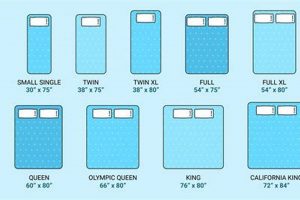
A sleeping arrangement featuring two beds stacked vertically, designed to accommodate individuals in a shared space, often includes a standardized sleeping platform dimensionally equivalent to 54 inches wide and 75 inches long. This configuration maximizes floor area in bedrooms, dormitories, and other space-constrained environments. The lower and upper levels of this arrangement typically require separate support structures and safety rails.
Such a configuration offers several advantages, including efficient use of limited room space, cost-effectiveness compared to purchasing separate beds, and potential enhancement of room aesthetics. Historically, this type of bed design has been prevalent in settings where maximizing occupancy and minimizing square footage per individual is critical, such as military barracks and summer camps. Its adaptability and practicality continue to make it a relevant solution for modern living spaces.
The subsequent sections will delve into the specific considerations for choosing appropriate bedding and support systems for these types of sleeping arrangements, focusing on safety standards, comfort levels, and durability requirements. Furthermore, various material options and design considerations will be explored to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Considerations for Selecting an Appropriate Sleeping Configuration
Selecting the correct components for a vertically stacked sleeping system requires careful evaluation. These considerations ensure optimal safety, comfort, and longevity. The following guidelines provide a structured approach to this process.
Tip 1: Height Restriction: Verify that the ceiling height accommodates the vertical dimension of the structure and occupant. Inadequate clearance increases the risk of head injuries.
Tip 2: Load Capacity: The supporting structure must demonstrably support the combined weight of the bedding and occupants. Manufacturer specifications must be consulted and strictly adhered to.
Tip 3: Mattress Thickness: Limit bedding thickness on the upper tier to ensure guardrail effectiveness. Excessive bedding diminishes the protective barrier, increasing fall risk.
Tip 4: Ladder Placement: Position the access ladder securely to prevent accidental dislodgement. Regular inspection of connection points is essential.
Tip 5: Material Selection: Opt for flame-retardant materials for bedding to mitigate fire hazards. Certifications indicating compliance with safety standards are critical.
Tip 6: Structural Integrity: Regularly inspect the frame for signs of stress, such as cracks or loose connections. Promptly address any deficiencies to maintain stability.
Tip 7: Ventilation: Ensure adequate air circulation to prevent moisture buildup and promote a comfortable sleeping environment. Proper ventilation minimizes the risk of mold and mildew.
Following these guidelines mitigates risks associated with vertically stacked sleeping systems, promoting user safety and maximizing the lifespan of the equipment.
The subsequent section will address specific maintenance procedures and strategies for ensuring continued safe operation.
1. Space Optimization
The primary design impetus behind vertically stacked sleeping arrangements incorporating a standardized sleeping platform is space optimization. This configuration directly addresses the challenge of accommodating multiple individuals within a constrained area. The effect of implementing such a system is a maximized usable floor area, permitting other furniture or activities within the same room footprint. The significance of this optimization is particularly evident in shared bedrooms, dormitories, and small living spaces where floor space is at a premium. For example, a room that would otherwise accommodate only one single bed and a desk can, with this setup, accommodate two occupants each with their own sleeping space and shared desk area.
Further analysis reveals practical benefits beyond simple space savings. The vertical arrangement reduces the horizontal surface area occupied by sleeping quarters, freeing up space for storage units, study areas, or recreational activities. This design feature directly influences the functionality and livability of the confined space. In shared children’s bedrooms, the available play area increases significantly, promoting physical activity and reducing the sense of crowding. In smaller apartments, the gained space can be utilized for essential furniture or living amenities, increasing overall quality of life. The efficiency provided by vertical sleeping arrangements is crucial in housing developments where unit sizes are minimized to maximize occupancy.
