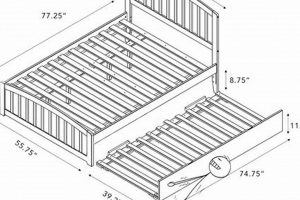
A sleeping arrangement featuring one bed frame stacked atop another, typically incorporating the sleeping surfaces themselves. This configuration is often selected to maximize floor space, particularly in shared bedrooms or smaller living quarters. An example would be a twin-over-twin model, suitable for children, equipped with two separate innerspring units.
These elevated sleeping systems offer several advantages. They can significantly increase usable area in a room, allowing for additional furniture or play space. Historically, such structures have been employed in settings like dormitories, ships, and military barracks where space is limited. Their adoption in private residences reflects a similar need for spatial efficiency, especially in urban environments or homes with multiple occupants.
The subsequent sections will delve into the diverse array of designs available, considerations for safety and construction, and factors influencing the selection of a suitable unit for a specific purpose. Further discussion will explore aspects like materials, dimensions, weight capacity, and the compatibility of various support surfaces, providing a detailed overview of this type of furniture.
Considerations for Elevated Sleeping Structures
Proper selection and implementation of a stacked bed frame and sleeping surface are essential for safety and longevity. The following points should be carefully considered prior to purchase and during assembly.
Tip 1: Assess Spatial Requirements: Prior to acquisition, meticulously measure the intended location. Account for vertical clearance, especially the distance between the top sleeping surface and the ceiling. Insufficient headroom can create discomfort and potential safety hazards. For example, a low ceiling may restrict movement and impede egress.
Tip 2: Verify Structural Integrity: Examine the frame’s construction. Steel or solid hardwood are preferable to particleboard or less robust materials. Ensure all joints are securely fastened and free from defects. A visual inspection and a review of the manufacturers specifications are critical steps.
Tip 3: Evaluate Support Surface Compatibility: Confirm that the chosen sleeping surface is appropriate for the frame’s design. Overly thick units may reduce safety rail height, while excessively thin units may compromise comfort and support. Adherence to the manufacturers recommendations is paramount.
Tip 4: Prioritize Safety Features: Examine the presence and adequacy of safety rails on the upper sleeping surface. Rails should extend sufficiently above the upper sleeping surface to prevent accidental falls. Consider models with integrated ladders or stairs designed for secure ascent and descent.
Tip 5: Adhere to Weight Limits: Scrupulously observe the weight capacity specified by the manufacturer. Exceeding these limits can compromise the frame’s structural integrity and potentially lead to collapse. Clearly communicate these limitations to all users, especially in shared living spaces.
Tip 6: Regular Maintenance is Crucial: Routinely inspect all fasteners and connections, ensuring they remain tight and secure. Promptly address any signs of wear, damage, or instability. This preventative maintenance will help to maintain the units safety and extend its service life.
Tip 7: Choose a Suitable Mattress Type: Consider the occupant’s needs and preferences when selecting the sleeping surface. Foam, innerspring, or hybrid units offer different levels of support and comfort. Ensure that the unit selected meets safety regulations regarding flammability and composition.
By carefully considering these points, a suitable stacked bed frame and sleeping surface can be selected and implemented safely and effectively. Attention to detail during purchase, assembly, and maintenance will contribute to a safe and comfortable sleep environment.
The following sections will discuss the different types of units available in the market and additional considerations for longevity and care.
1. Space Optimization
The inherent design of superimposed sleeping platforms directly addresses the challenge of restricted spatial availability. A “bunk bed with mattress” effectively doubles the sleeping capacity within a single floor area compared to two individual beds. This vertical arrangement is a primary driver for its adoption in environments where floor space is at a premium, such as shared bedrooms, dormitories, and small apartments. The resultant effect is the freeing up of valuable square footage for alternative uses, such as study areas, play spaces, or additional storage. For instance, in a small children’s bedroom, eliminating the footprint of a second single bed allows for the inclusion of a desk and chair, thereby enhancing the room’s functionality.
