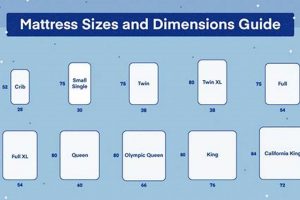
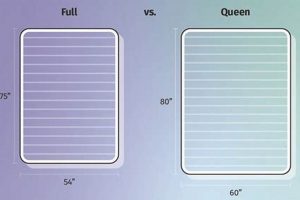
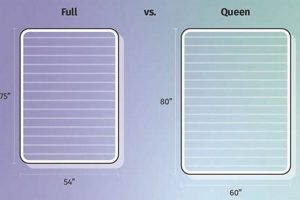
A sleeping surface designed specifically for a two-tiered bed frame that accommodates a 54-inch wide and 75-inch long mattress. This size provides more individual space compared to narrower options, enabling greater comfort for the occupant. Such bedding is often selected when a twin-sized mattress may feel too restrictive, especially for older children or adults.
The utilization of a larger mattress size in these elevated sleeping arrangements is important due to its capacity to enhance sleep quality and overall user satisfaction. Compared to its smaller counterpart, a full mattress offers added room for movement and reduces the feeling of confinement. This contributes to a less restless night’s sleep. Its implementation allows for more comfortable accommodation of a wider range of body sizes and sleep preferences, contributing to an improvement in the overall user experience in shared living spaces, maximizing floor space while not sacrificing sleeping area.
The subsequent sections will delve into the factors to consider when choosing the most appropriate mattress, explore different mattress types available in this specific size, and provide guidelines for ensuring safety and longevity in the context of bunk bed usage.
Considerations for Selecting a Full-Size Bunk Bed Mattress
Selecting an appropriate sleeping surface for a two-tiered bed system requires careful consideration of several factors. Prioritizing safety, comfort, and longevity is paramount to ensuring optimal use and user well-being.
Tip 1: Prioritize Thickness Compatibility: Adhere strictly to the manufacturer’s recommendations regarding maximum mattress thickness. Exceeding the specified limit may compromise the safety rails’ effectiveness, increasing the risk of falls.
Tip 2: Assess Weight Capacity: Verify that the chosen mattress, in conjunction with the user’s weight, does not exceed the bunk bed’s stated weight capacity. Overloading the structure can lead to instability and potential structural failure.
Tip 3: Opt for Low-Profile Options: Consider thinner mattresses to maximize headroom for occupants of the lower bunk. Sufficient space between the lower mattress and the upper bunk’s frame is essential for comfort and ease of movement.
Tip 4: Evaluate Mattress Type: Explore different mattress materials, such as memory foam, innerspring, or latex, based on individual comfort preferences and support needs. Each type offers distinct advantages and disadvantages in terms of pressure relief, temperature regulation, and durability.
Tip 5: Address Support and Firmness: Select a mattress firmness level that adequately supports the user’s weight and sleeping position. Proper spinal alignment is crucial for preventing discomfort and promoting restful sleep.
Tip 6: Prioritize Fire Safety: Look for mattresses that meet or exceed federal fire safety standards. Ensure the product’s labeling clearly indicates compliance with relevant regulations to mitigate fire hazards.
Adhering to these guidelines will facilitate the selection of a suitable mattress, optimizing comfort, safety, and the overall user experience within a bunk bed setting.
The subsequent section will address specific mattress types and their suitability for use in conjunction with bunk bed structures.
1. Thickness compatibility
Thickness compatibility is a critical factor when selecting a sleeping surface for a two-tiered bed. The height of the mattress directly impacts the effectiveness of the safety rails designed to prevent falls from the upper bunk. If the mattress is too thick, it reduces the height of the safety rails, potentially rendering them inadequate. Furthermore, excessive mattress thickness can decrease the available headroom for occupants on the upper bunk, leading to discomfort and increased risk of head injuries. For example, a bunk bed designed for a maximum 8-inch mattress will be unsafe if paired with a 12-inch model.
