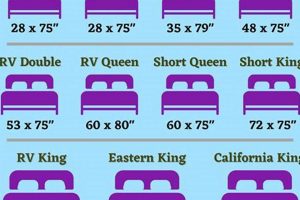
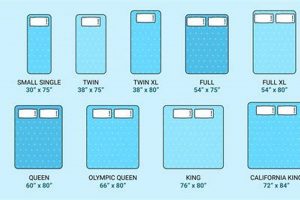
The spatial extent of a support surface utilized in healthcare settings is defined by its length, width, and thickness. These measurements are critical in ensuring compatibility with bed frames and accommodating patient size and needs. For instance, a standard support surface in these environments typically measures approximately 80 inches in length and 35 inches in width, although variations exist.
Appropriate sizing is essential for patient comfort, safety, and pressure ulcer prevention. A well-fitted support surface minimizes the risk of falls and ensures even weight distribution, reducing pressure points. Historically, standardized measurements have evolved to meet the increasing demands of diverse patient populations and advancements in healthcare equipment design, improving the overall quality of care.
The subsequent sections will delve into the standard and specialty sizes available, the factors influencing size selection, and the relevant regulatory considerations, providing a comprehensive understanding of these essential components within the medical environment.
Guidance on Selecting Support Surface Measurements
The appropriate selection of support surface measurements in a healthcare setting demands careful consideration of several key factors. Prioritizing these considerations ensures patient safety and optimizes the functionality of the equipment.
Tip 1: Patient Anthropometrics: Accurately assess patient height, weight, and body mass index. The selected support surface should adequately support the patient’s body without excessive overhang or compression.
Tip 2: Bed Frame Compatibility: Verify compatibility between the chosen support surface and the bed frame. Incompatible measurements can compromise patient safety and damage equipment.
Tip 3: Pressure Ulcer Prevention: Select measurements that facilitate effective pressure redistribution. Wider surfaces can provide more surface area for weight distribution, mitigating the risk of pressure ulcer development.
Tip 4: Maneuverability and Access: Consider the ease of patient repositioning and access for medical staff. Excessively wide surfaces can impede these activities, potentially hindering patient care.
Tip 5: Bariatric Considerations: In bariatric care, oversized surfaces are essential. Ensure the selected dimensions comply with weight capacity specifications and accommodate the patient’s unique needs.
Tip 6: Pediatric Considerations: Smaller support surface measurements are critical for pediatric patients to ensure proper support and reduce the risk of entrapment.
Tip 7: Regulatory Compliance: Adhere to relevant regulatory guidelines and standards regarding support surface dimensions and safety requirements within the healthcare facility.
Proper attention to these guidelines ensures optimized patient care and efficient resource allocation within the healthcare environment.
The subsequent section will present a conclusion summarizing the core components related to support surface sizing.
1. Standard Length
Standard length, a crucial component within the broader context of dimensions of a hospital bed mattress, refers to the established and widely accepted measurement of the longitudinal axis of the support surface. This dimension directly influences patient comfort, safety, and the overall effectiveness of medical care provided.
- Typical Measurement and Patient Accommodation
The standard length of a medical support surface typically measures around 80 inches (203 cm). This measurement is designed to accommodate the average adult patient, ensuring that individuals can lie comfortably without excessive bending or overhang. Deviations from this standard can lead to compromised patient posture and potential pressure points.
- Frame Compatibility and Equipment Integration
Standard length is a critical factor in ensuring compatibility between the support surface and the hospital bed frame. Manufacturers design bed frames with the expectation that they will accommodate a support surface of standard length. Mismatched dimensions can result in instability, difficulty in adjusting the bed, and potential safety hazards for both patients and healthcare providers.
- Pressure Ulcer Prevention and Weight Distribution
A support surface of appropriate length contributes to effective pressure redistribution across the patient’s body. If the support surface is too short, it can concentrate pressure on specific areas, increasing the risk of pressure ulcer development, especially in patients with limited mobility. The standard length aims to provide adequate surface area to distribute weight evenly.
- Specialty Bed Variations and Length Adjustments
While a standard length exists, some specialized medical beds may offer adjustable length options to accommodate patients of varying heights or specific medical conditions. For instance, certain bariatric beds may be longer to support individuals with larger body sizes. However, even with adjustable lengths, the initial reference point remains the established standard.
