A sleeping arrangement featuring two beds stacked vertically, where the lower bed accommodates a larger mattress size typically designed for two adults. This configuration maximizes floor space, particularly in rooms with limited square footage. For example, a children’s bedroom shared by siblings or a vacation rental property designed to house multiple guests might incorporate this type of bed.
These structures offer a practical solution for maximizing sleeping capacity while minimizing spatial footprint. Historically, bunk beds have been utilized in environments where space is at a premium, such as dormitories, military barracks, and ships. The adaptation to accommodate a larger mattress size on at least one tier caters to changing needs and preferences, offering increased comfort and flexibility for occupants. This design also facilitates efficient use of vertical space, making it a valuable asset in smaller living areas.
The following sections will examine specific design considerations, safety features, weight capacity, assembly instructions, and the target demographic for vertically stacked beds incorporating larger mattresses.
Tips for Selecting and Utilizing a Vertically Stacked Bed Designed for Larger Mattresses
The following tips provide practical guidance on choosing and using a vertically stacked bed that incorporates a larger mattress. Careful consideration of these points will contribute to safety, comfort, and longevity.
Tip 1: Verify Weight Capacity. Prior to purchase, confirm the maximum weight each tier can support. Exceeding this limit compromises structural integrity and poses a safety risk.
Tip 2: Assess Room Dimensions. Measure the ceiling height to ensure adequate clearance above the upper tier. Insufficient headroom restricts movement and comfort.
Tip 3: Prioritize Safety Features. Look for models that include sturdy guardrails on the upper tier and a secure ladder or staircase for accessing it. The guardrail height should meet or exceed safety standards.
Tip 4: Choose a Suitable Mattress. Select a mattress that conforms to the dimensions of the designated bed frame. Consider the thickness of the mattress, as excessive thickness can reduce the height of the safety rails.
Tip 5: Ensure Proper Assembly. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions meticulously during assembly. Incorrect assembly can weaken the structure and compromise its stability.
Tip 6: Consider Material Quality. Investigate the materials used in construction. Solid wood or heavy-gauge metal are generally more durable and stable than lighter materials.
Tip 7: Routine Inspection. Regularly inspect the frame, ladder, and safety rails for signs of wear, damage, or loose hardware. Address any issues promptly.
Adhering to these recommendations will contribute to a safe and comfortable experience with a vertically stacked bed that incorporates a larger mattress.
The subsequent section will offer a conclusion summarizing the benefits and potential applications of this type of sleeping arrangement.
1. Space Optimization
Space optimization, the efficient use of available area, represents a primary driver for the selection of vertically stacked beds with larger mattresses. In residential environments characterized by limited square footage, these configurations enable the accommodation of multiple occupants without compromising essential living space. The effect is a more functional and less cluttered environment. For example, in urban apartments or smaller homes, a vertically stacked bed frees up floor space that would otherwise be occupied by two separate beds, enabling the incorporation of additional furniture or activity areas.
The importance of space optimization as a component of vertically stacked beds stems from its direct impact on the quality of life within a dwelling. Overcrowding can lead to psychological stress and reduced functionality. By leveraging vertical space, these beds mitigate these negative effects. Consider student housing, where maximizing sleeping capacity within a small room is critical. Vertically stacked beds allow for individual sleeping areas while providing room for desks, storage, and common areas, thereby enhancing the overall learning and living experience. The practical significance of understanding this connection lies in the ability to make informed decisions about furniture selection, particularly in space-constrained environments.
In summary, vertically stacked beds with larger mattresses address the challenge of limited space by providing a compact and efficient sleeping solution. This is especially important in densely populated areas or smaller living spaces, linking furniture design directly to the broader themes of urban planning and interior design aimed at optimizing resource utilization and improving living conditions. The judicious application of vertically stacked beds contributes to more functional and comfortable living spaces.
2. Structural Integrity
The structural integrity of vertically stacked beds designed for larger mattresses is paramount to ensuring user safety and product longevity. It refers to the capacity of the entire structure to withstand applied loads, stresses, and environmental factors without critical deformation or failure. A deficiency in any structural component can lead to catastrophic collapse, posing a significant risk of injury to occupants. The increased weight of a larger mattress, coupled with the potential for multiple users, amplifies the stresses on the frame, joints, and support system, thereby intensifying the need for robust structural design and construction.
The materials used in the construction of these beds, along with the design of the joints and connections, directly influence structural integrity. Solid wood, heavy-gauge steel, and reinforced composite materials are commonly employed to provide adequate strength and stiffness. However, the quality of workmanship and the precision of assembly are equally crucial. Improperly tightened fasteners, misaligned joints, or substandard welding can compromise the load-bearing capacity of the structure. Consider the scenario of a student dormitory where a poorly constructed vertically stacked bed supporting a large mattress collapses under the combined weight of two occupants, resulting in severe injuries. This example underscores the practical significance of adhering to stringent manufacturing standards and conducting thorough quality control inspections.
