A sleep support system typically comprised of two primary components: a resilient base providing elevation and stability, and a conforming upper layer designed for comfort. The former, historically constructed with coils and a wooden frame, serves to absorb shock and distribute weight. The latter, composed of synthetic or natural materials, contours to the body, reducing pressure points and promoting spinal alignment.
This arrangement offers several advantages. The stable foundation enhances the lifespan of the sleep surface, preventing sagging and premature wear. The conforming layer enhances sleep quality by minimizing motion transfer, isolating movement, and relieving pressure on joints and muscles. Historically, this design evolved from simpler bedding arrangements to address evolving needs for comfort and support, impacting sleep habits and overall well-being.
The following sections will delve into the specific types of materials used in the construction of both the support structure and the comfort layer, exploring their individual properties, maintenance requirements, and potential health considerations. We will also examine alternative support systems and discuss factors to consider when selecting an appropriate sleep solution.
Selection and Maintenance Guidance
The selection of a suitable sleep system, encompassing both support and comfort components, requires careful consideration of individual needs and environmental factors. Proper maintenance extends the lifespan and optimizes the performance of this system.
Tip 1: Assess Support Needs: Evaluate individual weight, sleeping position, and any existing back or joint conditions. Firmer support structures may be preferable for individuals requiring increased spinal support.
Tip 2: Consider Material Composition: Investigate the materials used in the comfort layer. Different materials offer varying degrees of conforming ability, breathability, and durability. Consider certifications that indicate material safety and environmental responsibility.
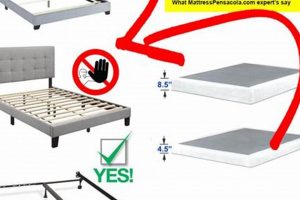
Tip 3: Evaluate Foundation Compatibility: Ensure that the selected sleep surface is compatible with the chosen support foundation. Incompatible combinations may lead to premature wear and reduced performance.
Tip 4: Implement Regular Rotation: Rotate the sleep surface regularly to promote even wear and prevent localized sagging. Frequency of rotation depends on the specific model and manufacturer recommendations.
Tip 5: Utilize a Protective Cover: Employ a waterproof and breathable protective cover to guard against spills, stains, and allergens. This preventative measure significantly extends the lifespan of the sleep system.
Tip 6: Maintain Proper Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation around the sleep system to prevent moisture buildup and the growth of mold or mildew. Periodic airing out of the components is advisable.
Tip 7: Adhere to Cleaning Instructions: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for cleaning and spot treating. Improper cleaning techniques can damage the materials and void warranties.
Adherence to these guidelines enhances the longevity and performance of the sleep system, maximizing comfort and support over time.
The following section provides a conclusion to the discussion, summarizing key aspects and offering closing remarks.
1. Support Structure
The support structure is a foundational element of any sleep system incorporating a conforming foam mattress, impacting its overall performance, longevity, and the quality of sleep experienced. The interaction between the mattress and its support base is crucial for achieving optimal weight distribution, spinal alignment, and preventing premature wear.
- Load Distribution and Stability
A well-designed support structure, such as a traditional box spring or a modern platform, distributes the weight of the mattress and occupants evenly. This even distribution prevents localized sagging or deformation of the foam, extending its lifespan. An unstable or inadequate base can lead to uneven wear, compromised support, and ultimately, premature failure of the foam layer.
- Impact Absorption and Motion Isolation
Traditional box springs, containing internal coils, offer a degree of impact absorption, minimizing the transmission of motion. Modern platform designs, while providing a more rigid base, can also incorporate motion-isolating features through the use of specific materials or construction techniques. Effective motion isolation contributes to undisturbed sleep, particularly for individuals sharing a bed.
- Ventilation and Moisture Management
The support structure plays a role in the overall ventilation of the sleep system. Some designs, particularly those with open coil systems, allow for greater airflow, reducing moisture buildup within the mattress. This ventilation is critical for preventing the growth of mold and mildew, promoting a healthier sleep environment. Solid platform bases may require alternative ventilation strategies to prevent moisture accumulation.
- Height and Accessibility
The height of the support structure affects the overall bed height, impacting accessibility and comfort. An appropriate height facilitates ease of getting in and out of bed, particularly for individuals with mobility limitations. The selection of a support structure should consider individual height preferences and physical needs.
The choice of support structure is not merely an aesthetic consideration but a functional one that directly influences the performance and lifespan of the foam mattress. The ideal selection depends on the specific type of foam, individual sleep preferences, and environmental factors within the sleep environment.