In summary, standard length serves as a foundational element in the overall dimensions of a hospital bed mattress. It impacts patient accommodation, frame compatibility, pressure ulcer prevention, and the design of specialty bed variations. Adherence to, or a well-reasoned deviation from, this standard is paramount to ensuring patient well-being and the efficacy of medical care within the hospital environment.
2. Standard Width
Standard width, as a key element of dimensions of a hospital bed mattress, defines the lateral extent of the patient support surface. Its proper consideration is vital for patient comfort, accessibility, and safety within the healthcare setting.
- Patient Accommodation and Comfort
The typical measurement for standard width is approximately 35 to 36 inches. This dimension is designed to accommodate a range of adult body sizes, providing sufficient space for patients to reposition themselves and maintain comfort. Deviations from this standard can compromise patient comfort and potentially restrict movement, particularly for larger individuals.
- Accessibility for Healthcare Providers
Standard width balances patient space with the accessibility needs of healthcare providers. A width that is too great can impede access for administering care, repositioning patients, or performing necessary procedures. The standardized dimension facilitates efficient and safe healthcare delivery.
- Side Rail Compatibility and Fall Prevention
The specified width directly impacts the functionality of side rails, which are integral to patient safety and fall prevention. Side rails are designed to fit within the established width parameters, ensuring that they can be effectively deployed to prevent patients from rolling out of bed. An incompatible width can render side rails ineffective, increasing the risk of falls.
- Space Utilization and Room Configuration
Within healthcare facilities, efficient space utilization is a crucial consideration. Standard width contributes to optimized room configuration, allowing for multiple beds within a confined space while maintaining adequate clearance for healthcare providers to move and operate equipment. Non-standard widths can disrupt room layouts and potentially compromise workflow efficiency.
In summation, standard width is a critical dimension impacting numerous aspects of patient care, including comfort, safety, accessibility, and efficient space utilization. Its proper consideration is essential for ensuring optimal outcomes within the healthcare environment, directly influencing the overall effectiveness and quality of care provided.
3. Thickness Variation
Thickness variation, as a component of dimensions of a hospital bed mattress, refers to the range of vertical measurements exhibited by the support surface. This variation is not arbitrary; it is a deliberate design element intended to address specific patient needs and clinical objectives. Cause and effect relationships between thickness and patient outcomes are well-documented. For instance, a thicker support surface generally provides greater immersion, distributing pressure over a larger area and reducing the risk of pressure ulcer formation. Conversely, excessively thick surfaces can hinder patient mobility and complicate transfers. The importance of thickness variation lies in its capacity to tailor support to diverse patient populations, ranging from pediatric cases to bariatric requirements. A practical example is the use of layered foam mattresses with varying densities, where the combined thickness and composition directly influence the support surface’s ability to conform to the patient’s body and redistribute weight effectively.
The practical significance of understanding thickness variation extends to equipment selection and procurement processes within healthcare facilities. Choosing a mattress with the appropriate thickness requires a thorough assessment of the patient population’s specific needs and the intended use of the bed. For example, a specialized pressure redistribution mattress may require a certain minimum thickness to achieve the desired therapeutic effect. Manufacturers often specify recommended thickness ranges for different patient weights and risk levels for pressure ulcer development. Furthermore, the thickness of the mattress can affect the overall height of the bed, which is a crucial factor in preventing falls, particularly among elderly or mobility-impaired patients. Facilities must consider adjustable bed frames to compensate for variations in mattress thickness.
In conclusion, thickness variation is a critical and purposefully engineered attribute within the overall dimensions of a hospital bed mattress. Its selection must be based on a comprehensive evaluation of patient characteristics, clinical objectives, and safety considerations. While a range of options exist, each thickness profile presents a unique set of advantages and challenges. By carefully considering these factors, healthcare providers can optimize patient comfort, minimize the risk of complications, and ensure the effective delivery of care. The ongoing challenge lies in developing standardized guidelines that provide clear and concise recommendations for selecting the appropriate mattress thickness for diverse patient populations.
4. Bariatric Sizing
Bariatric sizing represents a specialized subset within dimensions of a hospital bed mattress, specifically tailored to accommodate the unique needs of patients with obesity. Its proper implementation is critical for ensuring patient comfort, safety, and effective care delivery.
- Increased Weight Capacity
Bariatric support surfaces are engineered to withstand significantly higher weight loads compared to standard models. A typical bariatric mattress may have a weight capacity ranging from 500 to 1000 pounds or more. Failure to use an appropriately rated support surface can lead to equipment failure and potential patient injury. For example, a standard mattress used for a bariatric patient may compress excessively, compromising pressure redistribution and increasing the risk of skin breakdown.
