A support structure designed for a full-size sleep surface provides a stable and even platform. These structures elevate the mattress, promoting airflow and preventing sagging. An example would be a wooden frame with slats or a metal grid supporting a 54-inch wide by 75-inch long mattress.
The utilization of a proper base extends the lifespan of the sleeping surface and contributes to improved sleep quality. Historically, rudimentary frames evolved into sophisticated designs that offer enhanced support and durability. These support structures prevent premature wear, maintain mattress integrity, and can contribute to better spinal alignment for the sleeper.
The following discussion will delve into various types of these support systems, material considerations, and factors influencing their selection to optimize sleep and ensure the longevity of the chosen mattress.
Essential Considerations for Selecting a Mattress Foundation
Proper selection ensures optimal mattress support and longevity. These guidelines will assist in making an informed decision.
Tip 1: Determine Compatibility. Verify the selected foundation is designed for use with the specific type of mattress. Incompatible pairings can void warranties or degrade performance.
Tip 2: Assess Support Requirements. Consider the weight distribution needs of the mattress and occupants. Heavier individuals may require reinforced structures.
Tip 3: Evaluate Foundation Height. Determine the desired bed height. Consider room aesthetics and accessibility for users with mobility limitations.
Tip 4: Inspect Material Quality. Opt for foundations constructed from durable materials such as solid wood or heavy-gauge steel for extended lifespan.
Tip 5: Prioritize Proper Ventilation. Select foundations that promote airflow to prevent moisture buildup and maintain a hygienic sleep environment.
Tip 6: Examine Foundation Structure. Choose between solid platforms, slat systems, or adjustable bases based on desired support level and features.
Implementing these considerations ensures the chosen foundation contributes positively to sleep quality and extends the useful life of the accompanying mattress.
The subsequent sections will further detail specific foundation types and their applications.
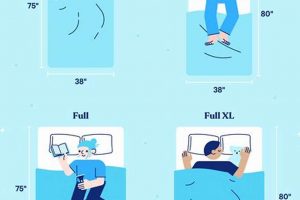
1. Size Compatibility
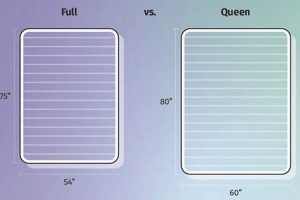
Size compatibility is a foundational element in achieving optimal performance from a mattress foundation. A full-size mattress, typically measuring 54 inches wide and 75 inches long, requires a foundation of corresponding dimensions. The effect of mismatched sizes can range from compromised mattress support to complete warranty invalidation. A foundation too small fails to provide adequate edge support, accelerating wear and creating an unstable sleeping surface. Conversely, a foundation too large allows the mattress to shift, increasing the risk of damage and discomfort.
For instance, consider a full-size memory foam mattress placed on a queen-size foundation. The overhang not only lacks necessary support but also concentrates pressure points, reducing the mattress’s lifespan. Real-life examples frequently illustrate the consequences of neglecting size compatibility: sagging edges, uneven weight distribution, and reduced sleep quality. Understanding this relationship is practically significant for extending mattress longevity and maximizing comfort.
In summary, ensuring precise size compatibility between a full-size mattress and its foundation is paramount. Challenges arise primarily from inconsistencies in manufacturing standards; therefore, careful measurement and verification are essential. Accurate pairing reinforces the broader goal of a durable and comfortable sleep environment, emphasizing the integral role of size compatibility in the selection and maintenance of a full mattress foundation.
2. Support Structure
The support structure of a full mattress foundation is the core element determining its functionality and effectiveness. It directly impacts the lifespan of the mattress, the quality of sleep experienced, and the overall integrity of the bed system. Varying support structures offer distinct advantages and disadvantages, influencing the distribution of weight, airflow, and the degree of motion isolation.
- Slat Systems
Slat systems involve a series of horizontal bars, typically made of wood or metal, spaced evenly across the foundation. These slats provide a flexible yet supportive base for the mattress. Examples include solid wood slats offering firm support, or flexible euro slats made with plywood that slightly flex under load to provide better pressure relief. The spacing between slats is critical; excessive gaps can lead to mattress sagging, while insufficient spacing can reduce airflow. Slat systems are often favored for their affordability and adaptability to different mattress types.
- Solid Platforms
Solid platforms present a completely uniform surface, usually constructed of wood or composite materials. This type of support maximizes mattress contact, providing a firm, stable base. An example is a sheet of plywood placed atop a frame, or a pre-fabricated platform with a fabric covering. The solid nature of the platform eliminates gaps, ensuring even weight distribution, but can potentially restrict airflow, leading to moisture buildup and reduced mattress breathability. These are commonly used with memory foam mattresses that benefit from maximum support.