2. Conforming Material
The “conforming material” in a sleep system primarily refers to the composition of the mattress itself, particularly in systems featuring a foam component. Within the context of “foam mattress and box spring,” the foam layer is designed to mold to the sleeper’s body, distributing weight and minimizing pressure points. The composition of this foam, whether memory foam, latex foam, or a hybrid blend, directly impacts the level of conforming ability. A higher conforming material promotes improved spinal alignment and reduced discomfort, contributing significantly to sleep quality.
The effect of conforming materials on the durability of the overall system should not be understated. Over time, repeated compression cycles can cause the foam to degrade, losing its original shape and support. A box spring, by providing a stable and even base, mitigates stress on the foam layer, extending its lifespan. Conversely, an inadequate or uneven box spring can accelerate foam degradation, reducing the mattress’s conforming effectiveness. For example, a memory foam mattress placed directly on a slatted frame with wide gaps may experience uneven compression, leading to premature sagging in the unsupported areas.
In conclusion, the “conforming material” represents a critical element in the “foam mattress and box spring” system. Its ability to contour to the body ensures pressure relief and spinal alignment, while the box spring provides the necessary support to maximize the lifespan and performance of the foam. The proper combination of conforming material and support structure is vital for a sleep environment that optimizes both comfort and long-term value. Any imbalance or defect in either element can lead to sleep discomfort and an early need for replacement.
3. Motion Isolation
Motion isolation, a crucial attribute in sleep systems, is significantly influenced by the interaction between the foam mattress and box spring. The foam material, particularly memory foam and latex, inherently dampens movement, minimizing the transfer of motion across the sleep surface. A disturbance on one side of the mattress is less likely to affect a sleeping partner on the other side. The box spring, acting as a shock absorber, further contributes to motion isolation by attenuating vibrations originating from movement on the mattress. Without adequate motion isolation, disturbances such as a partner getting in or out of bed can disrupt sleep cycles, reducing overall sleep quality.
The effectiveness of motion isolation in a “foam mattress and box spring” configuration is directly related to the quality and density of the foam and the structural integrity of the box spring. Higher-density foams generally provide superior motion isolation compared to lower-density alternatives. Similarly, a box spring with a robust coil system or a solid platform base will more effectively dampen vibrations compared to a worn or poorly constructed box spring. The practical implications of this are evident in shared sleep environments where partners have different sleep schedules or are prone to tossing and turning. The combination of a high-quality foam mattress and a supportive box spring minimizes sleep disruptions, promoting more restful sleep for both individuals.
In summary, motion isolation is a key functional benefit derived from the synergistic relationship between a “foam mattress and box spring.” The foam’s inherent damping properties, coupled with the box spring’s ability to absorb vibrations, create a sleep environment that minimizes disturbances caused by movement. This understanding is critical for consumers seeking to optimize sleep quality, particularly in shared sleep spaces. Failure to consider this aspect can result in frequent sleep interruptions and reduced overall well-being.
4. Spinal Alignment
Maintaining proper spinal alignment during sleep is critical for musculoskeletal health, and the selection of a “foam mattress and box spring” system directly impacts this aspect. The interplay between the conforming properties of the foam and the supportive nature of the base determines the extent to which the spine is properly supported throughout the night, thereby influencing sleep quality and reducing the risk of back pain.
- Contouring and Pressure Relief
The primary advantage of a foam mattress lies in its ability to contour to the body’s unique curves, distributing weight evenly and reducing pressure on key points such as the hips and shoulders. This conforming action allows the spine to maintain its natural alignment, preventing it from being forced into unnatural positions. For example, a side sleeper on a firm, non-conforming mattress may experience pressure on the shoulder, leading to spinal misalignment and discomfort. The “foam mattress and box spring” system, when appropriately chosen, mitigates this issue by providing targeted support and pressure relief.
- Support and Stability from the Base
While the foam layer provides conforming comfort, the box spring, or alternative foundation, is responsible for providing overall support and stability. A sagging or inadequate base compromises the foam’s ability to maintain spinal alignment, potentially leading to back pain and discomfort. A firm, level base ensures that the foam provides consistent support across its surface, allowing it to effectively contour to the body without collapsing under weight. An example would be a high-quality memory foam mattress placed on an old, worn box spring; the mattress’s conforming properties would be undermined by the base’s lack of support, defeating the purpose of the design.