Adhering to the manufacturer’s specified thickness limits is essential. Bunk bed manufacturers design their products with particular mattress dimensions in mind, factoring in rail height, structural integrity, and overall safety. Using a mattress that exceeds these specifications compromises the engineered safety features of the bed frame. Consider a scenario where a child, accustomed to a higher safety rail, inadvertently rolls off a bunk bed because the reduced rail height offers insufficient protection. This illustrates the practical importance of matching the sleeping surface’s depth to the frame’s requirements.
In summary, prioritizing thickness compatibility when choosing a sleeping surface ensures the safety and usability of bunk beds. Failure to do so can negate the intended safety measures, leading to potential accidents and diminished user comfort. Strict adherence to manufacturer guidelines regarding mattress thickness is paramount.
2. Weight Capacity
The weight capacity of a bunk bed system is directly and significantly impacted by the sleeping surface chosen. The weight of the mattress, when combined with the weight of the occupant, must remain within the manufacturer-specified limits to ensure structural integrity and user safety. Exceeding the designated capacity creates a risk of catastrophic failure, potentially leading to injury. A heavier mattress, although possibly providing enhanced comfort, contributes to the overall load on the frame, reducing the allowable weight for the individual using the bed.
For instance, consider a bunk bed with a stated weight limit of 250 pounds per bunk. If the mattress weighs 50 pounds, the maximum permissible weight of the occupant is reduced to 200 pounds. The implementation of a heavier mattress, such as a thick memory foam model, could further decrease this allowable occupant weight. This necessitates careful consideration of mattress weight during the selection process. Weight limits are often clearly marked on bunk bed frames, and compliance with these limits is paramount for safe operation. Regular inspections of the bed frame for signs of stress or damage are advisable, particularly in situations where heavier mattresses are utilized.
In summary, understanding and adhering to weight capacity limitations is crucial when selecting a sleeping surface for a bunk bed. The combined weight of the mattress and the user should always remain within the manufacturer’s specified limits to prevent structural failure and ensure the safety of the occupants. Vigilance and adherence to these guidelines are essential for maintaining a safe and reliable bunk bed system.
3. Low Profile
The concept of “low profile” is intrinsically linked to the safe and functional implementation of a full-sized sleeping surface in a two-tiered bed arrangement. Mattress thickness directly affects the remaining height of the safety rails surrounding the upper bunk. A mattress that is excessively thick reduces the protective barrier, increasing the risk of falls. Low-profile mattresses mitigate this hazard by maximizing the available height of the safety rails. Furthermore, diminished vertical space between the upper and lower bunks necessitates a thinner mattress to ensure adequate headroom for occupants on the lower level, preventing discomfort and potential head injuries. For example, a low-profile, six-inch mattress on the upper bunk of a standard bunk bed provides significantly more rail height protection than a standard ten-inch mattress.
The implementation of a low-profile design is not merely a matter of comfort; it is a critical safety consideration. Building codes and bunk bed safety standards often stipulate minimum safety rail heights above the sleeping surface. Failure to adhere to these standards can result in non-compliance and increased liability. Furthermore, many residential settings require bunk beds to fit within specific room dimensions. A thicker mattress, combined with a standard-height bunk bed frame, may result in the overall structure exceeding the available vertical space. This is often observed in older homes or apartments with lower ceiling heights. The integration of a thinner mattress is essential for addressing space constraints while maintaining the integrity of the sleeping arrangement.
In summary, the utilization of a low-profile mattress is a pragmatic and often essential component of deploying a full-sized mattress on a bunk bed. It directly influences safety, comfort, and compliance with building standards. Ignoring this aspect can compromise the protective function of the safety rails, diminish headroom, and potentially violate safety regulations. Therefore, careful consideration of mattress thickness is paramount when setting up a bunk bed system.
4. Mattress Type
The selection of a mattress type for a bunk bed is intrinsically linked to the overall safety, comfort, and longevity of the sleeping arrangement. Given the space constraints inherent in bunk bed design, the choice of mattress material and construction directly impacts factors such as weight, thickness, and support, all of which are critical for optimizing the user experience and minimizing potential hazards. For instance, a heavy innerspring mattress might exceed the weight capacity of the bunk bed frame, while a thick memory foam mattress could compromise the height of the safety rails on the upper bunk. Thus, the mattress type acts as a foundational component in determining the suitability of a particular mattress for two-tiered bed systems. In this context, a bunk bed mattress full refers to a mattress of a specific dimension intended for that purpose. The appropriateness of different mattress types becomes a prime consideration.