The importance of space optimization as a core characteristic of the elevated sleeping structure is further exemplified by variations in design that maximize efficiency. Models incorporating built-in drawers, shelves, or even entire workspaces beneath the upper level represent a continued evolution towards integrated solutions. Consider the modern micro-apartment, where every square inch is deliberately utilized; the selection of a “bunk bed with mattress” incorporating storage effectively reduces the need for separate chests of drawers or shelving units, streamlining the living space and improving overall organization. The practical significance lies in its capacity to enhance the quality of life in constrained environments.
In summary, the relationship between space optimization and the structure in question is one of fundamental cause and effect. The inherent design capitalizes on vertical space to conserve floor area, yielding increased functionality and versatility within the room. While challenges exist, such as accessibility for certain users and potential feelings of confinement, the benefits of maximized space often outweigh these drawbacks, solidifying its role in contemporary residential and institutional settings.
2. Structural Safety
The inherent vertical configuration of a “bunk bed with mattress” necessitates a robust structural design to ensure occupant safety. Unlike a standard single bed, this elevated system bears increased weight loads and introduces potential fall hazards, thus rendering structural integrity a paramount consideration.
- Material Composition
The selection of materials significantly impacts the overall structural robustness. Solid hardwoods and steel alloys offer superior strength and durability compared to composite materials like particleboard. For instance, a frame constructed from heavy-gauge steel is more resistant to deformation under stress and provides enhanced protection against catastrophic failure. The materials ability to withstand prolonged use and varying weight distributions
is crucial for maintaining safety over time. - Joint Integrity
The points where individual components connect represent critical areas of potential weakness. Joints should be meticulously engineered and reinforced to prevent loosening or separation. Examples include bolted connections with locking mechanisms, welded joints that create a seamless bond, or mortise-and-tenon joinery known for its inherent strength. Inadequate joint integrity can lead to instability and increase the risk of collapse, particularly under dynamic loads.
- Load-Bearing Capacity
Each “bunk bed with mattress” possesses a specified maximum weight capacity that must be strictly adhered to. Exceeding this limit can compromise the frame’s structural integrity and lead to catastrophic failure. Clear and conspicuous labeling of the weight capacity is essential for informing users of these limitations. Consider a scenario where multiple individuals occupy the upper bunk simultaneously, exceeding the designed load; the resulting stress could cause structural damage or collapse.
- Guardrail Design and Height
Effective guardrails are essential for preventing falls from the upper sleeping surface. These rails must extend sufficiently above the top of the “mattress” to provide adequate protection. Building codes and safety standards often specify minimum guardrail heights to mitigate fall risks. Inadequate guardrail height or spacing can create opportunities for accidental falls, particularly for restless sleepers or young children.
These facets underscore the criticality of structural safety in the design and implementation of “bunk bed with mattress” configurations. Compliance with relevant safety standards, rigorous testing protocols, and responsible user practices are vital for ensuring the well-being of occupants and preventing accidents. The selection of a unit should prioritize demonstrable structural integrity over purely aesthetic considerations, recognizing that safety is the foremost concern.
3. Mattress Compatibility
Mattress compatibility is a crucial element in the effective and safe utilization of a “bunk bed with mattress”. The relationship between the support surface and the frame is interdependent; the chosen mattress directly influences the safety, comfort, and longevity of the entire sleeping system. The intended mattress dimensions, thickness, and weight characteristics must align with the specific design parameters of the elevated bed frame. For instance, an overly thick mattress, although potentially providing increased comfort, may reduce the effective height of the safety rails on the upper bunk, thereby increasing the risk of falls. Similarly, an excessively heavy mattress could exceed the weight capacity of the bed frame, compromising its structural integrity and stability. This alignment is not merely a matter of dimensional fit; it extends to ensuring the chosen support surface complies with safety regulations, particularly regarding flammability and material composition. A practical example illustrates this point: Selecting a low-profile foam mattress specifically designed for bunk beds guarantees adequate safety rail height and reduces the overall weight load on the frame.
