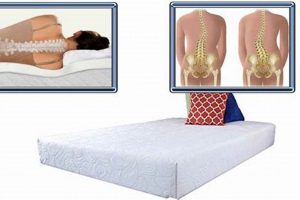
The selection of a sleep surface significantly impacts musculoskeletal health, particularly within the cervical spine. A supportive and appropriately conforming mattress is crucial for maintaining proper spinal alignment during sleep, which is paramount in mitigating discomfort and promoting restorative rest. The primary goal is to minimize pressure points and ensure the neck is adequately supported, preventing hyperextension or flexion that can exacerbate existing conditions.
Optimal spinal alignment fosters reduced muscle strain and improved blood circulation, thereby alleviating pain and stiffness often associated with cervical issues. Throughout history, advancements in sleep technology and materials have led to a greater understanding of how mattress design influences physiological well-being. The emphasis has shifted from simple comfort to the therapeutic benefits of a sleep surface that addresses specific orthopedic needs.
Therefore, understanding the material composition, firmness level, and support characteristics of various mattresses is essential. Subsequent sections will delve into specific mattress types and features, examining their suitability for individuals seeking relief from neck discomfort. We will also consider adjustable bed frames and specialized pillows, which can further enhance the therapeutic effects of a well-chosen sleep system.
Guidance for Mattress Selection
The following recommendations are designed to inform the selection process, ensuring a suitable sleep surface that mitigates discomfort and promotes optimal spinal alignment for individuals experiencing neck discomfort.
Tip 1: Prioritize Spinal Alignment. The selected mattress should facilitate a neutral spinal position. Side sleepers require adequate shoulder and hip compression to maintain a straight spine, while back sleepers benefit from support that prevents excessive arching of the lower back.
Tip 2: Consider Medium-Firm Support. A medium-firm mattress often provides a balance between support and pressure relief. This level of firmness generally caters to a wider range of body types and sleep preferences, offering sufficient resistance to prevent sinking while contouring to the body’s curves.
Tip 3: Evaluate Material Composition. Memory foam, latex, and hybrid mattresses each possess unique characteristics. Memory foam excels at pressure relief and conforming to the body, while latex offers a more responsive and breathable surface. Hybrid mattresses combine the benefits of both, incorporating innerspring coils for support and foam layers for comfort.
Tip 4: Assess Pressure Relief Capabilities. Pressure points, particularly in the shoulders and neck, can exacerbate discomfort. The mattress should distribute weight evenly to minimize pressure concentration in these areas. Pressure mapping can be a useful tool in evaluating a mattress’s pressure relief performance.
Tip 5: Investigate Edge Support. Adequate edge support prevents mattress sagging along the perimeter, which can compromise spinal alignment and make it difficult to get in and out of bed. Reinforced edges are a common feature designed to enhance edge support.
Tip 6: Account for Sleep Position. Individual sleep positions influence the optimal mattress type. Side sleepers generally require a softer surface to accommodate shoulder compression, while back and stomach sleepers often benefit from firmer support to prevent spinal misalignment.
Tip 7: Trial Period and Warranty. A sufficient trial period allows for thorough evaluation of the mattress’s suitability over several weeks. A comprehensive warranty provides assurance against manufacturing defects and premature wear.
Selection of an appropriate mattress is a crucial step in managing neck discomfort. The aforementioned tips offer practical guidance, enabling individuals to make informed decisions and improve sleep quality.
The subsequent sections will address the role of pillows and adjustable bed frames in further optimizing sleep posture and minimizing cervical pain.
1. Spinal Alignment
Spinal alignment constitutes a primary determinant in the selection of a mattress intended to mitigate cervical discomfort. Misalignment of the spine during sleep can exacerbate existing conditions and contribute to the development of new pain syndromes. The cervical spine, in particular, is vulnerable to pressure points and postural stress when a sleep surface fails to provide adequate support. A properly aligned spine maintains the natural curves of the neck and back, distributing weight evenly and minimizing muscle strain. This requires a mattress that conforms to the body’s contours without allowing excessive sinking or creating pressure concentrations.
