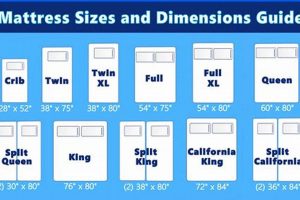
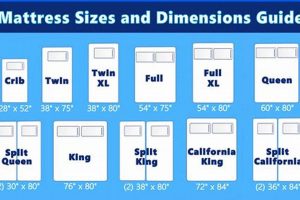
A sleeping platform designed for use in stacked sleeping arrangements and accommodating standardized bedding dimensions is a furniture configuration prevalent in shared living spaces. It efficiently utilizes vertical space, typically featuring a supportive structure to elevate one sleeping surface above another, thereby maximizing floor area. The lower platform is dimensioned to fit a standard 54-inch wide and 75-inch long sleeping pad.
The significance of this space-saving design lies in its ability to provide separate sleeping areas for multiple occupants within a single room, offering a practical solution for families, hostels, and shared apartments. Historically, these structures emerged as a response to limited living quarters, offering a cost-effective and space-conscious method to house individuals. The arrangement fosters a sense of individual space within a communal environment.
The subsequent discussion will explore various aspects related to selecting, maintaining, and optimizing the configuration for comfort and safety. This includes considerations for frame materials, safety features, bedding options, and guidelines for ensuring a secure and restful sleeping environment.
Considerations for Bunk Bed Full Size Mattress Selection and Use
Proper selection and utilization of sleeping pads designed for stacked bed arrangements are crucial for safety, comfort, and longevity. Prioritizing specific factors can optimize the sleeping experience and mitigate potential hazards.
Tip 1: Confirm Dimensional Accuracy: Prior to purchase, verify the precise dimensions of the intended mattress platform. Ensure the selected sleeping pad aligns with the frame’s specifications to prevent instability and potential falls. Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for permissible overhang or gaps.
Tip 2: Evaluate Support and Density: Select a mattress with adequate support based on the intended occupant’s weight and sleeping preferences. Higher density materials generally offer enhanced durability and resistance to sagging over extended use. Consider innerspring, memory foam, or hybrid constructions based on individual needs.
Tip 3: Prioritize Safety Certifications: Scrutinize the product for relevant safety certifications, such as those from CertiPUR-US or similar organizations. These certifications indicate the absence of harmful chemicals and adherence to established safety standards. Verify compliance with relevant consumer product safety regulations.
Tip 4: Assess Flammability Resistance: Evaluate the flammability resistance of the mattress. Look for products that meet or exceed federal flammability standards. This consideration is paramount in minimizing fire hazards and ensuring occupant safety.
Tip 5: Implement Regular Inspection Protocol: Establish a routine inspection schedule to assess the condition of both the sleeping pad and the supporting structure. Inspect for signs of wear, sagging, or damage. Promptly address any identified issues to prevent accidents and maintain structural integrity.
Tip 6: Adhere to Weight Restrictions: Strictly adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended weight limitations for both the upper and lower tiers of the stacked bed arrangement. Exceeding these limits can compromise structural stability and increase the risk of collapse.
Adhering to these guidelines contributes to a safer and more comfortable sleeping environment. Meticulous attention to detail during selection and ongoing maintenance are essential for maximizing the benefits and minimizing the risks associated with stacked sleeping arrangements.
The following sections will delve deeper into specific product recommendations and address common concerns related to durability and long-term performance.
1. Dimensions and Fit
Dimensional accuracy is paramount when selecting a sleeping pad for a stacked bed arrangement. A precise fit prevents shifting, instability, and potential falls. A sleeping surface that exceeds the frame’s interior dimensions will not properly seat within the supporting structure, creating an overhang and increasing the risk of dislodgment. Conversely, a sleeping pad that is significantly smaller than the frame leaves excessive gaps, posing a hazard for entrapment and potentially causing discomfort due to uneven support. Such dimensional mismatches reduce the overall safety and structural integrity of the assembled bed.
