A sleeping platform typically designed for young children, intended for use in a raised, multi-tiered bed frame, is a common element in shared or compact living spaces. This supportive surface must adhere to specific safety standards, considering the elevated nature of the structure. Dimensions are usually standardized to fit compatible frames, prioritizing the occupant’s protection.
The utilization of this bedding solution offers multiple advantages. It can efficiently maximize floor space, making it ideal for smaller rooms. Historically, similar structures have been used in dormitories and other communal living arrangements. The safety and well-being of the child using this sleeping arrangement are paramount, requiring careful construction and adherence to safety regulations.
The following sections will delve into the various types available, safety considerations, and factors to consider when selecting appropriate bedding for this unique sleeping arrangement. Topics such as material composition, size compatibility, and safety certifications will be discussed to provide a thorough understanding.
Guidance for Selecting Appropriate Bedding
The selection of suitable bedding for elevated sleeping structures requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure occupant safety and comfort.
Tip 1: Confirm Dimensional Compatibility: Prior to purchase, verify that the mattress dimensions precisely match the internal frame measurements. Gaps between the mattress and the frame pose a potential entrapment hazard.
Tip 2: Adhere to Thickness Restrictions: Bunk structures often have maximum height restrictions for the mattress. Exceeding this limit can compromise safety railing effectiveness and increase the risk of falls.
Tip 3: Prioritize Safety Certifications: Seek products that have been certified by recognized safety organizations, indicating compliance with relevant safety standards and regulations.
Tip 4: Evaluate Material Composition: Consider the materials used in construction, favoring options that are hypoallergenic, non-toxic, and resistant to dust mites and other allergens.
Tip 5: Assess Support and Firmness: The chosen mattress should provide adequate support and firmness for the occupant’s weight and developmental stage. Overly soft surfaces can present suffocation risks for infants.
Tip 6: Consider Fire Resistance: Ensure that the selected mattress meets fire safety standards, as this is a critical safety feature in any sleeping environment.
Tip 7: Inspect for Durability: Assess the overall construction and materials for durability to ensure the mattress maintains its shape and support over time, resisting sagging or compression.
By adhering to these guidelines, a safe and comfortable sleeping environment can be established within an elevated bedding system.
The following sections will examine frequently asked questions and address common concerns related to these specific types of bedding solutions.
1. Dimensions
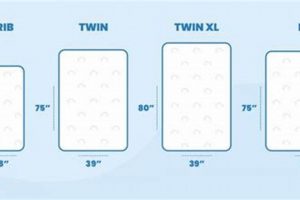
The dimensions of a sleeping surface for a tiered sleeping structure are paramount to its safe and effective operation. Specifically, the length and width must precisely correspond with the internal measurements of the frame intended for its use. A surface that is too small creates dangerous gaps where a child could become entrapped, leading to potential injury or suffocation. Conversely, a sleeping surface that is too large may be difficult to install correctly, potentially compromising the structural integrity of the entire sleeping structure. For instance, consider a scenario where the dimensions of the sleeping surface are several centimeters less than the frame. This creates a hazardous space where a limb or other body part could become lodged.
Furthermore, the thickness or height dimension is also critical. Many such sleeping structures have a maximum height limit, typically indicated by a line on the guardrail. If the sleeping surface exceeds this height, the effectiveness of the guardrail is significantly reduced, increasing the risk of falls. This is particularly relevant given that these sleeping structures are often used by children who may not yet possess mature motor skills or awareness of heights. A common issue arises when parents replace the originally supplied sleeping surface with a thicker, more comfortable one, without considering the height restriction. Such a modification can inadvertently negate the safety features of the structure, leading to a dangerous situation.
In summary, precise dimensions are an essential and non-negotiable aspect of elevated children’s sleeping surfaces. Incorrect dimensions can have severe safety consequences, undermining the intended protective function of the entire structure. Accurate measurement and adherence to manufacturer specifications are crucial steps in ensuring a safe sleeping environment. Prioritizing dimensional accuracy during selection and installation is therefore a fundamental responsibility for caregivers.
2. Safety Standards
Compliance with established safety standards is a fundamental aspect of design, manufacture, and use of sleeping surfaces in elevated, tiered beds. These standards are not arbitrary regulations but rather reflect a comprehensive understanding of potential hazards associated with such configurations, particularly when intended for young children. The cause-and-effect relationship is clear: substandard manufacturing or design, failing to meet established safety protocols, directly increases the risk of injury, including falls, entrapment, and suffocation.