Various mattress types offer distinct advantages and disadvantages in the bunk bed context. Memory foam mattresses, known for their pressure-relieving properties, can provide a comfortable sleeping surface but may retain heat, potentially causing discomfort in warmer environments. Innerspring mattresses, while generally more affordable, may lack the conforming support of memory foam and can be heavier. Latex mattresses offer a balance of support and breathability but tend to be more expensive. Hybrid mattresses, combining elements of both innerspring and foam construction, attempt to offer the benefits of both types while mitigating their respective drawbacks. The selection process should also incorporate the bunk bed user’s specific needs and preferences. A lighter child may require a softer mattress for adequate pressure relief, while a heavier adult may need a firmer mattress for proper spinal alignment.
Ultimately, the optimal mattress type for a bunk bed is contingent upon a careful evaluation of various factors, including weight limitations, safety requirements, comfort preferences, and budget considerations. No single mattress type is universally ideal; rather, the most appropriate choice is one that effectively balances these competing demands while ensuring a safe, comfortable, and supportive sleeping environment. This emphasizes the importance of aligning the mattress type with the specific dimensions and limitations inherent in using a “bunk bed mattress full” system.
5. Support & Firmness
The characteristics of support and firmness are integral to the selection of a suitable sleeping surface for a two-tiered bed. In the context of a “bunk bed mattress full,” these attributes directly influence spinal alignment, pressure distribution, and overall user comfort. Insufficient support can lead to spinal misalignment, potentially resulting in back pain or discomfort. Conversely, a mattress lacking appropriate firmness may not adequately distribute weight, leading to pressure points and restless sleep. As a component of a full mattress intended for bunk bed usage, the selection of proper support and firmness is not merely a matter of preference, but a critical factor in promoting physical well-being. For example, a child sleeping on a full-sized mattress lacking adequate support may experience chronic back pain, directly impacting their quality of life. An adult on the same sleeping arrangement could experience similar issues. The practical significance of understanding the interplay between support, firmness, and the “bunk bed mattress full” concept is therefore underscored by its potential impact on long-term health.
Different mattress types offer varying levels of support and firmness. Innerspring mattresses typically provide firmer support, while memory foam mattresses conform to the body’s contours, offering a softer feel and pressure relief. Hybrid mattresses often attempt to combine the benefits of both types. The user’s weight, sleeping position, and any pre-existing medical conditions should inform the selection process. A heavier individual may require a firmer mattress to prevent excessive sinking, while a side sleeper may benefit from a softer mattress that cushions the shoulders and hips. The dimensions of the “bunk bed mattress full” format do not negate the importance of individualized support; rather, they emphasize the need for careful consideration given the potentially limited space and the shared nature of bunk bed accommodations.
In summary, the attributes of support and firmness are paramount when choosing a mattress for a two-tiered bed. The proper combination promotes spinal alignment, pressure distribution, and overall user comfort. The potential challenges include navigating the diverse range of mattress types and balancing individual preferences with the constraints of bunk bed usage. Understanding the connection between support, firmness, and the specific requirements of a “bunk bed mattress full” is therefore critical for ensuring a safe, comfortable, and supportive sleeping environment. Failing to prioritize these factors can negatively impact the user’s health and well-being.
6. Fire Safety
The integration of stringent fire safety standards is paramount when considering the use of a “bunk bed mattress full.” Mattresses, due to their composition of flammable materials such as cotton, foam, and synthetic fibers, pose a significant fire hazard if ignited. The confined space within a bunk bed arrangement exacerbates this risk, potentially impeding egress and increasing the severity of any fire. For example, a smoldering cigarette left unattended on a mattress can quickly escalate into a full-blown fire, generating toxic fumes and posing a direct threat to occupants. The selection of mattresses that meet or exceed established fire safety regulations, therefore, becomes a critical component of mitigating these risks within the context of a bunk bed environment. In this case, a mattress that is deemed “bunk bed mattress full” must also abide by applicable fire safety guidelines.