The influence of spinal alignment on cervical pain is evident in cases of forward head posture. Individuals who habitually sleep on a mattress that lacks sufficient support often develop this condition, characterized by an anterior shift of the head relative to the shoulders. This misalignment places increased stress on the cervical muscles and ligaments, leading to chronic pain and stiffness. Conversely, a mattress that promotes proper spinal alignment can reduce muscle tension, improve blood circulation, and facilitate nerve function, ultimately alleviating discomfort.
In conclusion, the relationship between spinal alignment and cervical pain is direct and consequential. The ability of a sleep surface to maintain the natural curvature of the spine is a critical indicator of its suitability for individuals seeking relief from neck discomfort. Mattresses that fail to promote proper alignment can exacerbate existing conditions, while those that prioritize support and conformity can contribute to improved spinal health and reduced pain. Therefore, spinal alignment considerations are paramount in selecting a sleep surface designed to mitigate cervical pain.
2. Pressure Relief
Pressure relief is a critical performance attribute influencing the selection of a mattress intended to alleviate cervical pain. Elevated pressure concentration in specific areas, such as the neck and shoulders, impedes circulation and exacerbates discomfort. The selection of a mattress capable of effectively distributing weight and minimizing pressure points is therefore crucial for individuals experiencing neck pain.
The mechanism underlying this connection involves the reduction of localized stress on sensitive tissues. For instance, a memory foam mattress conforms to the contours of the head and neck, distributing weight across a wider surface area compared to a traditional innerspring mattress. This decreased pressure promotes improved blood flow and reduces nerve compression, resulting in diminished pain perception. Failure to adequately address pressure points can lead to muscle stiffness, headaches, and prolonged discomfor
t, directly affecting sleep quality and overall well-being. The development of mattresses with zoned support systems, where different areas of the mattress provide varying levels of firmness, further enhances pressure relief in critical areas.
In summary, pressure relief plays a direct and measurable role in the mitigation of cervical pain. The ability of a mattress to redistribute weight and minimize pressure concentrations on sensitive tissues is essential for promoting proper circulation, reducing muscle tension, and improving sleep quality. Selection should prioritize materials and designs demonstrably effective in achieving these goals.
3. Material Composition
The material composition of a mattress exerts a significant influence on its capacity to alleviate cervical pain. Material properties dictate the degree of support, pressure relief, and temperature regulation offered by the sleep surface, each factor contributing to the overall sleeping experience and its impact on the cervical spine.
- Memory Foam
Memory foam, composed of viscoelastic polyurethane foam, is known for its ability to contour to the body’s shape, providing targeted pressure relief. This property is advantageous in reducing stress on cervical muscles and joints. However, traditional memory foam can retain heat, potentially causing discomfort. Gel-infused or open-cell memory foam mitigates this issue by improving airflow. The density of memory foam influences its support level and longevity. Higher-density foam provides greater support and durability, while lower-density foam offers a softer feel but may degrade more quickly.
- Latex
Latex, derived from rubber trees, is available in two primary forms: Dunlop and Talalay. Dunlop latex is denser and firmer, offering robust support, while Talalay latex is lighter and more responsive. Both forms exhibit excellent breathability and resilience, contributing to a comfortable sleeping environment. Latex is naturally hypoallergenic and resistant to dust mites, making it suitable for individuals with allergies or sensitivities. The inherent elasticity of latex conforms to the body without the deep sinking sensation associated with memory foam.
- Innerspring
Innerspring mattresses utilize a system of coils to provide support. The coil type (e.g., Bonnell, pocketed) affects the mattress’s contouring ability and motion isolation. Bonnell coils are interconnected, offering a more uniform but less targeted support. Pocketed coils, individually wrapped in fabric, conform independently to body weight, reducing motion transfer. While innerspring mattresses can provide adequate support, they often lack the pressure-relieving properties of foam or latex, potentially exacerbating cervical pain.
- Hybrid
Hybrid mattresses combine the features of innerspring and foam or latex layers, seeking to balance support and comfort. They typically consist of a coil support core topped with layers of memory foam, latex, or both. The specific combination of materials determines the mattress’s overall performance. A hybrid mattress with pocketed coils and a thick layer of memory foam can offer targeted support, pressure relief, and motion isolation, making it a potentially suitable option for individuals with cervical pain.