Real-world examples illustrate the practical significance of these standards. The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) provides standards such as ASTM F1821, specifically addressing requirements for bunk beds. These standards mandate features like guardrail height, spacing between bed components to prevent entrapment, and ladder design to minimize falls. Failure to adhere to these guidelines has demonstrably led to incidents of serious injury and even death. The Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) also plays a vital role, recalling products that fail to meet safety regulations. The practical application involves rigorous testing during manufacturing and ongoing monitoring of product safety in the market. Without this adherence, the inherent risks associated with tiered beds, particularly for younger occupants, become unacceptably high.
In summary, safety standards are not merely a checklist item, but a critical component embedded in every facet of the sleeping surfaces. They mitigate identifiable risks and are essential for protecting children who use these beds. Challenges remain in ensuring universal compliance and raising awareness among consumers about the importance of verifying adherence to recognized safety certifications. The commitment to these standards directly translates to the well-being and safety of children within the domestic environment.
3. Material Composition
Material composition is a crucial consideration when selecting bedding for a tiered sleeping structure. The materials used directly impact safety, comfort, durability, and potential health risks for the child occupant.
- Flammability Resistance
Materials used in the construction of these mattresses must comply with flammability standards. Polyurethane foam, often used as a core material, typically requires the addition of flame retardants to meet these standards. However, the specific type and quantity of these retardants are significant. Certain chemicals, previously common, have been linked to potential health concerns, leading to a preference for alternatives with documented safety profiles. Natural fibers, such as wool, offer inherent flame resistance, presenting a viable alternative but often at a higher cost.
- Allergenicity and Toxicity
The choice of materials directly affects allergen exposure. Synthetic materials may off-gas volatile organic compounds (VOCs), potentially irritating respiratory systems. Hypoallergenic materials, such as organic cotton or latex, are often favored to minimize these risks. The presence of phthalates, lead, and other heavy metals must also be considered. Certifications like GREENGUARD Gold ensure that a product has been tested for low chemical emissions, contributing to a healthier indoor environment.
- Support and Durability
Core materials contribute significantly to support and durability. High-density foam provides more robust support and resists compression over time compared to lower-density options. Innerspring designs, while less common in modern sleeping surfaces for tiered beds due to weight considerations, offer a different type of support. The cover material also plays a role in durability. Tightly woven fabrics resist tearing and abrasion, extending the lifespan of the product.
- Breathability and Temperature Regulation
The breathability of materials influences temperature regulation. Poorly breathable materials can trap heat and moisture, leading to discomfort and potentially creating an environment conducive to microbial growth. Natural fibers, such as cotton and wool, generally offer better breathability compared to synthetic alternatives. Open-cell foam structures also enhance air circulation, contributing to a more comfortable sleeping environment.
Considering these facets of material composition is essential for making informed decisions when selecting a sleeping surface for a tiered bed. Prioritizing materials that are flame-resistant, hypoallergenic, durable, and breathable directly contributes to the safety, comfort, and overall well-being of the child using the structure. The selection of appropriate materials mitigates potential health risks and maximizes the longevity of the product, representing a significant investment in the child’s sleeping environment.
4. Support Firmness
The degree of resistance a sleeping surface offers to pressure, particularly in the context of a tiered structure, is a critical factor influencing safety and developmental well-being. Appropriate firmness for a structure designed for young children differs significantly from that suitable for an adult. This difference is not merely a matter of comfort; it directly affects the risks of suffocation, proper spinal alignment, and healthy skeletal development.
- Infant Suffocation Risk
An excessively soft sleeping surface presents a significant suffocation hazard for infants. Young children lack the motor skills to reposition themselves if their face becomes pressed against a yielding surface, obstructing their airways. Guidelines from pediatric medical organizations recommend a firm surface to minimize this risk. Real-world examples reveal instances where infants have suffocated on overly plush surfaces, underscoring the critical importance of adhering to firmness recommendations.
- Spinal Alignment and Development
Proper spinal alignment is essential for healthy skeletal development, especially during early childhood. A surface that lacks adequate support can lead to misalignment, potentially causing discomfort and long-term postural issues. The firmness should provide sufficient resistance to maintain the child’s spine in a neutral position, preventing excessive curvature or strain. This is particularly relevant for the developing spines of infants and toddlers.
