shoulders and hips. Products utilizing these materials often highlight their ability to alleviate discomfort associated with prolonged pressure, particularly for side sleepers.
- Zoned Support Systems
Zoned support systems involve varying the firmness or density of a mattress in different regions to provide targeted support and pressure relief. These systems are typically designed to offer firmer support in areas like the lumbar region, while providing more cushioning in areas like the shoulders and hips. Mattresses with zoned support aim to maintain proper spinal alignment while simultaneously reducing pressure point discomfort, thus enhancing sleep quality.
- Surface Layer Construction
The construction of the surface layer significantly impacts pressure relief. Techniques such as quilting, pillow tops, or euro tops can add an extra layer of cushioning and conformity, enhancing the mattress’s ability to alleviate pressure. These features effectively create a buffer between the sleeper and the underlying support structure, minimizing the potential for direct pressure on bony prominences. The choice of materials and construction methods for the surface layer directly affects the overall comfort and pressure-relieving properties of the mattress.
- Adaptability to Sleeping Position
Effective pressure relief necessitates adaptability to various sleeping positions. Individuals who sleep on their side typically require more cushioning in the shoulder and hip areas to prevent pressure buildup. Back sleepers may benefit from more uniform support to maintain spinal alignment while minimizing pressure. Mattresses that accommodate multiple sleeping positions often combine conforming materials with zoned support systems to provide targeted pressure relief regardless of the individual’s preferred sleeping position. The ability of the mattress to adapt to different positions is paramount in ensuring consistent comfort and pressure relief throughout the night.
In summary, pressure relief i
s a multifaceted characteristic dependent on material selection, construction techniques, and adaptability to sleeping position. The integration of conforming materials, zoned support systems, and thoughtfully designed surface layers contributes to a mattress’s ability to minimize pressure points and enhance sleep comfort. Products that prioritize pressure relief effectively address a fundamental aspect of sleep physiology, promoting restful sleep and minimizing the potential for pain or discomfort.
5. Temperature Regulation
Temperature regulation in the context of this mattress category refers to the ability of bedding materials and construction to maintain a stable and comfortable sleep temperature, preventing overheating or excessive cooling. The efficacy of temperature regulation directly influences sleep quality; deviations from an optimal temperature range can disrupt sleep cycles and lead to discomfort. The cause-and-effect relationship is straightforward: materials that trap heat or restrict airflow result in elevated body temperature, while materials promoting breathability and moisture wicking facilitate a more consistent thermal environment.
The importance of temperature regulation as a component is multifaceted. A stable sleep temperature minimizes tossing and turning, promoting deeper and more restorative sleep. Additionally, effective temperature regulation reduces the likelihood of night sweats and discomfort caused by overheating, thereby contributing to overall sleep hygiene. Real-world examples include mattresses incorporating gel-infused memory foam, which aims to dissipate heat more effectively than traditional memory foam, or those utilizing natural fibers like wool or cotton, known for their breathability and moisture-wicking properties. Consider, for instance, a mattress utilizing phase-change materials designed to absorb and release heat as needed, actively regulating temperature within a narrow range. The practical significance of understanding this connection lies in the ability to select bedding materials aligned with individual thermal preferences and physiological needs.
In summary, temperature regulation constitutes a critical factor influencing the effectiveness of a mattress. The capacity of materials and construction techniques to maintain a stable and comfortable sleep temperature significantly impacts sleep quality and overall well-being. Challenges remain in accurately assessing and comparing the temperature-regulating properties of different mattress systems. Consumers must prioritize material transparency and seek verifiable data to make informed decisions.
6. Durability Assessment
Durability assessment, in the context of this specific mattress type, refers to the systematic evaluation of a mattress’s ability to withstand prolonged use and maintain its structural integrity and performance characteristics over an extended period. The cause-and-effect relationship is direct: inadequate durability assessment leads to premature degradation, reduced comfort, and diminished support, ultimately negating the intended benefits and shortening the lifespan of the product. This assessment encompasses material fatigue, structural resilience, and resistance to environmental factors such as humidity and temperature variations, each contributing significantly to the long-term value proposition.