In conclusion, maintaining structural integrity is non-negotiable in the design and construction of vertically stacked beds intended for larger mattresses. Neglecting this aspect can have severe consequences, ranging from product failure and property damage to serious personal injury. Therefore, rigorous engineering analysis, high-quality materials, precise manufacturing processes, and diligent quality control measures are essential to ensure the safety and reliability of these sleeping structures. This understanding connects furniture design with engineering principles aimed at creating safe and durable living environments.
3. Occupant Safety
Occupant safety constitutes a critical design and usage consideration for vertically stacked beds with larger mattresses. Given the elevated sleeping position of at least one occupant, potential risks associated with falls and structural instability necessitate strict adherence to safety standards and responsible usage practices.
- Guardrail Height and Integrity
Adequate guardrail height on the upper tier is essential to prevent accidental falls during sleep. Guardrails must extend sufficiently above the mattress surface and possess structural integrity to withstand leaning or accidental impacts. For instance, standards often dictate a minimum guardrail height of 5 inches above the mattress. Failure to meet this specification increases the risk of serious injury.
- Ladder or Stairway Stability and Design
The ladder or stairway providing access to the upper tier must be securely attached to the bed frame and designed to prevent slips or falls. Steps should be adequately spaced and textured to provide a secure foothold. Insufficiently stable ladders or stairways pose a significant risk, particularly for children or individuals with mobility limitations.
- Weight Capacity Adherence
Exceeding the stated weight capacity of either the upper or lower tier can compromise the structural integrity of the bed frame and increase the likelihood of collapse. Weight limits must be clearly communicated and strictly observed. Ignoring weight restrictions can lead to catastrophic failure and potential injury.
- Mattress Selection and Fit
The mattress chosen for the upper tier must fit snugly within the frame, preventing movement or gaps that could create a fall hazard. An improperly sized mattress can shift or slide, increasing the risk of an occupant falling between the mattress and the guardrail.
These facets collectively underscore the importance of prioritizing safety in the selection, assembly, and utilization of vertically stacked beds incorporating larger mattresses. Diligence in adhering to safety standards and responsible usage practices are paramount to mitigating potential risks and ensuring occupant well-being.
4. Mattress Compatibility
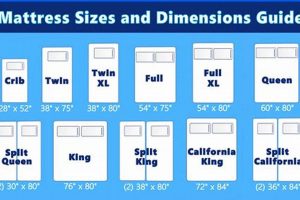
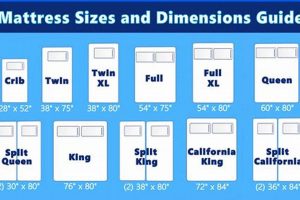
Mattress compatibility is a critical factor in the safe and effective utilization of a vertically stacked sleeping configuration incorporating a larger mattress, often referred to as a “full mattress bunk bed.” Ensuring that the selected mattress appropriately corresponds with the dimensions and structural requirements of the bunk bed frame is essential for stability, support, and occupant safety.
- Dimensional Fit
The mattress must precisely fit the designated space within the bunk bed frame. Overly large mattresses may not properly seat within the frame, compromising structural integrity and potentially causing instability. Conversely, undersized mattresses create gaps that pose a risk of entrapment or falls, particularly on the upper tier. The internal dimensions of the bunk bed frame must be meticulously matched to the mattress dimensions to prevent these hazards. For example, a mattress marketed as “full-size” can vary slightly in actual measurements; therefore, precise measurements and verification are necessary.
- Thickness Considerations
Mattress thickness influences the effective height of safety rails on the upper tier. An excessively thick mattress reduces the vertical clearance provided by the safety rails, diminishing their ability to prevent falls. Conversely, a very thin mattress may not provide adequate support and comfort. Manufacturers often specify a maximum recommended mattress thickness for each bunk bed model, and adhering to this guideline is critical to maintaining safety standards. An example includes a recommendation that an upper bunk bed mattress should be no more than 8 inches thick.
- Weight Compliance
The combined weight of the mattress and the intended occupant must not exceed the weight capacity specified by the bunk bed manufacturer. Overloading the bunk bed frame can compromise its structural integrity, leading to deformation, instability, or even collapse. The mattress weight must be factored into the overall weight assessment to ensure compliance with the bunk bed’s safety limitations. This consideration is amplified when a larger mattress is involved, as the increased mass places greater stress on the frame components.
- Material Composition and Support
The material composition and internal support structure of the mattress directly impact its ability to provide adequate support and weight distribution. A mattress that is too soft or lacks sufficient support can sag or deform, creating uneven sleeping surfaces and potentially exacerbating back problems. Furthermore, inadequate support can increase the risk of rolling off the mattress, especially on the upper tier. Selecting a mattress with appropriate firmness and internal structure, such as innerspring or memory foam, is crucial for optimizing comfort and safety in a bunk bed setting.