- Weight Distribution and Durability
The firmness of the core material affects weight distribution and overall durability. A denser, firmer core distributes weight more evenly, preventing localized sagging and maintaining its shape over time. This is important because uneven surfaces can create pressure points, leading to discomfort and disrupting sleep. A more durable mattress also represents a better long-term investment, as it is less likely to require premature replacement.
- Age and Developmental Appropriateness
The ideal firmness level varies with the child’s age and developmental stage. Infants require a firm surface, as previously noted, while toddlers and older children may benefit from a slightly more yielding surface that still provides adequate support. Considerations include the child’s weight, sleeping position, and any specific medical conditions that may affect spinal alignment or comfort. Selecting a surface with appropriate firmness is a key factor in promoting restful sleep and healthy development.
In summary, the firmness of a sleeping surface in a tiered sleeping structure is not a mere comfort preference but a critical safety and developmental consideration. Factors such as infant suffocation risk, spinal alignment, weight distribution, and age-appropriateness must be carefully evaluated to ensure a safe and supportive sleeping environment. Choosing a mattress with appropriate firmness contributes to the overall health and well-being of the child occupant, mitigating potential hazards and promoting optimal development.
5. Height Restriction
Height restriction, in the context of tiered sleeping structures for young children, constitutes a critical safety parameter. It defines the maximum permissible thickness of the bedding, directly influencing the effectiveness of safety barriers and fall prevention measures. Ignoring this restriction can negate the intended safety design, increasing the risk of injury.
- Guardrail Effectiveness
The primary function of guardrails is to prevent occupants from falling from the elevated sleeping surface. Exceeding the specified height restriction for the bedding effectively lowers the guardrail’s protective barrier. For instance, a guardrail designed to extend 5 inches above the sleeping surface could be rendered ineffective if a bedding surface significantly increases the overall height. This compromises the occupant’s safety, especially during sleep when awareness is diminished.
- Ladder Safety
The position and angle of the ladder are calibrated to ensure safe access to and egress from the upper sleeping surface. Increasing the height of the sleeping surface affects the distance between the top rung of the ladder and the sleeping platform. If the distance is too great, it becomes more difficult for the occupant to climb onto or off the bed safely, increasing the risk of slips or falls. This effect is compounded for younger children with less developed motor skills.
- Entrapment Hazards
While typically associated with gaps, excessive mattress height can contribute to entrapment risks. A too-thick sleeping surface could create pressure points against the guardrail or the structure itself, potentially trapping a limb or other body part. Although less common than entrapment in gaps, this scenario represents a genuine hazard, particularly if the occupant is unable to free themselves.
- Structural Stability
Although less direct, exceeding the recommended bedding height can indirectly affect the structural stability of the sleeping structure. The increased weight, particularly if the mattress is significantly heavier than the original, can place additional stress on the frame. This effect is compounded over time, potentially leading to structural weakening or failure. Adhering to height restrictions contributes to maintaining the overall integrity of the structure.
In summary, height restriction represents a critical safety control mechanism in the design of children’s tiered sleeping structures. Its purpose extends beyond mere aesthetic considerations, directly impacting the effectiveness of guardrails, ladder safety, entrapment prevention, and structural stability. Disregarding this restriction undermines the safety design, increasing the risk of injury for the occupant. Therefore, strict adherence to the manufacturer’s specified height restriction is paramount.
6. Frame Compatibility
Frame compatibility, in the context of tiered sleeping structures intended for young children, is a paramount safety and functional consideration. It signifies the precise alignment of sleeping surface dimensions with the internal measurements of the bed frame, ensuring safe and effective operation.
- Dimensional Conformance
Dimensional conformance is the core of frame compatibility. It demands that the length and width of the sleeping surface exactly match the interior dimensions of the frame. Gaps between the mattress edge and the frame present entrapment hazards for limbs or other body parts. Real-world incidents demonstrate that inadequate dimensional conformance can lead to serious injuries or even fatalities, particularly among infants and toddlers.
- Support System Integration
The support system, whether consisting of slats, a solid platform, or a wire grid, must be fully compatible with the selected sleeping surface. A mismatch can compromise the structural integrity of the arrangement. If, for example, the slats are spaced too far apart, the sleeping surface may sag or become uneven, potentially leading to discomfort, improper spinal alignment, or even mattress failure. A proper fit ensures even weight distribution and long-term stability.
