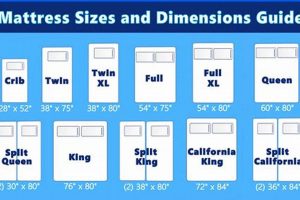
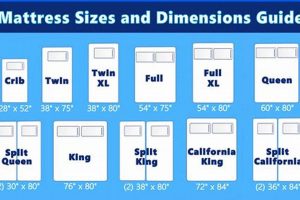
Encasing a 54-inch wide and 75-inch long mattress for protection during transit and storage requires specialized materials and techniques. This encasement typically involves layers of robust plastic sheeting, often polyethylene, sealed to prevent moisture and physical damage. An example is a tightly sealed mattress within several layers of thick plastic, reinforced at the seams to withstand handling.
Proper protection offers several advantages. It safeguards against dirt, dust, and potential infestations during warehousing and transportation. Furthermore, it can prevent tearing or compression, preserving the integrity of the sleeping surface and ensuring customer satisfaction upon delivery. Historically, inadequate protection led to significant product loss and increased return rates for mattress retailers, driving the development of improved packaging methods.
The following sections will delve into specific materials used, optimal packaging methods, considerations for sustainability, and best practices for ensuring secure and cost-effective delivery of these mattresses. Attention will also be given to challenges faced and innovative solutions being developed in the realm of mattress product protection.
Packaging Best Practices
Effective strategies are crucial to ensure the safe and efficient handling of these mattresses. Implementing the following recommendations can minimize damage and reduce associated costs.
Tip 1: Select Robust Materials: Utilize polyethylene sheeting with a minimum thickness of 6 mil to provide adequate puncture and tear resistance during handling and transportation. Thicker gauges offer enhanced protection against sharp objects and rough surfaces.
Tip 2: Ensure Airtight Sealing: Employ heat-sealing techniques to create a complete barrier against moisture, dust, and potential pests. Overlapping seams and reinforced edges are essential to prevent breaches during transit.
Tip 3: Implement Vacuum Compression: Consider vacuum-sealing to reduce the overall volume, which lowers shipping costs and minimizes the risk of shifting during transport. Ensure compatibility with the mattress type to prevent damage.
Tip 4: Add Corner Protection: Incorporate reinforced cardboard or plastic corner protectors to mitigate damage from impacts and stacking. These reinforcements should be securely affixed to the mattress corners before wrapping.
Tip 5: Utilize Proper Labeling: Clearly label each package with handling instructions, including “Fragile” and “This Side Up” to alert handlers to exercise caution. Include a barcode for efficient tracking and inventory management.
Tip 6: Consider Edge Reinforcement: Add edge protection to safeguard against abrasion and tearing, especially along the mattress perimeter. This reinforcement can take the form of additional layers of film or specialized edge guards.
Tip 7: Conduct Drop Tests: Perform simulated drop tests from various heights to evaluate the effectiveness of the current method. Adjust the method as needed to improve resilience.
Adhering to these practices contributes significantly to minimizing damage, lowering shipping expenses, and ensuring the safe arrival of the product in optimal condition, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction.
The subsequent section will explore the future of the practice, examining sustainable alternatives and emerging technologies that are reshaping the industry.
1. Material Strength
Material strength is a paramount consideration in the realm of protection for mattresses. The ability of the protective encasement to withstand external forces dictates the integrity of the mattress during transit, storage, and handling. Choosing materials with inadequate strength can lead to tears, punctures, and subsequent contamination or damage to the product.
- Tensile Strength and Tear Resistance
Tensile strength, measured in pounds per square inch (PSI), indicates the material’s resistance to breaking under tension. Tear resistance, typically measured in grams, defines the material’s ability to resist tearing when a force is applied. For mattress protection, high tensile strength prevents stretching and rupture during handling, while high tear resistance minimizes the risk of puncture propagation from minor abrasions. For example, polyethylene films with a tensile strength exceeding 2000 PSI and tear resistance above 500 grams are commonly used to protect mattresses during transportation.