Federal regulations, such as those outlined in the Consumer Product Safety Commission’s (CPSC) standards for mattress flammability, mandate that all mattresses sold in the United States must meet specific burn-resistance criteria. These regulations are designed to delay ignition and slow the spread of flames, providing occupants with valuable time to escape in the event of a fire. Flame-retardant treatments, such as borate-based chemicals or inherently flame-resistant fibers, are commonly employed in mattress construction to achieve compliance with these standards. The implementation of such fire-resistant properties is of particular importance in bunk bed settings where children or individuals with limited mobility may be present. The mattress itself could be constructed so that, if it were to burn, it would release fewer toxic fumes. For a “bunk bed mattress full” selection, checking such ratings might be a safety-conscientious selection.
In summary, the relationship between fire safety and the selection of a “bunk bed mattress full” is a critical consideration. Compliance with fire safety regulations, achieved through the use of flame-retardant materials and rigorous testing, is essential for minimizing the risk of fire-related injuries and fatalities. Challenges include ensuring continued compliance with evolving safety standards and educating consumers about the importance of selecting fire-safe mattresses. Recognizing the potential hazards associated with mattress flammability and prioritizing fire safety is an integral aspect of creating a safe and secure sleeping environment within the confines of a bunk bed arrangement.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries and misconceptions regarding the selection and use of full-size mattresses specifically designed for bunk bed configurations. The following questions and answers are intended to provide clarity and guidance for safe and informed decision-making.
Question 1: What are the standard dimensions of a “bunk bed mattress full”?
A mattress designated as “full” for bunk bed use typically measures 54 inches in width and 75 inches in length. Variations may occur based on manufacturer specifications, but these dimensions are generally consistent.
Question 2: Is a box spring required for a “bunk bed mattress full”?
A box spring is generally not required for bunk bed mattresses. Most bunk beds are designed with a built-in support system, such as slats or a metal grid, which provides adequate support for the mattress.
Question 3: What is the recommended maximum thickness for a “bunk bed mattress full” to ensure safety rail effectiveness?
The recommended maximum thickness varies depending on the bunk bed frame. Adhering to the manufacturer’s specified limit is crucial. A general guideline is to maintain a mattress thickness that does not reduce the safety rail height below the minimum required safety standard, commonly around 5 inches above the mattress surface.
Question 4: How does the weight of a “bunk bed mattress full” affect the bunk bed’s overall weight capacity?
The weight of the mattress contributes to the total weight load on the bunk bed frame. Ensure that the combined weight of the mattress and the intended occupant does not exceed the bunk bed’s stated weight capacity to prevent structural failure.
Question 5: Are there specific fire safety certifications to look for when purchasing a “bunk bed mattress full”?
It is important to select mattresses that meet federal flammability standards, such as those outlined in 16 CFR Part 1633. Look for labels indicating compliance with these regulations to ensure fire safety.
Question 6: What type of mattress is best suited for a “bunk bed mattress full” considering both comfort and safety?
The ideal mattress type depends on individual preferences and the bunk bed’s specifications. Low-profile memory foam or hybrid mattresses are often suitable due to their balance of comfort, support, and manageable thickness. However, always prioritize safety considerations, such as thickness and weight limits, over personal preferences.
These FAQs provide essential information to guide the selection process. Careful consideration of these points ensures a safe and comfortable sleeping environment within the context of a bunk bed configuration.
The subsequent section will provide a summary and key takeaways from this article.
Conclusion
This exploration of “bunk bed mattress full” underscored the importance of considering dimensional compatibility, weight limitations, material composition, and regulatory compliance. Safe and appropriate selection of the mattress is paramount for bunk bed function, accounting for thickness, weight, occupant requirements, and applicable fire safety standards. These elements interact to either ensure or compromise the intended safety and utility of a bunk bed system.
Given the potential for serious injury resulting from improper selection or installation, adherence to manufacturer guidelines and relevant safety regulations is essential. Thoughtful and informed decision-making, rather than prioritizing cost or convenience, must guide the selection and maintenance of mattresses used in bunk bed configurations. Continued awareness and scrutiny are vital for fostering a safe and functional sleeping environment.