Consider the example of a sleeping surface intended for a standard 54-inch wide and 75-inch long frame. If the actual measurements deviate by more than an inch in either direction, the fit will be compromised. This deviation can lead to premature wear on the mattress edges, damage to the frame, and a reduced lifespan for both components. Moreover, improperly fitted sleeping pads can compromise the intended ergonomic support, leading to discomfort and potentially contributing to musculoskeletal issues. Manufacturers typically provide tolerance ranges for their frames, and selecting sleeping pads within these specified ranges is crucial.
In summary, the dimensional relationship between the stacked bed frame and its accompanying sleeping pad is a critical determinant of safety, stability, and long-term performance. Meticulous attention to accurate measurements and adherence to manufacturer specifications are essential to mitigate potential risks and ensure a functional, comfortable, and secure sleeping environment. The practical significance of this understanding directly translates to enhanced user safety and increased product longevity.
2. Material Density
Material density within a sleeping surface significantly impacts its suitability for a stacked bed configuration. Higher density materials, such as high-density memory foam or innerspring units with a greater coil count, generally provide enhanced support and durability compared to lower density alternatives. The increased density offers superior resistance to compression and sagging, which is particularly crucial in a setting where the mattress may experience concentrated weight distribution. Conversely, lower density foams or sparsely coiled innerspring systems are prone to quicker degradation under similar conditions, resulting in reduced support and a shorter lifespan. This is significant because a sagging sleeping surface can compromise spinal alignment and lead to discomfort for the user. For instance, a lower-density foam might exhibit significant compression over time, leading to uneven support and pressure points, particularly for heavier individuals. In terms of safety, a more supportive surface helps to maintain proper body positioning, reducing the likelihood of falls or other accidents, particularly from the upper bunk.
Practical applications of understanding material density extend to informed purchasing decisions. Consumers should scrutinize product specifications, paying particular attention to foam density ratings (measured in pounds per cubic foot) or coil counts for innerspring mattresses. A higher rating generally indicates a more durable and supportive product. Additionally, considering the intended user’s weight and sleeping habits is essential. Individuals with higher body weights will benefit disproportionately from higher density materials. In scenarios involving shared sleeping arrangements, a durable, high-density surface minimizes the likelihood of needing frequent replacements, offering a more cost-effective solution over time. For example, hotels and hostels often prioritize high-density mattresses to withstand heavy use and prolonged occupancy.
In summary, material density is a critical determinant of a sleeping surface’s performance in a stacked bed arrangement. Its influence on support, durability, and safety cannot be overstated. Challenges arise in accurately assessing material density based solely on product descriptions; therefore, seeking reputable brands and verifying certifications, such as CertiPUR-US, can provide added assurance. The practical significance of this understanding lies in enabling informed decisions that prioritize comfort, safety, and long-term value, all of which are essential when selecting a sleeping surface for a stacked bed system.
3. Support System
The “support system” within a sleeping surface designed for a stacked bed configuration plays a pivotal role in ensuring proper spinal alignment, weight distribution, and overall comfort. This system, whether composed of innerspring coils, foam layers, or a hybrid construction, directly affects the user’s sleep quality and long-term musculoskeletal health. A robust and well-engineered support structure mitigates the risk of pressure points, which can lead to discomfort and disrupted sleep patterns. Conversely, an inadequate or poorly designed support system may result in spinal misalignment, exacerbating existing back problems or contributing to the development of new ones. For instance, a sleeping surface with insufficient support can cause the spine to curve unnaturally, leading to muscle strain and stiffness. The connection, therefore, is causal: the quality of the support system directly influences the physical well-being of the user.
The practical significance of understanding the support system lies in informed product selection. Consider the difference between a traditional innerspring mattress and a memory foam mattress. Innerspring systems utilize interconnected coils to provide support, while memory foam conforms to the body’s contours. The choice depends on individual preferences and needs. Individuals seeking firm support may prefer an innerspring system with a high coil count, while those prioritizing pressure relief may opt for a memory foam construction with varying density layers. Hybrid mattresses combine both technologies, attempting to offer a balance of support and comfort. Hotels, for instance, often select hybrid systems for stacked beds, as they aim to cater to a broad range of guest preferences and body types. In addition, the weight capacity of the support system must be considered, especially for the upper tier. The weight of the occupant should not exceed the manufacturer’s recommendations, ensuring stability and preventing premature sagging of the support structure.