- Puncture Resistance
Puncture resistance is a critical attribute, quantifying the material’s ability to withstand penetration by sharp objects. This characteristic is particularly important in warehouse and shipping environments where mattresses may come into contact with protruding edges or debris. Materials with higher puncture resistance ratings, often achieved through multi-layer construction or the incorporation of reinforcing fibers, offer enhanced protection against potential damage. A material’s puncture resistance might be measured with an impact test or dart drop test.
- Compression Resistance
Compression resistance refers to the material’s ability to withstand crushing forces without significant deformation or failure. Mattresses are often stacked during storage and transport, subjecting the lower units to considerable compressive loads. Materials that maintain their structural integrity under these conditions prevent the mattress from being misshapen or damaged. This can be achieved by adding corner protectors or utilizing a material that is naturally resistant to compression, like a thicker gauge plastic.
- Abrasion Resistance
Abrasion resistance describes a material’s ability to withstand surface wear caused by rubbing or friction. During transportation, mattresses may rub against other objects or surfaces, potentially leading to abrasion and weakening of the packaging. Materials with good abrasion resistance maintain their integrity, preventing the formation of holes or tears that could compromise the protection of the mattress. One way to ensure abrasion resistance is to use multiple layers of material to act as a buffer, preventing the mattress itself from undergoing the abrasion.
In summation, the selection of materials with appropriate strength characteristicsincluding tensile strength, tear resistance, puncture resistance, compression resistance, and abrasion resistanceis fundamental to effective protection. Choosing materials that adequately address these factors mitigates the risks associated with handling, transportation, and storage, ultimately preserving the condition of the mattress and ensuring customer satisfaction.
2. Sealing Integrity
Sealing integrity is a critical element in the protection of full size mattresses during storage and transit. The effectiveness of any protective material is contingent upon the ability to maintain a complete and impermeable barrier against external elements.
- Barrier Against Moisture Intrusion
A compromised seal permits moisture to penetrate the protective encasement. Humidity and condensation can lead to the growth of mold and mildew on the mattress, rendering it unsellable and potentially harmful to human health. Maintaining an airtight seal is therefore essential to prevent moisture-related damage and preserve the mattress’s hygiene and structural integrity. For example, inadequate sealing during humid weather can cause moisture to seep into the packaging during transit causing the mattress to grow mold.
- Prevention of Pest Infestation
Breaches in the seal provide entry points for insects, rodents, and other pests. These organisms can damage the mattress fibers, introduce allergens, and compromise the overall cleanliness of the product. A robust and continuous seal acts as a physical barrier, preventing pests from accessing and infesting the mattress during storage and transportation. Bed bugs, for instance, can easily infest mattresses with even minor breaches in protection.
- Containment of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
New mattresses often emit VOCs, which can be unpleasant or even harmful in high concentrations. A well-sealed encasement helps contain these emissions, preventing them from dissipating into the surrounding environment during storage and transit. This is particularly important for mattresses made with foam or treated with chemical finishes. Mattress manufacturers will often try to minimize these emissions, and sealing integrity helps to keep any residual compounds contained inside the packaging.
- Maintenance of Vacuum Compression
Many mattresses are vacuum-compressed prior to packaging to reduce their volume and shipping costs. The integrity of the seal is crucial for maintaining this compressed state. A leak in the seal will allow air to re-enter, causing the mattress to expand and negating the benefits of vacuum compression. This can increase shipping expenses and potentially damage the mattress if it is subjected to excessive force during expansion. A tear or weak seal on the packaging for a mattress compressed for shipping will cause the mattress to expand and be at risk of damage.
Consequently, maintaining a high level of sealing integrity is indispensable for safeguarding mattresses from environmental contaminants, pests, and premature expansion. Proper sealing techniques and rigorous quality control measures are essential to ensuring the long-term protection and marketability of these products. The choice of sealing method, such as heat sealing or adhesive sealing, significantly impacts the overall efficacy of the protective measure. These sealing factors contribute to the mattresses quality and longevity, helping provide customer satisfaction.