In conclusion, the intrinsic link between vertically stacked sleeping configurations and space optimization directly impacts both the practicality and usability of limited environments. Understanding this relationship enables informed decisions when selecting furniture for space-conscious living. The effectiveness of this design depends on adherence to safety standards and thoughtful consideration of the occupants’ needs; however, its inherent ability to maximize available space remains a significant advantage, particularly in densely populated urban environments and shared living spaces.
2. Weight Distribution
Weight distribution is a paramount consideration in the structural design and safe operation of vertically stacked sleeping arrangements using a standardized sleeping platform. The integrity of the frame, the stability of the overall structure, and the safety of its occupants are directly contingent upon how effectively the load is distributed.
- Material Strength and Frame Design
The composition of the frame materials, such as metal alloys or solid wood, plays a vital role in handling static and dynamic loads. Engineering principles dictate that the frame design must ensure that weight is evenly distributed across all support points. For instance, reinforced corner joints and strategically placed support beams are essential to prevent stress concentration and potential failure.
- Load Capacity and Occupancy Limits
Each component of the vertically stacked sleeping arrangement, including the frame, supporting slats, and ladder, possesses a maximum load capacity. Exceeding these limits compromises structural integrity, increasing the risk of collapse. Manufacturers provide specific guidelines regarding occupancy limits, taking into account the combined weight of occupants and bedding. Adherence to these guidelines is non-negotiable for safety.
- Bedding Material and Support System
The type of bedding and the support system (e.g., wooden slats, metal grid) directly impact weight distribution. A high-density mattress, for example, exerts more downward force than a lighter, thinner one. Similarly, a robust support system with closely spaced slats provides more uniform weight distribution than a system with fewer, widely spaced supports. Uneven support leads to mattress sagging and potential structural damage.
- Impact of Dynamic Loads
While static load (the resting weight) is a crucial factor, dynamic loadssudden movements, jumping, or shifting weightexert additional stress on the structure. The frame must be designed to withstand these intermittent forces without compromising stability. Reinforcements, such as crossbars and bolted connections, enhance resistance to dynamic loads, preventing wobbling or collapse.
In summation, effective weight distribution is not merely a design feature; it’s a fundamental safety requirement. Overlooking this aspect can lead to structural failure, posing a significant risk to occupants. The selection of robust materials, adherence to occupancy limits, appropriate bedding support, and attention to dynamic load factors are all critical to ensure the long-term safety and stability of this configuration.
3. Ladder Accessibility
Ladder accessibility represents a critical safety and usability aspect of vertically stacked sleeping arrangements utilizing a standardized sleeping platform. The design and placement of the access ladder directly influence the ease and safety with which occupants can enter and exit the upper tier, mitigating the risk of falls and injuries.
- Angle and Inclination
The angle of the ladder significantly impacts its usability. A steeper angle, while conserving floor space, increases the effort required for climbing and descent, posing a greater risk of slipping. A shallower angle, while easier to navigate, consumes more room space. Optimal ladder design seeks a balance between these competing factors. For instance, ladders with an angle between 60 and 75 degrees from the horizontal are frequently cited as offering a reasonable compromise between ease of use and space efficiency. This angle provides a more natural climbing posture, reducing strain and improving grip security.
- Step Width and Spacing
The width of the steps and the vertical distance between them dictate the comfort and safety of each step. Narrow steps provide insufficient foot support, increasing the likelihood of missteps. Excessive spacing between steps necessitates greater vertical reach, demanding more physical exertion and raising the risk of falls. Ladder designs often incorporate step widths of at least 12 inches and vertical spacing of no more than 12 inches to maximize foot support and minimize reach distance. Wider steps provide a more secure platform for the foot, reducing the chance of slipping. Closer spacing between steps allows for a more controlled and less strenuous climb, particularly for children and the elderly.
- Material and Surface Texture
The material composition and surface texture of the ladder steps directly influence grip and stability. Smooth or slippery surfaces increase the risk of accidental slips, particularly when wet or when wearing socks. Ladders constructed from materials with inherent grip, such as textured metal or rubberized surfaces, enhance traction and reduce the likelihood of slipping. For example, ladders with knurled metal steps or treads covered in slip-resistant rubber provide a more secure foothold, minimizing the chance of accidents. The chosen material must also exhibit sufficient structural integrity to withstand repeated use and varying weights without bending or breaking.