- Expanded Width Dimensions
Bariatric models feature increased width to provide adequate surface area and prevent patients from feeling confined or at risk of falling off the edge. While standard support surfaces typically measure 35-36 inches in width, bariatric options often range from 42 to 48 inches or more. This increased width allows for proper positioning and reduces the potential for pressure points on bony prominences. Insufficient width can lead to discomfort, restricted movement, and an elevated risk of pressure ulcers.
- Reinforced Construction and Materials
Bariatric support surfaces employ reinforced construction techniques and durable materials to withstand the increased stress and wear associated with higher weight loads. These enhancements may include high-density foam cores, reinforced seams, and heavy-duty covers. Failure to utilize robust materials can result in premature degradation of the support surface, compromising its ability to provide adequate support and pressure redistribution. Regular inspection for signs of wear is essential to ensure continued functionality.
- Adjustable Frame Compatibility
Bariatric sizing must be considered in conjunction with the bed frame. Bariatric support surfaces require compatible bed frames that are also designed to accommodate higher weight capacities and expanded dimensions. Attempting to use a bariatric mattress on a standard bed frame can create an unstable and potentially hazardous situation. Adjustable bariatric bed frames offer additional features such as powered positioning and Trendelenburg capabilities, further enhancing patient care and safety.
The implementation of bariatric sizing in dimensions of a hospital bed mattress is not merely an issue of increased dimensions and weight capacity. It is a multifaceted consideration that encompasses materials, construction, bed frame compatibility, and patient safety. Adherence to these standards ensures that bariatric patients receive the appropriate level of support and care, minimizing the risk of complications and promoting positive outcomes.
5. Pediatric Sizes
Pediatric sizes, within the context of dimensions of a hospital bed mattress, represent a critical adaptation of standard measurements to meet the physiological and safety requirements of infant and child patients. The application of appropriate dimensions directly impacts patient comfort, musculoskeletal development, and the prevention of adverse events. Standard adult mattress sizes are unsuitable for pediatric populations due to the risk of entrapment, inadequate support, and compromised respiratory function. For example, an infant placed on an adult-sized support surface may become wedged between the mattress and side rails, leading to suffocation. Pediatric-specific dimensions minimize these risks while promoting proper alignment and pressure distribution. These considerations are paramount to ensure optimal therapeutic outcomes.
Specific examples of pediatric sizes include crib mattresses, which typically measure approximately 27-28 inches in width and 52-53 inches in length, and youth bed mattresses, which may approximate twin-size dimensions but often feature reduced thickness to accommodate smaller body masses. These dimensions are meticulously engineered to fit corresponding crib and bed frames, thereby preventing gaps that could pose entrapment hazards. Moreover, the composition of pediatric support surfaces often differs from adult models, emphasizing hypoallergenic materials and reduced off-gassing to minimize potential respiratory irritation. The proper selection of pediatric sizes contributes directly to improved patient outcomes and reduced liability for healthcare institutions. Regular monitoring and adherence to established safety guidelines are essential components of pediatric patient care.
In summary, pediatric sizes constitute a vital adaptation within the broader framework of dimensions of a hospital bed mattress. The implementation of appropriate dimensions is not merely a matter of scaling down adult sizes; it is a multifaceted consideration that encompasses safety, comfort, developmental needs, and material composition. By adhering to established guidelines and prioritizing pediatric-specific requirements, healthcare providers can create a safer and more therapeutic environment for their youngest patients. The ongoing development and refinement of pediatric support surface standards represent a continuous effort to improve patient outcomes and minimize risks within the pediatric healthcare setting.
6. Weight Capacity
Weight capacity, when considered in conjunction with the dimensions of a hospital bed mattress, represents a critical safety parameter that dictates the maximum load the support surface can safely accommodate. It directly influences patient safety, equipment longevity, and the efficacy of pressure redistribution therapies.
- Structural Integrity and Mattress Dimensions
The weight capacity of a hospital bed mattress is fundamentally linked to its internal construction and external dimensions. Larger dimensions, particularly in terms of thickness and width, often correlate with increased weight-bearing capabilities due to the greater volume of supportive materials. Manufacturers must consider the interplay between dimensions and material properties (e.g., foam density, spring coil gauge) to ensure the mattress can withstand the specified weight without compromising structural integrity. Exceeding the weight limit can lead to mattress deformation, reduced support, and potential patient injury.