These facets collectively highlight the crucial role of mattress compatibility in the safe and functional deployment of a “full mattress bunk bed.” Ensuring a proper fit, appropriate thickness, weight compliance, and adequate support are paramount to mitigating risks and maximizing the utility of these space-saving sleeping arrangements. Neglecting these factors can compromise the structural integrity of the bed, the safety of its occupants, and the overall quality of the sleep experience.
5. Assembly Complexity
The assembly complexity associated with a vertically stacked bed accommodating a larger mattress represents a significant determinant of its overall safety and long-term structural integrity. These configurations typically involve numerous components, intricate connection mechanisms, and a precise sequence of steps necessary for proper construction. Inadequate assembly, stemming from unclear instructions, missing hardware, or insufficient user expertise, directly compromises the stability and load-bearing capacity of the entire structure. For example, a failure to securely fasten critical support beams or properly align joint connections can create weak points susceptible to failure under normal use conditions.
The importance of addressing assembly complexity stems from its direct impact on occupant safety and potential liability issues. A poorly assembled vertically stacked bed poses a significant risk of collapse, resulting in potential injuries to individuals using it. Manufacturers bear a responsibility to provide clear, comprehensive, and user-friendly assembly instructions, supported by appropriate diagrams and visual aids. Furthermore, the design of the bed itself should minimize the potential for errors during assembly, incorporating features such as pre-drilled holes, clearly labeled components, and intuitive connection mechanisms. Consider the implications of a vacation rental property owner assembling several such beds without sufficient expertise, potentially creating hazardous sleeping arrangements for unsuspecting guests.
In summary, the assembly complexity associated with vertically stacked beds designed for larger mattresses necessitates careful consideration by both manufacturers and consumers. Clear instructions, intuitive designs, and diligent adherence to recommended procedures are essential to ensure structural integrity and occupant safety. Neglecting the assembly process can have severe consequences, ranging from product failure to significant personal injury, reinforcing the need for a proactive approach to mitigating assembly-related risks. This directly links product design and consumer responsibility to ensuring safer living environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the selection, safety, and utilization of vertically stacked beds configured to accommodate a larger mattress. These answers aim to provide clarity and promote informed decision-making.
Question 1: What is the standard weight capacity for the upper tier of a full mattress bunk bed?
The standard weight capacity varies by manufacturer and model but typically ranges from 200 to 250 pounds. Always consult the manufacturer’s specifications to determine the precise weight limit for the specific product in question. Exceeding the stated weight capacity can compromise structural integrity.
Question 2: What are the minimum recommended ceiling height requirements?
Minimum ceiling height depends on the bed’s overall height. It is recommended to have at least 24 to 36 inches of clearance between the top of the upper mattress and the ceiling to allow for comfortable movement. Measurement prior to purchase is essential.
Question 3: What safety features should be considered when purchasing?
Essential safety features include sturdy guardrails on the upper tier that extend at least 5 inches above the mattress surface, a stable ladder or staircase with non-slip treads, and a robust frame construction made from durable materials such as solid wood or heavy-gauge steel.
Question 4: Can any full-size mattress be used on the lower bunk?
While most standard full-size mattresses are compatible with the lower bunk, confirm that the dimensions of the mattress match the internal dimensions of the bed frame to ensure a proper and secure fit. An ill-fitting mattress can pose safety risks.
Question 5: How frequently should the frame be inspected for signs of wear or damage?
The frame, ladder, and all connection points should be inspected at least every three months for loose hardware, cracks, or other signs of damage. Promptly address any issues discovered to maintain structural integrity.
Question 6: What is the recommended age range for individuals using the upper bunk?
It is generally recommended that children under the age of six years should not use the upper bunk due to the risk of falls. Older children and adults should exercise caution and adhere to all safety guidelines.
These responses serve to clarify common concerns regarding the construction and utilization of vertically stacked beds which include a larger sized mattress. Responsible application of this information will contribute to a safer experience.
The following sections will elaborate on the proper setup and maintenance procedures for these structures.
Conclusion
This exploration has illuminated the salient aspects of the full mattress bunk bed configuration, emphasizing design considerations, safety protocols, and optimal utilization strategies. Key points addressed encompass structural integrity, weight capacity adherence, occupant safety measures, and the imperative of meticulous assembly procedures. A comprehensive understanding of these elements is paramount for ensuring both the longevity of the structure and the well-being of its occupants.
Responsible application of the principles outlined herein is essential for mitigating potential risks and maximizing the benefits associated with vertically stacked sleeping arrangements incorporating larger mattresses. Prioritizing safety, adhering to manufacturer guidelines, and conducting regular inspections constitute fundamental practices for fostering a secure and functional living environment. Future advancements in materials and design may further enhance the safety and efficiency of these space-saving solutions; however, a steadfast commitment to established safety standards remains paramount.


![Best Full Size Daybed with Mattress [Deals] Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Best Full Size Daybed with Mattress [Deals] | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-2863-300x200.jpg)


![Buy the Best Full Futon with Mattress - [Year] Guide Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Buy the Best Full Futon with Mattress - [Year] Guide | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-2858-300x200.jpg)