- Metal Grid Systems
Metal grid systems utilize a network of interconnected metal wires or bars to create a supportive surface. These systems often feature open designs that promote airflow, reducing the risk of moisture accumulation. Examples include welded wire grids or interconnected metal coils stretched across a frame. While durable and supportive, some metal grid systems can be prone to squeaking or creaking noises over time. These are often seen in adjustable bed frames or heavy-duty foundations.
- Adjustable Bases
Adjustable bases provide motorized, dynamic support, allowing users to customize the angle of the mattress. These foundations offer unique comfort and health benefits, such as improved circulation and reduced snoring. An example would be an adjustable base that allows the head and foot of the bed to be elevated to various angles. While versatile, adjustable bases can be more expensive and may not be compatible with all mattress types. Their complex mechanisms also require more maintenance compared to simpler foundation designs.
In conclusion, the choice of support structure within a full mattress foundation is pivotal. Each type presents a unique balance of support, airflow, durability, and cost. Understanding these facets allows for an informed decision, optimizing both the mattress performance and the overall sleep experience. Examples of real-world usage further illustrate the practical impact of these support structures, solidifying their importance within the overall mattress system.
3. Material Durability
Material durability constitutes a critical aspect of a full mattress foundation, directly influencing its lifespan and ability to provide consistent support. The selection of robust materials mitigates the risk of premature structural failure, preventing sagging and ensuring uniform weight distribution over time. For example, a full mattress foundation constructed with kiln-dried hardwood is demonstrably more resistant to warping and cracking compared to one assembled with lower-grade softwood. The use of heavy-gauge steel in the frame and support system further enhances durability, particularly in withstanding the dynamic stresses associated with movement during sleep. Consequently, the material composition directly affects the foundation’s capacity to maintain its structural integrity under sustained use.
The practical significance of material durability extends to cost-effectiveness. While initial cost savings might be achieved by opting for foundations made from less durable materials, the long-term implications involve increased susceptibility to damage, reduced support capabilities, and ultimately, the need for premature replacement. Conversely, investing in a foundation crafted from durable materials, such as reinforced steel or solid hardwood, represents a more sustainable approach. Consider the case of a rental property owner furnishing multiple units; the selection of durable foundations minimizes replacement frequency, yielding considerable cost savings over the long term. The consideration of material durability should also encompass the fabric or covering materials, as these components are subject to wear and tear. A foundation upholstered with a high-quality, abrasion-resistant fabric maintains its aesthetic appeal and structural integrity over extended periods.
In summary, material durability is an indispensable element in the design and selection of a full mattress foundation. Its influence extends from structural stability and long-term cost-effectiveness to sustained support performance. Challenges in assessing material durability lie in differentiating between superficial aesthetics and genuine structural robustness. Therefore, a thorough understanding of material properties and construction techniques is essential for making an informed decision, ensuring that the foundation provides reliable and lasting support for the mattress, thereby enhancing overall sleep quality and mattress lifespan.
4. Height considerations
Height considerations play a pivotal role in the selection and integration of a full mattress foundation, influencing both the functionality and ergonomics of the bed system. The height of the foundation, in conjunction with the mattress thickness, determines the overall bed height, a factor that directly impacts ease of access, particularly for individuals with mobility limitations. For example, a low-profile foundation paired with a thick mattress might result in a bed height that is challenging to enter and exit for elderly users or those with joint pain. Conversely, an excessively tall foundation combined with a thin mattress can lead to an uncomfortably elevated sleeping surface. The intended user demographic and their specific physical needs must therefore inform the height selection process.
Furthermore, height considerations extend beyond mere accessibility to encompass aesthetic integration within the bedroom environment. The proportion of the bed relative to other furniture and architectural elements within the room contributes significantly to the overall visual harmony. A foundation that elevates the mattress to a visually balanced height can enhance the room’s aesthetic appeal, while a disproportionate height can create a sense of imbalance. Practical examples of this dynamic are evident in interior design principles, where the bed often serves as a focal point, and its height is carefully considered in relation to bedside tables, lamps, and wall dcor. Moreover, storage space beneath the bed is often dictated by the foundation height, providing an opportunity for maximizing space utilization in smaller living environments. This space, in turn, can impact the perceived spaciousness and organization of the room.
In summary, height considerations represent a multifaceted aspect of full mattress foundation selection. The ergonomic implications for accessibility, the aesthetic integration within the room, and the potential for under-bed storage all underscore the importance of carefully assessing height requirements. Challenges in this selection process arise from the variability in mattress thicknesses and individual user preferences. Understanding and addressing these challenges ensures the selection of a full mattress foundation that not only provides adequate support but also contributes to a comfortable, functional, and aesthetically pleasing sleep environment.