In summary, the support system is an integral component of a sleeping surface for stacked beds, directly impacting user comfort, spinal health, and overall safety. Challenges arise in accurately assessing the quality and suitability of a support system based solely on marketing materials. Independent reviews, professional assessments, and certifications like those from the International Chiropractors Association can provide additional insights. Ultimately, selecting a sleeping pad with an appropriate support system necessitates careful consideration of individual needs, preferences, and the structural integrity of the bed itself. Prioritizing quality and durability ensures a comfortable and supportive sleep environment, contributing to the long-term health and well-being of the user.
4. Safety Standards
Rigorous adherence to safety standards is paramount in the design, manufacturing, and use of stacked bed arrangements incorporating standardized bedding dimensions. These standards serve to mitigate potential hazards associated with elevated sleeping platforms and ensure occupant well-being.
- Guardrail Height and Design
Minimum guardrail height requirements, typically mandated by regulatory bodies, are crucial for preventing falls from the upper tier. The design must preclude easy climbing and incorporate closely spaced slats or solid panels to minimize the risk of entrapment. Non-compliance can lead to severe injuries, especially among children. Real-world examples of injuries from inadequate guardrails underscore the necessity of strict adherence to these specifications. Standards often specify minimum height above the mattress as well as gap restrictions between the guardrail and mattress surface.
- Ladder or Stairway Construction
The construction and placement of the ladder or stairway provide access to the upper tier. Standards dictate minimum rung or step spacing, slip-resistant surfaces, and secure attachment to the bed frame. Poorly designed or inadequately attached ladders can lead to falls and injuries. Regulations mandate that the ladder or stairway withstand specific weight loads and resist tipping. A robust and well-positioned access structure is essential for safe entry and exit from the elevated sleeping surface.
- Mattress Thickness Limitations
Standards often impose limitations on the maximum mattress thickness for the upper tier. Exceeding the specified thickness can reduce the effective height of the guardrail, compromising its protective function. This reduction can create a significant fall hazard. Real-world incidents demonstrate that using overly thick sleeping pads on the upper tier significantly increases the risk of occupants rolling over the guardrail and falling. Compliance with mattress thickness limitations is therefore a critical safety consideration.
- Structural Integrity and Stability
Comprehensive safety standards address the structural integrity and stability of the entire stacked bed frame. This includes testing for weight-bearing capacity, resistance to tipping, and the strength of joints and connections. Frame materials and construction methods must withstand sustained use and prevent collapse or separation. Standards dictate specific testing protocols to simulate real-world stress and ensure that the bed can safely support its intended load. Adequate structural integrity is fundamental to occupant safety and prevents catastrophic failure of the sleeping arrangement.
Collectively, these safety standards provide a framework for minimizing risks associated with elevated sleeping platforms. Adherence to these standards during manufacturing, assembly, and use is essential to ensure a safe sleeping environment. Deviations from these standards increase the likelihood of accidents and injuries. Therefore, selecting products that demonstrably comply with established safety regulations is crucial for protecting occupants. Consumers must verify certifications and adherence to standards before purchasing and using these products.
5. Durability and Lifespan
The durability and lifespan of a sleeping surface designed for use within a stacked bed configuration are critical factors influencing its long-term value and safety. The intended application of a standard-dimension sleeping pad within a stacked bed frame subjects it to specific stresses that can accelerate wear. These stresses arise from the concentrated weight distribution, frequent ingress and egress, and the potential for impacts or abrasions. The material composition, construction techniques, and inherent quality of the sleeping pad directly determine its resistance to these stresses, ultimately dictating its lifespan. A sleeping surface with compromised durability can exhibit premature sagging, loss of support, and structural degradation, potentially leading to discomfort, musculoskeletal issues, and even safety hazards. The practical impact of this on residential, commercial, and institutional levels is significant.
Consider, for example, the use of these sleeping arrangements in a hostel setting. High occupancy rates and frequent turnover place significant demands on the sleeping surfaces. A low-quality mattress may only withstand a year or two of such use, requiring frequent replacements and incurring substantial costs. In contrast, a more durable mattress, constructed with high-density materials and reinforced seams, could last five years or more, representing a considerable cost saving. Further, durability impacts safety. A sagging sleeping surface can create an uneven sleeping plane, increasing the risk of occupants, particularly those on the upper tier, rolling off the edge. The long-term stability of the sleeping surface also depends on the material used. A high-density material will likely provide a better support structure for a longer period of time. A low-density material is highly likely to degrade much more quickly and will negatively affect a user’s quality of sleep.