- Height and Guardrail Alignment
Frame compatibility extends vertically. The combined height of the frame’s support structure and the sleeping surface must adhere to the specified guardrail height requirements. A frame that is too low, or a sleeping surface that is too thick, compromises the protective function of the guardrail. This directly increases the risk of falls, especially for active children. Therefore, verifying compatibility with guardrail height specifications is critical.
- Fastening and Security
Certain tiered sleeping structures incorporate fastening mechanisms to secure the sleeping surface to the frame. These mechanisms, such as straps or clips, prevent the mattress from shifting or sliding during use. If the sleeping surface is not compatible with these fastening mechanisms, the mattress may move unexpectedly, creating a potential hazard. The presence and proper functioning of these security features are essential components of overall frame compatibility.
Achieving optimal frame compatibility is not simply a matter of convenience; it is a fundamental prerequisite for safe operation of tiered children’s sleeping structures. The interconnectedness of dimensional conformance, support system integration, height and guardrail alignment, and fastening security dictates the overall safety and stability of the arrangement. Thorough verification of these aspects is essential when selecting or replacing a sleeping surface.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common concerns and misconceptions surrounding the use of crib mattresses within bunk bed structures, clarifying critical safety and suitability considerations.
Question 1: Is a standard crib mattress suitable for all bunk beds?
The suitability of a standard crib mattress for a bunk bed is dependent on specific dimensional and safety requirements. While a crib mattress might fit within the bunk bed frame, its thickness could exceed the maximum allowable height restriction, compromising guardrail effectiveness and increasing the risk of falls. Further consideration should be paid to the frame, to determine any potential gaps.
Question 2: What are the key safety considerations when using a crib mattress in a bunk bed?
Key safety considerations include verifying the dimensions to ensure a snug fit within the frame to prevent entrapment, confirming that the mattress thickness does not exceed the height restriction specified for the bunk bed, and ensuring the mattress material is non-toxic and flame-resistant. A firm mattress is also necessary.
Question 3: How does the weight capacity of a crib mattress impact its use in a bunk bed?
The weight capacity of the mattress is a crucial consideration. While a standard crib mattress is designed to support the weight of an infant, it may not be adequate for an older or heavier child using the bunk bed. Exceeding the weight limit can compromise support, durability, and overall safety.
Question 4: What types of materials are recommended for a crib mattress used in a bunk bed?
Recommended materials include those that are hypoallergenic, non-toxic, and flame-resistant. Organic cotton, natural latex, and foam products certified for low VOC emissions are preferable. Breathable materials are also important for regulating temperature and preventing moisture buildup.
Question 5: How often should a crib mattress used in a bunk bed be inspected?
Regular inspections are essential to ensure ongoing safety and performance. The mattress should be inspected at least monthly for signs of wear, sagging, or damage. The frame itself should also be regularly inspected. Any compromised components should be promptly replaced.
Question 6: Are there specific certifications to look for when selecting a crib mattress for a bunk bed?
Certifications to seek include GREENGUARD Gold, which indicates low chemical emissions; CertiPUR-US, confirming foam composition without harmful substances; and compliance with federal flammability standards (16 CFR Part 1633 or 1632). These certifications offer assurance of product safety and quality.
In summary, selecting a sleeping surface suitable for a tiered sleeping structure requires attention to dimensions, weight capacity, material safety, and adherence to recognized certifications. Prioritizing these factors promotes a safer and more comfortable sleeping environment.
The following section will provide resources for finding additional information and guidance on selecting appropriate sleeping arrangements for children.
Conclusion
The preceding examination of the characteristics, safety imperatives, and selection criteria associated with the term “crib mattress bunk bed” underscores the complexities involved in providing safe sleeping arrangements for young children in shared or space-constrained environments. Dimensions, materials, safety certifications, and appropriate firmness are all integral to mitigating identified risks and ensuring structural integrity.
Given the potential for serious injury resulting from improper implementation or oversight, adherence to established safety guidelines and diligent product evaluation are non-negotiable responsibilities for caregivers and manufacturers alike. Continued vigilance and a commitment to informed decision-making remain essential for safeguarding the well-being of children within these sleeping environments.