5. Ventilation design
Ventilation design, as an integral component of a full mattress foundation, directly impacts the mattress’s lifespan and the sleeper’s health. Insufficient airflow within the foundation leads to moisture accumulation from perspiration and humidity, creating a breeding ground for mold, mildew, and dust mites. The resulting deterioration of mattress materials compromises support and creates an unhealthy sleeping environment. An example is the contrast between a solid platform foundation, which inherently restricts airflow, and a slat system, which allows for greater ventilation. In the case of memory foam mattresses, known for trapping heat, the foundation’s ventilation design becomes even more critical. A well-ventilated foundation mitigates these risks, promoting a drier, more hygienic sleep surface. The practical significance lies in preventing premature mattress degradation and minimizing exposure to allergens and irritants.
The type of materials used in the foundation construction also influences ventilation. Open-weave fabrics covering the foundation facilitate airflow, while solid, non-breathable materials impede it. Slat systems, particularly those with wider spacing between slats, offer enhanced ventilation compared to solid platforms. Further optimization can be achieved through design features such as strategically placed ventilation holes or channels within the foundation structure. For instance, some foundations incorporate mesh panels to promote airflow around the mattress perimeter. Adjustable bed frames, while offering unique benefits, often require careful consideration of ventilation to prevent moisture buildup in the enclosed space. The effectiveness of any ventilation design must be evaluated in the context of the overall sleep environment, including room humidity and temperature.
In summary, ventilation design is a crucial factor in the functionality and longevity of a full mattress foundation. It directly impacts the mattress’s health and the sleeper’s well-being by mitigating moisture accumulation and promoting a more hygienic sleep environment. Challenges in optimizing ventilation design lie in balancing support requirements with airflow needs and selecting appropriate materials. Addressing these challenges ensures the foundation contributes positively to the overall sleep experience, preventing premature mattress degradation and minimizing exposure to allergens and irritants.
6. Warranty adherence
Warranty adherence is a crucial, yet often overlooked, aspect of selecting a full mattress foundation. Mattress warranties frequently stipulate specific foundation requirements, and failure to comply can result in warranty voidance, leaving the consumer responsible for repair or replacement costs.
- Foundation Type Requirements
Many mattress manufacturers specify the acceptable types of foundations, such as slat systems, solid platforms, or adjustable bases. For example, a memory foam mattress warranty may mandate the use of a solid, non-yielding foundation to ensure proper support and prevent sagging. Deviating from these requirements, like using an incompatible box spring with insufficient support, can invalidate the warranty. This stipulation safeguards the manufacturer against damage arising from improper support.
- Slat Spacing Specifications
For slat-based foundations, manufacturers often dictate the maximum permissible spacing between individual slats. Excessive spacing can lead to uneven weight distribution and premature mattress wear. A common example involves warranties requiring no more than a 2-inch gap between slats to maintain adequate support. Failure to meet this specification can void the warranty, particularly if mattress sagging occurs in the unsupported areas. The slat spacing requirement ensures uniform support and prevents localized stress points.
- Frame Construction Standards
Mattress warranties may impose standards on the construction and materials used in the foundation frame. For instance, a warranty may require a frame constructed from solid wood or heavy-gauge steel to withstand the weight of the mattress and occupants. Using a flimsy or poorly constructed frame that collapses or deforms under load can void the warranty. This requirement aims to prevent damage to the mattress resulting from inadequate frame support. The construction standards ensure the frame is capable of bearing the intended weight without compromising mattress integrity.
- Proper Assembly and Usage
Warranties typically require proper assembly and usage of the foundation according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Improper assembly can lead to structural instability and premature wear, while misuse, such as exceeding the weight limit, can cause damage. A common example is failing to properly tighten bolts during assembly, resulting in a wobbly foundation that compromises mattress support. Neglecting these instructions can void the warranty, as damage resulting from improper assembly or misuse is not covered. Adhering to assembly and usage guidelines ensures the foundation functions as intended and provides the necessary support.
These facets of warranty adherence underscore the importance of carefully reviewing warranty terms prior to selecting a full mattress foundation. Non-compliance can have significant financial implications, rendering the warranty null and void. The connection between a mattress and its foundation is intrinsically linked, and adhering to the manufacturer’s specifications is paramount for preserving the warranty and maximizing the lifespan of the mattress.
7. Noise reduction
Noise reduction constitutes a significant aspect of a full mattress foundation’s design and functionality, directly impacting sleep quality and environmental comfort. The mitigation of extraneous sounds emanating from the bed system is essential for minimizing sleep disturbances and creating a more restful sleep environment. The following details key facets of noise reduction in relation to these foundations.