The importance of durability assessment as a component is considerable, extending beyond mere cost considerations. A durable mattress provides consistent support and comfort, preserving proper spinal alignment and minimizing pressure points over time. For example, mattresses utilizing high-density foams and reinforced coil systems are generally expected to exhibit greater resistance to sagging and deformation compared to those constructed with lower-quality materials. Similarly, mattresses with durable outer fabrics and reinforced seams are less susceptible to tearing and wear, maintaining their aesthetic appeal and structural integrity for a longer duration. The practical significance of this understanding lies in informed purchasing decisions, allowing consumers to prioritize products that offer a demonstrable return on investment through extended lifespan and consistent performance. Warranty provisions, while offering some assurance, do not fully compensate for the inconvenience and potential health implications associated with a prematurely degraded mattress.
In summary, durability assessment is a critical factor influencing the long-term value and performance characteristics of a mattress. This assessment addresses material quality, construction techniques, and resistance to environmental stressors, each contributing to the product’s ability to withstand prolonged use and maintain its intended functionality. Challenges persist in accurately quantifying durability through standardized testing methodologies and communicating these findings to consumers in a clear and transparent manner. Greater emphasis on rigorous durability testing and comprehensive product information is essential for fostering consumer confidence and promoting the selection of products that offer sustained comfort, support, and value.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding this bedding product. It seeks to provide clarity and informed perspectives on key aspects.
Question 1: What factors determine the suitability of such a mattress for individuals with back pain?
The appropriateness of a mattress for back pain hinges on its capacity to maintain proper spinal alignment and provide adequate support. Consider firmness level, zoning technology, and material properties. Mattresses offering targeted lumbar support may be advantageous.
Question 2: How do the materials used in this product influence its temperature regulation capabilities?
Material composition directly impacts temperature regulation. Natural fibers like wool and cotton promote breathability, while open-cell foams enhance airflow. Gel infusions in memory foam may also contribute to heat dissipation. Evaluate material specifications for optimal thermal comfort.
Question 3: What is the expected lifespan of a mattress within this category, and what factors affect its durability?
The expected lifespan varies based on material quality, construction, and usage patterns. High-density foams and reinforced coil systems typically enhance durability. Regular rotation and proper maintenance practices can extend the lifespan. A reasonable expectation falls between seven and ten years.
Question 4: Are there specific certifications to look for when evaluating the safety and environmental impact of this bedding?
Certifications such as CertiPUR-US and OEKO-TEX indicate that the materials have been tested for harmful substances and meet specific environmental standards. These certifications provide assurance regarding product safety and responsible manufacturing practices.
Question 5: What are the key differences between various types of foam (e.g., memory foam, latex, polyfoam) used in these mattresses, and how do these differences impact performance?
Memory foam conforms closely to the body, offering pressure relief but potentially trapping heat. Latex is responsive and breathable, providing a balance of comfort and support. Polyfoam serves a
s a versatile base layer, offering varying levels of firmness and support depending on density and formulation. The choice depends on individual preferences and needs.
Question 6: What steps should be taken to properly maintain and clean a bedding product to maximize its lifespan and hygiene?
Employ a mattress protector to safeguard against spills and stains. Vacuum the surface regularly to remove dust and allergens. Follow manufacturer instructions for spot cleaning. Avoid using harsh chemicals that could damage the materials. Regular rotation promotes even wear.
In summary, evaluating such bedding necessitates a careful consideration of factors like support, materials, durability, and certifications. Informed decision-making ensures optimal comfort and long-term satisfaction.
The subsequent section provides detailed specifications to evaluate before purchase.
Nest Bedding Mattress
This exploration of the nest bedding mattress category has highlighted key factors influencing performance and suitability. Spinal alignment, material breathability, pressure relief, and temperature regulation emerged as critical determinants of sleep quality. Furthermore, durability assessment and adherence to safety certifications underscore the long-term value proposition and responsible manufacturing practices. These elements, when considered holistically, inform a well-reasoned selection process.
The information presented underscores the significant investment represented by the acquisition of a nest bedding mattress. Prioritizing research and aligning product selection with individual physiological needs, sleeping preferences, and documented product specifications will yield the most beneficial results. Consistent evaluation of emerging technologies and evolving material science within this domain remains crucial for informed future purchasing decisions and continued optimization of sleep health.