Further considerations extend beyond basic fit and weight. The mattress type whether innerspring, foam, or hybrid influences the overall comfort and support provided. Innerspring mattresses offer traditional support but may be heavier than foam options. Foam mattresses, conversely, are often lighter and conform more closely to the body, but may retain more heat. The frame construction itself also plays a role in mattress selection. Some frames are designed to accommodate specific mattress types, featuring slatted supports that provide adequate ventilation or reinforced edges to prevent sagging. The lack of such considerations can lead to premature mattress wear or an uncomfortable sleep experience. As an illustration, a memory foam mattress placed on a solid, non-ventilated surface may trap moisture, fostering mold growth and reducing the mattress’s lifespan.
In summary, mattress compatibility is not a peripheral concern but an integral aspect of “bunk bed with mattress” selection and utilization. Neglecting this critical element can compromise safety, comfort, and the overall lifespan of the sleeping arrangement. Adhering to manufacturer recommendations, considering mattress type and weight, and ensuring compliance with safety standards are essential steps in optimizing the performance and safety of this space-saving furniture solution. The selection process necessitates a holistic approach, recognizing that the frame and mattress function as a cohesive system, where the characteristics of one element directly impact the efficacy of the other.
4. Ladder/Stair Design
The design of the access mechanism, whether a ladder or stairs, is an integral component of a “bunk bed with mattress,” directly influencing user safety and accessibility. The configuration of the ladder or stairs dictates the ease and security with which an individual can ascend and descend from the upper bunk, particularly significant for children and the elderly. A poorly designed access point increases the risk of falls and injuries, thereby negating the space-saving benefits if safety is compromised. For instance, a ladder with narrow rungs and a steep angle presents a higher risk of slipping, especially during nighttime use. Conversely, stairs with wider treads and a shallower incline provide a more stable and secure means of access, reducing the likelihood of accidents. The connection is causal: the design of the ladder or stairs directly impacts the probability of safe and comfortable usage of the upper bunk. The integration of handrails further enhances safety and provides additional support during ascent and descent.
The selection of ladder versus stairs often depends on the available space and the intended user demographics. Ladders generally require less floor space, making them suitable for smaller rooms. However, stairs offer greater stability and can incorporate built-in storage, maximizing utility. The practical application of understanding this connection involves carefully evaluating the specific needs of the user and the spatial constraints of the room. For example, if the “bunk bed with mattress” is intended for young children, stairs with a robust handrail and non-slip treads are the preferred choice. Alternatively, in a cramped dormitory setting where space is limited, a ladder with wide, contoured rungs might be a more practical solution, balancing space efficiency with acceptable levels of safety. Material choice also plays a role; wooden ladders can splinter, whereas metal ladders may become slippery if not properly textured.
In summary, the ladder or stair design is not a mere afterthought but a critical factor in the overall safety and usability of a “bunk bed with mattress.” The design must prioritize safety, accessibility, and user comfort, taking into account the specific spatial constraints and the intended user population. The challenge lies in balancing space efficiency with safety considerations, ensuring that the access mechanism provides a secure and comfortable means of accessing the upper bunk. Neglecting this critical element can significantly increase the risk of accidents and injuries, undermining the intended benefits of the space-saving design.
5. Weight Capacity
h3>
Weight capacity is a critical specification for a “bunk bed with mattress,” representing the maximum load the structure can safely support. Exceeding this limit poses a significant risk of structural failure, potentially leading to collapse and serious injury. The weight capacity is not an arbitrary figure; it is derived from engineering calculations based on the materials used, the design of the frame, and the integrity of the joints. For example, a “bunk bed with mattress” constructed from heavy-gauge steel will typically have a higher weight capacity than one made from particleboard. The importance of adhering to the specified weight capacity cannot be overstated; it is directly linked to the safety and well-being of the occupants. A real-life scenario might involve multiple children simultaneously occupying the upper bunk, inadvertently exceeding the weight limit and placing undue stress on the frame. Understanding and respecting the weight capacity is, therefore, of paramount practical significance.