- Adaptability to Sleeping Position
Different sleeping positions require varying degrees of support to maintain optimal spinal alignment. Side sleepers generally benefit from a softer foam that allows the shoulder and hip to sink in, maintaining a straight spine. Back sleepers typically require a firmer surface to prevent the hips from sinking too far, which can cause lower back pain. Stomach sleepers often require the firmest support to prevent excessive arching of the back. A well-chosen “foam mattress and box spring” system should accommodate the individual’s preferred sleeping position, providing the appropriate level of support and conforming ability to promote proper spinal alignment.
- Long-Term Musculoskeletal Health
Consistent spinal misalignment during sleep can contribute to chronic back pain, muscle stiffness, and other musculoskeletal issues. Investing in a “foam mattress and box spring” system that promotes proper alignment is therefore a long-term investment in overall health and well-being. By minimizing stress on the spine and surrounding muscles, the system can help prevent the development of chronic pain conditions and improve overall quality of life. For instance, individuals with pre-existing back problems often find significant relief by switching to a system that provides both conforming comfort and adequate support, allowing them to sleep more comfortably and wake up feeling refreshed.
In summary, the selection of a “foam mattress and box spring” system should prioritize spinal alignment as a key factor. The combination of a conforming foam layer and a supportive base works synergistically to maintain the natural curvature of the spine during sleep, reducing the risk of discomfort and promoting long-term musculoskeletal health. Thoroughly assessing individual sleeping habits and needs is essential to choosing the system that best facilitates proper spinal alignment and overall well-being.
5. Durability Factors
Durability is a paramount consideration in the selection of a “foam mattress and box spring” system. The lifespan of these components is directly influenced by the quality of materials, construction techniques, and maintenance practices. Understanding the factors that contribute to the longevity of the mattress and foundation allows consumers to make informed purchasing decisions and maximize the return on their investment.
- Foam Density and Composition
The density of the foam within the mattress is a primary determinant of its durability. Higher-density foams, while often more expensive, exhibit greater resistance to compression and deformation over time. Lower-density foams tend to break down more quickly, leading to sagging and reduced support. The specific type of foam, such as memory foam, latex, or polyurethane, also impacts durability. Latex foam, for example, is known for its inherent resilience and long lifespan, while conventional polyurethane foam may be more susceptible to degradation. Consider the example of two seemingly identical mattresses; one constructed with high-density memory foam and the other with low-density polyurethane foam. After several years of use, the former will likely retain its shape and support, while the latter may exhibit significant sagging and require replacement.
- Box Spring Construction and Materials
The construction and materials used in the box spring significantly influence its ability to support the mattress and maintain its structural integrity. A robust box spring with a solid frame and durable coils, or a well-constructed platform base, will provide consistent support, preventing premature wear of the mattress. Conversely, a poorly constructed box spring with weak coils or a flimsy frame can contribute to mattress sagging and reduce its overall lifespan. A scenario to consider is a high-quality foam mattress placed upon a deteriorated box spring. The mattress will eventually conform to the degraded shape of the box spring, leading to uneven wear and reducing the lifespan of the mattress.
- Fabric Quality and Stitching
The quality of the fabric covering the mattress and box spring, as well as the stitching used to bind the components, impacts their resistance to wear and tear. Durable fabrics that resist abrasion and tearing will protect the internal materials from damage, extending the lifespan of the system. Strong, reinforced stitching prevents seams from unraveling, maintaining the structural integrity of the mattress and box spring. For example, a mattress with a thin, loosely woven fabric cover will be more susceptible to damage from friction and wear compared to a mattress with a thick, tightly woven fabric cover. Similarly, a box spring with poorly stitched seams may begin to separate over time, compromising its ability to provide adequate support.
- Maintenance and Environmental Factors
Proper maintenance and environmental control contribute significantly to the longevity of a “foam mattress and box spring” system. Regularly rotating and flipping the mattress, using a mattress protector, and controlling humidity levels can prevent premature wear and damage. Exposure to excessive moisture, direct sunlight, or harsh chemicals can degrade the foam and fabric, shortening the lifespan of the system. Consider a mattress left uncovered in a humid environment; the moisture will penetrate the foam, leading to the growth of mold and mildew, and ultimately, causing the mattress to deteriorate. Routine maintenance, such as vacuuming and spot cleaning, can help remove dust, allergens, and spills, preventing them from causing lasting damage.