The selection of appropriate materials is integral to achieving the desired balance of support, pressure relief, and temperature regulation. Individuals seeking a sleep surface conducive to cervical health should carefully consider the properties of each material and its potential impact on spinal alignment and comfort.
4. Firmness Level
Firmness level represents a crucial determinant in mattress selection, directly influencing spinal alignment and pressure distribution, key factors in mitigating cervical pain. An inappropriate firmness level can exacerbate existing conditions, while a carefully chosen firmness can promote proper posture and alleviate discomfort.
- Support and Spinal Alignment
Excessively soft mattresses allow the spine to sink, disrupting natural alignment and placing undue stress on cervical muscles. Conversely, overly firm mattresses fail to conform to the body’s contours, creating pressure points and restricting blood flow. The optimal firmness level provides sufficient support to maintain spinal alignment while accommodating the body’s natural curves. Medium-firm mattresses are often recommended as a starting point, offering a balance between support and pressure relief.
- Body Weight Considerations
Individual body weight significantly impacts the perception of firmness. Lighter individuals may find a medium-firm mattress too rigid, while heavier individuals may require a firmer surface to prevent excessive sinking. It is crucial to consider body weight when selecting a mattress firmness, as a mattress that feels comfortable for one person may not provide adequate support for another.
- Sleep Position Influences
Sleep position also plays a critical role in determining the appropriate firmness level. Side sleepers typically require a softer mattress to allow for shoulder and hip compression, maintaining spinal alignment. Back sleepers often benefit from a medium-firm mattress that provides support for the lumbar region while allowing the shoulders and hips to sink slightly. Stomach sleepers generally require a firmer mattress to prevent excessive arching of the back and neck.
- Impact on Pressure Distribution
Firmness level dictates how weight is distributed across the mattress surface. A softer mattress distributes weight more evenly, reducing pressure points but potentially compromising support. A firmer mattress provides greater support but may concentrate pressure on bony prominences. The optimal firmness level balances support and pressure relief, minimizing stress on sensitive areas while maintaining proper spinal alignment. Individuals experiencing neck discomfort should prioritize mattresses that effectively distribute weight and reduce pressure on the cervical spine.
The selection of an appropriate firmness level is an individualized process, influenced by body weight, sleep position, and personal preferences. A well-chosen firmness level can significantly contribute to improved sleep quality and reduced cervical pain by promoting proper spinal alignment and minimizing pressure points.
5. Edge Support
Edge support, a structural feature often overlooked, plays a consequential role in optimizing the therapeutic efficacy of a mattress intended to mitigate cervical pain. The integrity of the mattress perimeter directly influences spinal alignment, ease of egress, and the overall usable sleep surface area, all factors impacting the experience of an individual with neck discomfort.
- Spinal Alignment Maintenance
Inadequate edge support leads to perimeter compression when sitting or lying near the edge of the mattress. This compression can induce spinal misalignment, particularly in the cervical region, as the body compensates for the lack of support. This misa
lignment exacerbates existing neck pain and stiffness. Mattresses with reinforced edges provide a stable, level surface, ensuring consistent spinal support across the entire sleep area and promoting a neutral cervical position. - Ease of Egress and Ingress
Individuals experiencing cervical pain often find movements such as getting in and out of bed challenging. Weak edge support necessitates greater muscular effort to transition from a seated to a lying position, increasing the risk of exacerbating pain. Robust edge support provides a stable platform for sitting, facilitating easier and less painful transitions, thereby reducing strain on the neck muscles.
- Usable Sleep Surface Area
A mattress with poor edge support effectively reduces the usable sleep surface. Individuals may avoid sleeping near the edge for fear of rolling off, thereby restricting their movement and potentially affecting sleep quality. For those with cervical pain, constrained sleep positions can worsen discomfort. Strong edge support maximizes the usable sleep area, allowing for greater freedom of movement and promoting more comfortable sleep positions.
- Durability and Longevity
Mattresses lacking adequate edge support are prone to sagging and deformation along the perimeter over time. This compromises the overall support and comfort of the mattress, ultimately reducing its lifespan. For individuals with cervical pain, a prematurely sagging mattress can negate the benefits of other supportive features, requiring more frequent replacement and potentially leading to recurrent pain exacerbations.