- Secure Attachment and Stability
The method of attachment and the overall stability of the ladder are essential for preventing accidents. A poorly secured ladder can detach or wobble during use, leading to falls. Ladders must be securely fastened to the frame of the vertically stacked sleeping arrangement using robust connectors, such as bolts or screws. The base of the ladder must also rest firmly on the floor, providing a stable foundation. Designs that incorporate stabilizing feet or floor anchors further enhance stability, preventing movement or tipping during climbing and descent. Regular inspection of the attachment points is crucial to ensure continued stability and safety.
In conclusion, ladder accessibility is not merely a convenience feature but a fundamental safety consideration for vertically stacked sleeping configurations utilizing a standardized sleeping platform. The angle, step dimensions, material, and stability of the ladder all contribute to the ease and safety of accessing the upper tier. Optimizing these features reduces the risk of falls and injuries, ensuring a more secure and comfortable sleeping environment. Regular inspection and maintenance of the ladder are essential for preserving its functionality and promoting occupant safety.
4. Guardrail Height
Guardrail height is a critical safety parameter directly influencing the secure use of vertically stacked sleeping arrangements with a standardized sleeping platform. The primary function of the guardrail is to prevent occupants on the upper tier from accidentally falling during sleep or while moving within the bed. The effectiveness of this safety feature is directly proportional to its height relative to the mattress surface. Insufficient guardrail height diminishes its protective capability, increasing the risk of falls, particularly for children. For instance, if the guardrail height is significantly reduced by the addition of a thick mattress, the barrier may become ineffective, negating its intended safety function.
Regulatory bodies establish minimum guardrail height requirements to ensure an adequate safety margin. These standards often stipulate that the guardrail must extend a minimum distance above the top surface of the mattress. For example, safety standards may mandate a minimum guardrail extension of 5 inches above the mattress. The type of bedding used directly impacts the compliance with these standards. Thicker mattresses reduce the effective guardrail height, potentially rendering the sleeping arrangement non-compliant with safety regulations. Therefore, selecting a mattress with a compatible thickness is essential for maintaining the intended safety level. Furthermore, the guardrail design itself influences its effectiveness. Continuous guardrails, which span the entire length of the bed, offer greater protection than those with gaps or openings.
In conclusion, guardrail height is not merely a design element, but a fundamental safety component in vertically stacked sleeping configurations utilizing a standardized sleeping platform. Proper guardrail height, coupled with appropriate bedding selection, mitigates the risk of falls and ensures compliance with safety standards. Regular inspection to confirm adherence to minimum height requirements is imperative to maintain occupant safety.
5. Material Flammability
Material flammability is a critical safety consideration directly impacting the risk profile of vertically stacked sleeping arrangements incorporating a standardized sleeping platform. The inherent combustibility of materials used in the construction of the bedding and frame components significantly influences the speed and intensity with which a fire can spread, potentially endangering occupants. A vertically stacked sleeping arrangement concentrates flammable materials in a relatively small volume, creating a heightened fire hazard compared to single-level beds. For instance, if a fire originates from a faulty electrical outlet near the structure, highly flammable bedding can rapidly ignite, creating a dangerous situation, particularly when occupants are asleep and less responsive.
The selection of flame-retardant materials plays a crucial role in mitigating this risk. Bedding, including mattresses, sheets, and blankets, should meet or exceed established fire safety standards, such as those defined by regulatory agencies or industry associations. For example, mattresses conforming to specific fire resistance standards incorporate materials designed to slow ignition and reduce the spread of flames. Similarly, frame components constructed from inherently fire-resistant materials or treated with flame-retardant coatings offer an added layer of protection. Failure to prioritize fire safety can have dire consequences. History provides examples of dormitory fires, where highly flammable bedding contributed significantly to rapid fire spread and loss of life. Conversely, facilities that implement rigorous fire safety protocols, including the use of flame-retardant materials and regular fire drills, demonstrate a commitment to occupant safety and minimize fire-related risks.