3. Size Optimization
In the context of full size mattress packaging, size optimization refers to the strategic reduction of the packaging’s dimensions to minimize material usage, reduce shipping costs, and improve storage efficiency, while simultaneously ensuring adequate protection of the mattress.
- Minimizing Material Waste
Optimizing the size directly reduces the amount of packaging material required. For example, precise measurements of the mattress enable manufacturers to tailor the protective encasement, eliminating excess plastic or cardboard. Decreasing material usage translates to cost savings and reduces the environmental impact associated with packaging production and disposal. Failure to reduce material waste would lead to excess costs.
- Reducing Shipping Costs
Dimensional weight pricing, a common practice in the shipping industry, calculates costs based on package volume rather than actual weight. Compressing the packaging tightly around the mattress minimizes its dimensional footprint, thereby lowering shipping charges. This is particularly relevant for large items like full size mattresses, where volume can significantly impact transportation expenses. Reducing shipping costs is vital to improving product profit margin.
- Improving Storage Efficiency
Optimized dimensions allow for more efficient storage in warehouses and retail environments. Smaller, more compact packages maximize the use of available space, reducing storage costs and streamlining inventory management. The ability to stack more mattresses in a given area enhances operational efficiency. This benefit is particularly important because storing items in an appropriate environment helps to maintain product quality.
- Enhancing Handling Ease
A well-optimized package size facilitates easier handling throughout the supply chain. Smaller, more manageable packages are easier for workers to load, unload, and maneuver, reducing the risk of damage or injury. This can lead to improved productivity and reduced labor costs. By optimizing the packaging size, the workers’ jobs will be easier and more efficient, leading to greater job satisfaction and improved profits for the company.
These facets of size optimization are interwoven and collectively influence the economic and environmental sustainability of the full size mattress packaging process. Careful consideration of these factors is crucial for manufacturers seeking to minimize costs, reduce their environmental footprint, and ensure efficient distribution of their products.
4. Damage Prevention
Damage prevention is intrinsically linked to full size mattress packaging. The primary objective of encasing a mattress is to safeguard it from potential harm during shipping, handling, and storage. Defects such as tears, punctures, stains, or compression can render a mattress unsellable, leading to financial losses and reputational damage for the manufacturer and retailer. Effective packaging acts as a barrier, mitigating these risks. For example, a mattress improperly packaged may suffer edge damage during transit if it rubs against the inside of a truck, causing the product to need to be sold as a discount, resulting in financial loss.
The effectiveness of protection depends on several factors, including the materials employed, the sealing method, and the overall design. High-strength polyethylene films resist punctures and tears, while proper sealing prevents moisture ingress and pest infestation. Corner protectors mitigate damage from impacts, and adequate cushioning absorbs shocks during handling. Vacuum compression minimizes movement within the package, reducing the risk of abrasion. Failure in any of these areas can compromise protection, increasing the likelihood of defects. An unprotected or poorly protected mattress may suffer moisture damage during transit which causes it to grow mold, a scenario that causes the retailer to have to dispose of the mattress which results in a total financial loss.
In summary, effective protection strategies are essential for preserving the integrity of full size mattresses throughout the supply chain. Prioritizing robust packaging materials, secure sealing techniques, and thoughtful design considerations minimizes the risk of damage, ensuring that the product arrives in optimal condition, thereby reducing financial losses and maximizing customer satisfaction. Manufacturers should continuously evaluate and improve their protection protocols to adapt to evolving challenges in transportation and storage.
5. Cost Efficiency
Cost efficiency, in the context of full size mattress packaging, refers to the optimization of resources to minimize expenses associated with materials, labor, transportation, and potential damage during distribution. Achieving this balance is crucial for maintaining profitability and competitiveness in the mattress industry.