In conclusion, the durability and lifespan of a sleeping pad utilized within a stacked bed arrangement directly correlate with its cost-effectiveness, safety, and user satisfaction. While initial purchase price is a consideration, prioritizing high-quality materials and robust construction techniques is essential for maximizing long-term value and minimizing the risks associated with premature wear. Challenges arise in accurately assessing durability based solely on product specifications; therefore, consulting independent reviews, seeking expert advice, and verifying certifications are crucial steps in making informed purchasing decisions. Ultimately, investing in a durable sleeping surface translates to a safer, more comfortable, and more sustainable sleeping environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries concerning dimensions and selection criteria for sleeping surfaces intended for stacked sleeping arrangements.
Question 1: Are all “full size” mattresses truly standardized in their dimensions?
While the term “full size” implies standardization (approximately 54 inches wide by 75 inches long), slight variations may exist between manufacturers. It is imperative to verify precise measurements before purchase to ensure proper fit and stability within the bunk bed frame.
Question 2: What is the recommended maximum thickness for a mattress used on the upper bunk?
Maximum mattress thickness is governed by safety standards to maintain adequate guardrail height. Exceeding the recommended thickness compromises the guardrail’s effectiveness and increases the risk of falls. Consult the bunk bed frame manufacturer’s specifications for explicit guidance.
Question 3: How does mattress density affect its suitability for a bunk bed?
Higher density materials offer superior support and resistance to sagging, crucial in bunk bed applications where weight distribution may be concentrated. Lower density mattresses are prone to premature wear and reduced support, compromising comfort and potentially safety.
Question 4: What type of mattress is most suitable for a bunk bed: innerspring, foam, or hybrid?
The optimal mattress type depends on individual preferences and requirements. Innerspring systems offer firm support, foam conforms to body contours, and hybrid models attempt to balance both. Consider the occupant’s weight, sleeping habits, and any pre-existing back conditions.
Question 5: How often should a bunk bed mattress be inspected for wear and tear?
Regular inspections are essential to identify signs of sagging, damage, or structural compromise. A recommended inspection frequency is at least every three months, or more often with heavy use, to ensure safety and prevent accidents.
Question 6: Can any “full size” mattress be used on either the upper or lower bunk?
While dimensions may be compatible, consider weight limitations. Exceeding weight capacities on the upper bunk can compromise structural integrity. Confirm that the mattress and bed frame’s combined weight capacity meets or exceeds the occupant’s weight.
These considerations contribute to a safer and more comfortable sleeping environment. Prioritizing accurate measurements, appropriate density, and adherence to safety guidelines are essential for maximizing the benefits and minimizing the risks associated with stacked sleeping arrangements.
The subsequent section will provide a decision matrix to help with mattress selection.
Concluding Remarks on Bunk Bed Full Size Mattress Selection
The preceding discussion has illuminated critical considerations surrounding the procurement and implementation of standardized bedding dimensions within stacked sleeping configurations. Aspects encompassing dimensional accuracy, material characteristics, adherence to safety protocols, and evaluations of durability have been meticulously explored. Selecting a sleeping surface for these arrangements necessitates a comprehensive understanding of these interrelated factors to ensure both occupant safety and prolonged product performance.
Prudent decision-making in this regard extends beyond mere transactional considerations. It constitutes a commitment to fostering secure and supportive sleeping environments. Individuals are encouraged to rigorously assess their specific needs, meticulously evaluate product specifications, and prioritize compliance with established safety standards. Through diligent research and informed choices, a responsible contribution is made toward the enhancement of well-being within shared living spaces. The lasting benefits of such judicious decisions warrant careful consideration, reflecting a dedication to prioritizing safety and promoting responsible stewardship.


![Best Full Size Daybed with Mattress [Deals] Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Best Full Size Daybed with Mattress [Deals] | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-2863-300x200.jpg)


![Buy the Best Full Futon with Mattress - [Year] Guide Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Buy the Best Full Futon with Mattress - [Year] Guide | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-2858-300x200.jpg)