- Material Selection
The choice of materials significantly influences the noise generated by a foundation. Metal frames, particularly those with loose joints or connections, are prone to squeaking or creaking sounds during movement. Solid wood frames, when properly constructed, tend to be quieter due to their inherent damping properties. Examples of noise-reducing materials include wood with high density and steel frames with welded joints instead of bolted ones. The selection of these materials minimizes friction and vibration, reducing the potential for noise generation.
- Joint Construction and Fasteners
The method of joining the various components of a foundation plays a crucial role in noise reduction. Bolted connections can loosen over time, leading to squeaking and creaking. In contrast, welded joints and interlocking designs provide a more secure and stable connection, minimizing movement and noise. Furthermore, the use of noise-dampening fasteners, such as rubber washers or nylon inserts, can mitigate noise transmission between components. An example is using a mortise and tenon joint in a wooden frame, which provides a tight and stable connection.
- Slat Design and Support System
The design of the slat system and its interaction with the frame can be a source of noise. Slats that are loosely fitted or inadequately supported can rattle against the frame during movement. Rubberized slat holders or fabric-lined contact points can dampen vibrations and reduce noise. An example is a slat system with rubber end caps that prevent direct contact between the wood and the metal frame. Ensuring a snug and secure fit for each slat is critical for minimizing noise generation.
- Fabric Upholstery and Padding
The presence of fabric upholstery or padding on the foundation can contribute to noise reduction by absorbing vibrations and muffling sounds. Thick, dense fabrics provide better sound insulation compared to thin, loosely woven materials. An example is a foundation fully upholstered with a layer of foam padding beneath the fabric, which dampens vibrations and minimizes noise transmission. The selection of appropriate fabrics and padding materials enhances the overall quietness of the bed system.
These facets collectively contribute to the noise reduction capabilities of a full mattress foundation. The integration of noise-reducing materials, secure joint construction, optimized slat design, and strategic use of fabric upholstery enhances sleep quality by minimizing disturbances caused by bed frame noise. While complete noise elimination is difficult to achieve, a focus on these design elements significantly reduces the potential for disruptive sounds and promotes a more restful sleep environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding full mattress foundations, providing clarity on their selection, usage, and maintenance.
Question 1: What are the primary indicators that a full mattress foundation requires replacement?
Observable sagging, audible squeaking or creaking, and visible structural damage suggest the foundation’s load-bearing capacity has diminished. An uneven sleeping surface is a definitive sign, affecting sleep quality and mattress lifespan.
Question 2: How does the choice of foundation material influence the mattress’s ventilation and potential for mold growth?
Solid platform foundations restrict airflow, increasing humidity and mold risk. Slat systems, with proper spacing, promote ventilation, reducing moisture accumulation. Material selection is crucial for optimizing air circulation beneath the mattress.
Question 3: Is it permissible to use a full-size mattress on a queen-size foundation frame?
Deviation from the prescribed dimensions is not recommended. A mismatch undermines support, causes uneven wear, and potentially invalidates the mattress warranty. Precise size compatibility is crucial.
Question 4: How does the foundation’s height affect accessibility, particularly for individuals with mobility challenges?
The combined height of the foundation and mattress dictates bed accessibility. Low-profile foundations can present challenges for those with limited mobility, while excessively tall configurations pose safety risks. Careful consideration of user needs is paramount.
Question 5: What is the recommended slat spacing for a full mattress foundation to prevent mattress sagging?
Slat spacing should not exceed two inches to provide adequate support. Wider gaps compromise weight distribution, accelerating mattress wear and potentially voiding the warranty. Adhering to recommended spacing is essential.
Question 6: How can one assess the noise-reduction capabilities of a full mattress foundation before purchase?
Inspect construction quality, material selection, and joint stability. Evaluate the presence of noise-dampening features such as rubberized slat holders or fabric upholstery. A well-constructed foundation minimizes squeaking and creaking sounds.
In summary, the selection and maintenance of a suitable foundation requires attention to dimensions, materials, and design. Addressing these considerations will ensure optimal sleep quality and prolong the lifespan of the investment.
The next section explores foundation maintenance and troubleshooting strategies.
In Conclusion
This exploration has detailed the essential aspects of a full mattress foundation, emphasizing the criticality of size compatibility, support structure, material durability, height considerations, ventilation design, warranty adherence, and noise reduction. These elements collectively determine the foundation’s ability to support the mattress effectively, ensure a comfortable sleep environment, and maximize mattress lifespan.
The selection of a full mattress foundation should not be viewed as an ancillary decision but rather as an integral component of the overall sleep system. Careful evaluation of the aforementioned factors is paramount. Doing so protects the mattress investment, promotes restful sleep, and ensures long-term value. Further research and consultation with professionals are encouraged to make the optimal selection.





![Best Size Full Mattress [Guide] Comfort & Value! Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Best Size Full Mattress [Guide] Comfort & Value! | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-2874-300x200.jpg)