Further considerations extend beyond the static weight of the occupants. Dynamic loads, such as jumping or sudden movements, exert significantly greater forces on the structure. The weight capacity rating typically accounts for these dynamic loads, but it is still imperative to discourage activities that could subject the bed to excessive stress. Moreover, the weight distribution across the sleeping surface also plays a role. Uneven weight distribution can concentrate stress on specific points of the frame, potentially compromising its integrity even if the total weight is within the specified limit. Regularly inspecting the frame for signs of stress, such as bending or cracking, is essential for identifying potential problems before they escalate. A practical application involves ensuring that the mattress is properly supported by the frame to distribute weight evenly and prevent localized stress concentrations.
In summary, weight capacity is not merely a technical specification but a fundamental safety parameter for any “bunk bed with mattress”. Adhering to the manufacturer’s stated weight limits, accounting for dynamic loads, and ensuring proper weight distribution are essential practices for maintaining the structural integrity of the unit and preventing accidents. The challenge lies in effectively communicating these limitations to all users, particularly in shared living spaces or children’s bedrooms, and ensuring that responsible usage is consistently practiced. Recognizing the inherent relationship between weight capacity and safety is crucial for maximizing the benefits of space-saving furniture while minimizing the risks associated with its use.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries and clarifies potential misconceptions regarding the selection, installation, and safe utilization of superimposed sleeping structures incorporating sleeping surfaces.
Question 1: What are the primary safety considerations when purchasing a bunk bed with mattress?
Key safety factors include adherence to weight capacity limits, the presence of adequate safety rails on the upper bunk, a sturdy ladder or stair design with non-slip treads, and ensuring the unit complies with relevant safety standards, such as those pertaining to flammability.
Question 2: How does mattress thickness affect the safety of a bunk bed?
Mattress thickness directly impacts the height of the safety rails above the sleeping surface. An overly thick mattress reduces this height, potentially compromising the effectiveness of the rails in preventing falls. Manufacturer guidelines regarding maximum mattress thickness should be strictly observed.
Question 3: What materials are recommended for bunk bed construction?
Solid hardwoods, steel alloys, and engineered wood products with high structural integrity are preferable. Materials should be durable, resistant to deformation under stress, and free from defects that could compromise safety. Avoid particleboard and less robust materials.
Question 4: How should a bunk bed be properly maintained?
Regular inspection of all fasteners and connections is essential to ensure they remain tight and secure. Any signs of wear, damage, or instability should be addressed promptly. Periodic cleaning and adherence to manufacturer’s instructions regarding care are also recommended.
Question 5: Are there specific age recommendations for using the upper bunk of a bunk bed?
Safety guidelines typically advise against allowing children under the age of six to use the upper bunk due to the increased risk of falls. Older children should be instructed on safe climbing practices and the importance of not engaging in rough play on or around the bunk bed.
Question 6: Can a bunk bed with mattress be disassembled and reassembled multiple times?
The ability to disassemble and reassemble a bunk bed depends on the design and construction. Repeated disassembly and reassembly can weaken joints and compromise structural integrity. It is advisable to minimize disassembly and to carefully follow manufacturer instructions if disassembly is necessary.
In summary, responsible selection, installation, and maintenance are essential for ensuring the safe and effective use of superimposed sleeping structures. Understanding and adhering to safety guidelines is paramount for minimizing the risk of accidents.
The subsequent section will explore design trends and emerging innovations within the realm of elevated sleeping platforms.
Concluding Remarks
The preceding analysis has explored critical facets of the “bunk bed with mattress” arrangement. Emphasis has been placed on safety considerations, encompassing structural integrity, mattress compatibility, and access mechanism design. Weight capacity adherence and regular maintenance were identified as paramount for long-term safe operation. Space optimization benefits and typical application scenarios were also outlined to provide a comprehensive understanding of this particular furniture configuration.
Ultimately, responsible selection and implementation of a “bunk bed with mattress” are essential. The information presented serves to underscore the significance of informed decision-making. Continued vigilance regarding safety standards and user education remains crucial for maximizing the benefits of this space-saving solution while mitigating potential risks. Future advancements may further enhance safety features and optimize space utilization within superimposed sleeping structures, warranting ongoing evaluation and adaptation of best practices.