In conclusion, the durability of a “foam mattress and box spring” system is a multifaceted consideration encompassing material quality, construction techniques, and maintenance practices. By prioritizing these factors, consumers can make informed decisions that ensure the longevity and performance of their sleep system, maximizing their comfort and investment over time. The long-term benefits of a durable system include improved sleep quality, reduced risk of back pain, and a greater overall value for money.
6. Ventilation Capacity
Ventilation capacity, referring to the ability of a sleep system to promote airflow and dissipate moisture, plays a crucial role in the long-term performance and hygiene of a “foam mattress and box spring” configuration. Inadequate ventilation can lead to the accumulation of humidity, fostering the growth of mold, mildew, and dust mites, compromising both the structural integrity of the components and the sleeper’s health.
- Foam Type and Structure
The type and structure of foam used in the mattress significantly impact its ventilation capacity. Open-cell foams, such as some latex and advanced memory foam formulations, inherently allow for greater airflow compared to closed-cell foams. The open structure facilitates the dissipation of body heat and moisture, reducing the risk of microbial growth. Conversely, dense, closed-cell foams tend to trap heat and humidity, creating a less hygienic sleep environment. A practical example is the comparison between a traditional memory foam mattress, which often exhibits limited ventilation, and a latex mattress with pinholes, which enhances airflow and breathability.
- Box Spring Design and Airflow
The design of the box spring or foundation directly affects the overall ventilation capacity of the sleep system. Traditional box springs with open coil systems promote airflow beneath the mattress, aiding in moisture dissipation. Platform bases, while providing solid support, may restrict airflow if not properly designed. Some platform bases incorporate ventilation channels or slats to improve airflow and prevent moisture accumulation. The selection of a base should therefore consider its impact on ventilation, particularly when paired with a foam mattress that may already have limited airflow. Imagine a dense memory foam mattress placed on a solid platform bed; the combination could lead to a buildup of heat and moisture, potentially shortening the lifespan of the mattress and affecting sleep quality.
- Fabric Cover and Breathability
The material used for the mattress cover is a critical factor in ventilation capacity. Breathable fabrics, such as cotton, bamboo, or specialized performance fabrics, allow for the passage of air and moisture, promoting a cooler and more hygienic sleep surface. Non-breathable fabrics, such as vinyl or certain synthetic materials, impede airflow and can contribute to heat buildup. The cover functions as the first line of defense against moisture, and its breathability directly affects the overall ventilation of the “foam mattress and box spring.” Consider a mattress with a tightly woven, non-breathable cover; this cover will trap heat and moisture against the body, leading to discomfort and potentially promoting the growth of microorganisms.
- Environmental Factors and Humidity Control
The environmental conditions in the bedroom also play a significant role in the ventilation needs of the sleep system. High humidity levels can exacerbate the problem of moisture accumulation within the mattress and box spring, increasing the risk of mold and mildew growth. Adequate ventilation in the bedroom, through the use of fans or air conditioning, can help to mitigate this risk. Additionally, using a mattress protector that is both waterproof and breathable can prevent moisture from penetrating the mattress while still allowing for some degree of airflow. A “foam mattress and box spring” in a humid climate will require greater attention to ventilation to maintain its hygiene and longevity.
The ventilation capacity of a “foam mattress and box spring” system is a critical factor in its overall performance and hygiene. By considering the foam type, box spring design, fabric cover, and environmental conditions, consumers can select a system that promotes airflow, dissipates moisture, and contributes to a healthier and more comfortable sleep environment. Addressing ventilation concerns is not only essential for maximizing the lifespan of the components but also for safeguarding the sleeper’s health and well-being. The lack of proper airflow can negate even the highest quality materials of foam mattress.
7. Cost Effectiveness
Evaluating the cost-effectiveness of a “foam mattress and box spring” necessitates a comprehensive assessment extending beyond the initial purchase price. The long-term value proposition hinges on factors such as durability, performance retention, and potential healthcare cost implications.
- Initial Investment vs. Lifespan
A lower initial price point may be attractive, but often correlates with reduced lifespan and performance degradation. A “foam mattress and box spring” system constructed with lower-density foams and less robust support structures is likely to require more frequent replacement, ultimately negating the initial cost savings. Conversely, a higher upfront investment in durable materials and construction may yield a longer lifespan and sustained performance, resulting in lower long-term costs. For example, a memory foam mattress with a ten-year warranty, paired with a solid platform base, may represent a greater long-term value compared to a cheaper innerspring mattress and flimsy box spring that requires replacement after five years.