- Material Selection and Minimization
Choosing cost-effective yet durable materials is paramount. Utilizing thinner gauge polyethylene, where structurally feasible, reduces material costs without compromising protection. Optimizing packaging dimensions to closely fit the mattress minimizes wasted material, further reducing expenses. The initial cost of materials must be balanced with the need to prevent damage, as cheaper materials may lead to higher damage rates and increased overall costs.
- Labor Optimization
Streamlining the process minimizes labor costs. Automation of wrapping and sealing operations can increase throughput and reduce reliance on manual labor. Designing the packaging for ease of handling and application simplifies the process, enabling faster and more efficient packaging. Investments in automated equipment require careful consideration of the payback period and the potential for reduced labor expenses.
- Transportation Cost Reduction
Minimizing the size and weight of the packaged mattress reduces transportation costs, particularly when dimensional weight pricing is applied. Vacuum compression can significantly reduce volume, leading to lower shipping fees. Optimizing palletization and loading strategies maximizes the number of mattresses that can be transported per shipment. These strategies are crucial for reducing distribution expenses and maintaining competitive pricing.
- Damage Prevention and Loss Mitigation
Investing in robust protection minimizes the risk of damage during handling and transit, reducing the incidence of returns, replacements, and lost sales. While higher quality packaging may have a higher upfront cost, it can significantly reduce the downstream costs associated with damaged goods. A comprehensive cost-benefit analysis should consider the potential savings from reduced damage rates when evaluating packaging options.
In conclusion, cost efficiency in mattress protection is achieved through a holistic approach that considers material selection, labor optimization, transportation cost reduction, and damage prevention. Balancing these factors requires careful analysis and strategic decision-making to minimize overall expenses while ensuring the safe and efficient delivery of full size mattresses.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries related to the protective encasement of 54-inch by 75-inch mattresses. This aims to provide clarity on best practices and considerations.
Question 1: What is the standard material used for encasing these mattresses?
Polyethylene film is generally employed. The thickness, often measured in mils, varies depending on the desired level of protection. Higher mil values indicate greater puncture and tear resistance.
Question 2: Why is airtight sealing considered a necessity?
An impermeable barrier prevents moisture intrusion, mitigating the risk of mold and mildew growth. It also protects against pest infestations and assists in containing volatile organic compounds emitted by certain mattress materials.
Question 3: How does vacuum compression influence the overall packaging strategy?
This technique reduces the overall volume, leading to decreased shipping costs. Furthermore, it minimizes movement during transit, reducing the potential for abrasion and other forms of damage.
Question 4: What role do corner protectors play?
Corner protectors provide localized reinforcement, safeguarding against impacts and compression forces that are commonly encountered during stacking and handling.
Question 5: Are there specific labeling requirements for packaged mattresses?
Clearly marked handling instructions, including “Fragile” and “This Side Up,” are essential. Barcodes facilitate efficient tracking and inventory management throughout the supply chain.
Question 6: How can manufacturers ensure sustainability in their choices?
Consideration should be given to utilizing recycled or bio-based materials. Furthermore, optimizing dimensions minimizes waste, and partnering with recycling programs promotes responsible disposal practices.
Effective implementation requires attention to detail across all stages of the process. Prioritizing quality materials and proper techniques ensures the product’s safe arrival.
The subsequent section will delve into emerging technologies and innovative solutions in the mattress packaging landscape.
Conclusion
This exploration of encasing full size mattresses has highlighted crucial factors: material strength, sealing integrity, size optimization, damage prevention, and cost efficiency. These elements collectively determine the effectiveness and financial viability of protecting these products during transit, storage, and handling. A comprehensive approach, considering each factor, is essential for mitigating risks and ensuring product integrity.
The ongoing pursuit of innovative materials and enhanced techniques will continue to shape the future of mattress product preservation. Vigilance in adopting best practices and a commitment to continuous improvement will ultimately contribute to minimizing waste, reducing environmental impact, and maximizing customer satisfaction in the mattress industry.



![Best Full Size Daybed with Mattress [Deals] Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Best Full Size Daybed with Mattress [Deals] | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-2863-300x200.jpg)