In summation, robust edge support serves as a critical component in the holistic design of a mattress intended to alleviate cervical pain. By maintaining spinal alignment, facilitating ease of movement, maximizing usable sleep area, and enhancing mattress durability, strong edge support contributes significantly to the overall therapeutic effectiveness of the sleep surface.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Mattress Selection for Cervical Pain Mitigation
The following questions address common concerns surrounding the selection of a suitable mattress designed to alleviate discomfort associated with cervical pain. These responses aim to provide clarity and inform decision-making in this critical area.
Question 1: Is a firmer mattress always preferable for cervical pain relief?
A mattress that is excessively firm may not conform adequately to the contours of the body, leading to pressure points and increased discomfort. The optimal firmness is subjective, often falling within the medium-firm range, contingent upon individual body weight, sleep position, and specific spinal conditions. A mattress should provide adequate support to maintain spinal alignment without creating localized pressure concentrations.
Question 2: How does mattress material composition impact cervical pain?
The material composition directly influences a mattresss capacity for pressure relief and spinal support. Memory foam excels at contouring and pressure redistribution, while latex offers a balance of support and responsiveness. Innerspring mattresses, lacking significant conforming properties, may not be optimal for individuals experiencing cervical pain. Hybrid models combine the features of these materials, potentially offering a beneficial compromise.
Question 3: Can an adjustable bed frame further enhance the benefits of a mattress designed for cervical pain?
An adjustable bed frame can complement the benefits of a supportive mattress by allowing for customized sleep positions. Elevating the head and upper body can reduce pressure on the cervical spine and alleviate associated discomfort. Furthermore, adjustable bed frames may improve circulation and reduce inflammation, potentially contributing to overall pain management.
Question 4: How does edge support influence the effectiveness of a mattress in mitigating cervical pain?
Inadequate edge support can lead to spinal misalignment as the sleeper approaches the perimeter of the mattress. The resulting postural stress can exacerbate cervical pain. A mattress with robust edge support provides a stable and level surface, ensuring consistent spinal alignment across the entire sleep area. This feature is particularly important for individuals who tend to sleep near the edge of the bed.
Question 5: Is there a single “best” mattress type for all individuals experiencing cervical pain?
The ideal mattress type is highly individualized. Factors such as body weight, sleep position, pre-existing medical conditions, and personal preferences all contribute to the optimal mattress selection. Trial periods and consultations with healthcare professionals can aid in identifying the most appropriate sleep surface for specific needs.
Question 6: How long should a trial period be to adequately assess the suitability of a mattress for cervical pain relief?
A trial period of at least 30 nights is recommended to allow for sufficient acclimatization and evaluation of the mattress’s impact on cervical pain. This timeframe allows the body to adjust to the new sleep surface and provides ample opportunity to assess its long-term comfort and support. Extended trial periods offer even greater confidence in the mattress selection.
Selecting a suitable mattress is a critical step in managing cervical pain. The aforementioned FAQs provide practical guidance, enabling individuals to make informed decisions and improve sleep quality. Careful consideration of these factors can lead to improved sleep quality and reduced cervical pain.
The following sections will delve into specific mattress types and features, examining their suitability for individuals seeking relief from neck discomfort.
Conclusion
The selection of a sleep surface represents a critical intervention for individuals experiencing cervical pain. This discussion has illuminated the nuanced interplay between mattress characteristicsspinal alignment, pressure relief, material composition, firmness level, and edge supportand their impact on musculoskeletal health. A judicious choice necessitates a comprehensive understanding of these factors, tailored to individual needs and physiological considerations. Ultimately, selecting a suitable mattress to reduce cervical pain is a crucial decision that needs comprehensive consideration
The pursuit of optimal sleep health necessitates a proactive and informed approach. While this exploration provides a framework for informed decision-making, consultation with healthcare professionals remains paramount. Continued advancements in sleep technology and a deeper understanding of the biomechanics of sleep will further refine the process of mattress selection, offering increasingly targeted solutions for those seeking relief from cervical pain.





![Find Your Best Cheap King Mattress [Deals!] Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Find Your Best Cheap King Mattress [Deals!] | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-7824-300x200.jpg)