- Performance Retention and Sleep Quality
The ability of a “foam mattress and box spring” to maintain its support and comfort characteristics over time directly impacts sleep quality and potential healthcare costs. A system that sags or loses its conforming ability can lead to back pain, poor sleep, and increased reliance on pain medication or other interventions. The resulting healthcare expenses can far outweigh any initial savings from a cheaper mattress. Conversely, a system that retains its support and comfort properties promotes restorative sleep and reduces the risk of musculoskeletal issues. High-density foams and robust support structures contribute to sustained performance and long-term cost savings.
- Maintenance and Replacement Costs
Maintenance requirements and potential replacement costs contribute significantly to the overall cost-effectiveness equation. A “foam mattress and box spring” system that requires frequent rotation, cleaning, or component replacement can quickly erode any initial cost savings. Features such as removable, washable covers, stain-resistant fabrics, and durable construction minimize maintenance costs and extend the lifespan of the system. Regular mattress flipping and box spring inspection are essential maintenance routines that directly influence the longevity. Systems prone to sagging or developing indentations may necessitate premature replacement, representing a significant financial burden.
- Health and Well-being Implications
The correlation between sleep quality and overall health necessitates considering the potential long-term health implications of a “foam mattress and box spring” system. A system that promotes proper spinal alignment and pressure relief can reduce the risk of back pain, neck pain, and other musculoskeletal issues, potentially lowering healthcare costs and improving overall well-being. Conversely, a system that provides inadequate support or promotes poor posture can contribute to chronic pain and reduced quality of life. The long-term cost of neglecting these health considerations can far exceed any initial savings on the mattress and base.
In conclusion, assessing the cost-effectiveness of a “foam mattress and box spring” requires a holistic perspective that encompasses initial investment, lifespan, performance retention, maintenance requirements, and health implications. Prioritizing durability, performance, and potential long-term health benefits offers the greatest opportunity for maximizing value and minimizing total cost of ownership. A cheap mattress and box spring isnt always the most effective solution.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding sleep systems composed of a foam mattress and box spring, providing informative answers to assist in informed decision-making.
Question 1: What is the typical lifespan of a foam mattress and box spring system?
The lifespan varies depending on material quality, construction, and usage. High-density foam mattresses paired with a well-constructed box spring can last 7-10 years, while lower-quality systems may only last 3-5 years.
Question 2: How does a box spring contribute to the performance of a foam mattress?
A box spring provides a stable, supportive base, distributing weight evenly and preventing sagging. This extends the mattress’s lifespan and ensures consistent support throughout its surface.
Question 3: Are all foam mattresses compatible with any box spring?
No. The box spring should be appropriate for the mattress type and weight. Incompatible combinations can lead to premature wear and reduced performance. Consult manufacturer recommendations for compatibility guidelines.
Question 4: What maintenance is required for a foam mattress and box spring?
Regular rotation and flipping of the mattress, using a mattress protector, and vacuuming are recommended. The box spring should be inspected periodically for damage and structural integrity.
Question 5: How do I address concerns about off-gassing from a new foam mattress?
Off-gassing is a common phenomenon with new foam products. Adequate ventilation in the room for several days can help dissipate odors. Look for CertiPUR-US certified mattresses, which indicates low VOC emissions.
Question 6: What are the key factors to consider when selecting a foam mattress and box spring for back pain?
Consider the firmness level, conforming ability, and spinal support offered by the mattress. A supportive box spring is essential. Consulting a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations is advisable.
Selecting a foam mattress and box spring system involves careful consideration of individual needs and product characteristics. Prioritizing quality and compatibility ensures optimal performance and longevity.
The following will summarize key aspects and offer concluding remarks regarding foam mattresses and box springs.
Conclusion
This exploration has underscored the multifaceted nature of sleep systems comprised of foam mattresses and box springs. Key points highlighted include the impact of foam density and composition on durability and comfort, the crucial role of the box spring in providing support and extending mattress lifespan, the significance of ventilation in maintaining hygiene, and the long-term cost-effectiveness considerations beyond initial price. Proper spinal alignment, motion isolation, and material safety are additional crucial factors for evaluation.
The informed selection and diligent maintenance of such systems represent a significant investment in individual health and well-being. Continued research and development in materials science and ergonomic design will likely further refine these sleep solutions. Careful evaluation of individual needs and a commitment to understanding the intricacies of these components are essential for achieving optimal sleep quality and maximizing the return on this investment.






![Boost Your Box Spring Mattress Firmness: [GUIDE] Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Boost Your Box Spring Mattress Firmness: [GUIDE] | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-3455-300x200.jpg)