- Pressure Redistribution and Weight Limits
Effective pressure redistribution, a key function of hospital bed mattresses, is directly affected by weight capacity. A mattress designed for a specific weight range will optimally distribute pressure across the patient’s body within those parameters. When the weight limit is exceeded, the support surface may compress excessively, concentrating pressure on bony prominences and increasing the risk of pressure ulcer development. Consequently, the dimensions and materials must be chosen to maintain pressure redistribution efficacy across the stated weight range.
- Bed Frame Compatibility and Safety Standards
Weight capacity is not solely a function of the mattress; it must be considered in conjunction with the bed frame. The bed frame must be capable of supporting the mattress and the patient’s weight safely. Incompatible combinations can lead to structural failure and patient injury. Safety standards, such as those promulgated by regulatory agencies, often specify minimum weight capacity requirements for both the mattress and the bed frame, underscoring the importance of matching components. Mattress dimensions must also align with the bed frame’s specifications to ensure proper weight distribution and stability.
- Bariatric Considerations and Expanded Dimensions
Bariatric mattresses represent a specialized category where weight capacity and dimensions are significantly expanded to accommodate patients with obesity. These mattresses typically feature increased width, thickness, and reinforced internal structures to support higher weight loads while maintaining pressure redistribution capabilities. The expanded dimensions and enhanced construction are essential for providing adequate support and preventing mattress failure in bariatric care settings. Proper consideration of weight capacity and dimensions is paramount to ensuring the safety and comfort of bariatric patients.
In conclusion, the interplay between weight capacity and dimensions of a hospital bed mattress is a multifaceted consideration that impacts structural integrity, pressure redistribution, bed frame compatibility, and specialized patient populations. Adherence to specified weight limits and proper matching of mattress and bed frame components are essential for maintaining patient safety and optimizing therapeutic outcomes. The dimensions of the mattress should be appropriate for not only the patient’s size but also weight to maintain optimal support and weight distribution, thus maximizing patient safety.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding hospital bed support surface measurements, focusing on accuracy, safety, and clinical implications. These responses are designed to provide clear and concise information for healthcare professionals and stakeholders.
Question 1: What are the standard measurements for a typical hospital bed support surface?
The commonly accepted dimensions are approximately 80 inches in length and 35 inches in width. These measurements are designed to accommodate the average adult patient while ensuring compatibility with standard bed frames.
Question 2: How does the measurement influence pressure ulcer prevention?
Appropriate sizing promotes proper weight distribution, minimizing pressure concentration on bony prominences. Inadequate measurements can lead to increased pressure and a higher risk of skin breakdown, especially in immobile patients.
Question 3: What considerations are essential when selecting measurements for a bariatric patient?
Bariatric support surfaces require significantly larger dimensions and higher weight capacities. These often exceed standard sizes to accommodate the patient’s weight and ensure adequate support and safety.
Question 4: How does mattress thickness impact patient safety and comfort?
The thickness affects the degree of immersion and envelopment, influencing pressure redistribution. Insufficient thickness can compromise pressure relief, while excessive thickness can hinder patient mobility and access.
Question 5: Are there specific measurement considerations for pediatric patients?
Pediatric support surfaces necessitate smaller dimensions to prevent entrapment and ensure appropriate support for smaller body sizes. Standard adult sizes are unsuitable and pose significant safety risks.
Question 6: What is the relationship between support surface measurements and bed frame compatibility?
Accurate alignment between the support surface and the bed frame is crucial for stability and safety. Incompatible measurements can compromise the integrity of the bed system and increase the risk of falls or equipment malfunction.
Understanding the nuances of these measurements is paramount for ensuring patient safety, comfort, and the delivery of effective medical care. This knowledge facilitates informed decision-making regarding equipment selection and patient management.
The subsequent section will present a concise summary, reinforcing key concepts.
Conclusion
This article has comprehensively examined the dimensions of a hospital bed mattress, emphasizing their critical role in patient care. Standard measurements, variations for bariatric and pediatric populations, and the significance of weight capacity have been detailed. The interplay between length, width, thickness, and intended use directly impacts patient safety, comfort, and the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions.
The appropriate selection and implementation of these measurements are not merely logistical considerations; they represent a fundamental commitment to patient well-being. Continued adherence to established guidelines and a proactive approach to adapting support surface specifications to individual patient needs are essential to optimizing outcomes and mitigating risks within the healthcare environment. Further research into advanced materials and adjustable dimensions holds the promise of even greater improvements in patient care in the future.