In summary, material flammability is a non-negotiable safety concern that must be addressed in the design, construction, and maintenance of vertically stacked sleeping configurations utilizing a standardized sleeping platform. The use of flame-retardant materials is essential to reducing the risk of fire-related injuries and fatalities. Compliance with fire safety standards, regular inspections, and occupant education are all crucial components of a comprehensive fire safety strategy, ensuring a safer environment. The challenge lies in balancing cost considerations with safety imperatives, recognizing that the long-term benefits of investing in fire-resistant materials far outweigh the potential costs associated with fire-related incidents.
Frequently Asked Questions
The subsequent section addresses common inquiries regarding vertically stacked sleeping arrangements using a standardized sleeping platform. These questions and answers aim to provide clarity on critical aspects of safety, dimensions, and usage.
Question 1: What are the standardized dimensions?
A full-size sleeping surface within a vertically stacked configuration typically measures 54 inches in width and 75 inches in length. These dimensions align with industry standards for full-size mattresses, ensuring compatibility and ease of bedding selection. Deviation from these measurements may necessitate custom-sized bedding, potentially increasing costs and limiting available options.
Question 2: What is the recommended maximum weight capacity for the upper tier?
The maximum weight capacity varies based on the frame’s material composition and design. The manufacturer’s specifications should be consulted and strictly adhered to. Exceeding the stated weight limit compromises structural integrity, potentially leading to catastrophic failure. Generally, a capacity of 200-250 pounds is common, but this value is contingent upon the specific product and construction.
Question 3: What type of bedding is most suitable?
Low-profile mattresses are generally recommended for the upper tier. Thicker mattresses can reduce the effective height of the guardrail, diminishing its protective function. Flame-retardant materials are also crucial, mitigating fire hazards. Consider the dimensions carefully to ensure a snug fit within the frame, minimizing movement and potential safety risks.
Question 4: What are the essential safety considerations for children?
Children under the age of six should not occupy the upper tier due to the risk of falls. Secure ladder placement and regular inspection are essential. Guardrails must be securely fastened and of adequate height. Educating children on safe climbing practices and prohibiting jumping or playing on the structure are paramount to prevent injuries.
Question 5: How often should the structure be inspected for safety?
A thorough inspection should be conducted at least every six months. Examine all connections for tightness and stability. Inspect the frame for cracks, bends, or signs of stress. Verify the integrity of the ladder and guardrails. Address any deficiencies promptly to maintain structural integrity and ensure occupant safety.
Question 6: What cleaning and maintenance procedures are recommended?
Regular cleaning with mild detergents prevents the accumulation of dust and allergens. Avoid using abrasive cleaners or solvents that could damage the frame’s finish. Periodically tighten all bolts and screws to maintain structural stability. Replace any damaged or worn components immediately to prevent further deterioration and potential hazards.
Adherence to these guidelines promotes safe and effective use of vertically stacked sleeping arrangements. Regular inspections and proactive maintenance are essential for ensuring long-term functionality and minimizing potential risks.
The subsequent section will explore various design considerations and stylistic options.
Conclusion
This exposition has thoroughly examined the characteristics, safety considerations, and practical applications of the `bunk bed full mattress`. Key elements discussed include space optimization, weight distribution, ladder accessibility, guardrail height requirements, and the importance of material flammability. The information presented underscores the criticality of adhering to safety standards and manufacturer guidelines for responsible implementation and long-term use.
Given the inherent risks associated with elevated sleeping platforms, it is incumbent upon both manufacturers and users to prioritize safety above all other considerations. Diligent adherence to recommended practices and ongoing vigilance are essential for mitigating potential hazards and ensuring the well-being of occupants. The information provided herein serves as a foundation for informed decision-making, promoting the safe and effective utilization of this space-saving sleeping configuration.