A sleeping surface composed of foam, designed to fold into three sections for compact storage or portability. This type of bed commonly offers a balance of comfort and convenience, finding use in temporary sleeping arrangements, guest accommodations, or situations where space is limited. Its structure facilitates easy transportation and storage when not in use, differentiating it from traditional mattresses.
The practicality of such a bed derives from its space-saving design and relative lightness. Historically, solutions for temporary bedding have ranged from cots to futons; this particular design offers a compromise between the comfort of a conventional mattress and the portability of simpler alternatives. The folding capability addresses the need for adaptable sleeping solutions, providing a comfortable option without requiring permanent floor space. This becomes especially relevant in smaller living spaces or when hosting guests.
The subsequent sections will delve into the materials commonly used in these mattresses, the range of available sizes and thicknesses, considerations for selecting the appropriate firmness level, and the diverse applications where this type of bed proves most beneficial.
Selection and Maintenance Tips
Optimal utilization requires careful consideration of several factors, ensuring both comfort and longevity of the product.
Tip 1: Assess Density and Firmness. Higher density foam generally indicates increased durability and support. Firmness should align with individual sleep preferences and postural needs.
Tip 2: Evaluate Fold Integrity. Inspect the hinge points where the mattress folds. Reinforcement in these areas prevents premature wear and tear.
Tip 3: Consider Cover Material. Opt for a cover made from breathable, durable fabric. Features such as water resistance or hypoallergenic properties enhance utility.
Tip 4: Measure Available Storage Space. Accurately measure storage dimensions to ensure the folded mattress fits designated areas without compression or distortion.
Tip 5: Implement Proper Storage Practices. Store in a dry, well-ventilated environment to prevent mildew and odor accumulation.
Tip 6: Rotate Regularly. Periodic rotation distributes wear evenly across the surface, prolonging the lifespan.
Tip 7: Use a Mattress Protector. A mattress protector can help prevent stains, spills, and other damage from shortening the product’s lifespan.
Adherence to these guidelines promotes optimal sleep quality and maximizes the lifespan, offering long-term value.
The following sections provide a comprehensive overview of cleaning protocols and ideal use-case scenarios.
1. Comfort and Support
Comfort and support are paramount considerations when evaluating suitability. The nature of foam and its construction significantly influence the overall sleep experience. The ability to provide adequate spinal alignment and pressure relief differentiates high-quality options from those designed primarily for convenience.
- Density and Firmness
The foam’s density dictates its resistance to compression, while firmness is a subjective measure of surface feel. Higher density typically translates to greater support and longevity, resisting sagging over time. A balanced combination ensures the body remains properly aligned, minimizing pressure points and discomfort. For example, individuals with back pain may require a firmer surface, while side sleepers often benefit from a softer, more conforming feel.
- Foam Type
Various foam types, including memory foam, polyurethane foam, and latex foam, exhibit distinct characteristics impacting comfort and support. Memory foam contours to the body, distributing weight evenly and reducing pressure points. Polyurethane foam offers a more resilient feel, providing a firmer sleeping surface. Latex foam combines both support and responsiveness, offering a balance between contouring and bounce. The choice of foam type should align with individual preferences and specific needs.
- Thickness and Layering
The overall thickness and layering configuration influence the degree of cushioning and support provided. Thicker mattresses generally offer greater comfort, accommodating a wider range of body weights and sleeping positions. Layering different foam types can enhance comfort and support, combining the pressure-relieving properties of memory foam with the support of a firmer base layer. Insufficient thickness may result in bottoming out, compromising spinal alignment and comfort.
- Weight Distribution
A bed should distribute weight evenly to prevent pressure points from forming. Uneven weight distribution can lead to discomfort, restless sleep, and even pain. Mattresses with good weight distribution provide a more comfortable and supportive sleeping surface by conforming to the body’s natural curves and contours.
The interplay between density, foam type, thickness, layering, and weight distribution determines the overall comfort and support characteristics. Careful consideration of these factors ensures the selected product meets individual requirements, promoting restful sleep and mitigating potential discomfort.
2. Portability and Storage
The defining feature of a foam bed that folds is its enhanced capacity for relocation and space conservation when not in use. This capability distinguishes it from traditional mattresses, catering to situations where flexibility and compact storage are paramount.
- Folding Mechanism and Design
The tri-fold design inherently reduces the footprint when stowed. Engineering considerations include hinge durability and overall folded dimensions. The integrated folding mechanism impacts the ease of setup and breakdown, with designs optimizing for both stability when deployed and compactness when stored. Examples include reinforced hinges and secure fastening systems that prevent unwanted unfolding during transport or storage.
- Weight and Material Composition
The choice of foam and outer materials contributes significantly to the overall weight, impacting ease of transportation. Lighter materials, while enhancing portability, must maintain structural integrity to withstand repeated folding and unfolding. Material density is often a trade-off between weight and long-term durability. For instance, a high-density memory foam offers superior support but increases weight compared to a less dense polyurethane option.
- Storage Space Requirements
The folded dimensions dictate the necessary storage space. Evaluating available closet space or trunk capacity ensures proper fitment. Compact storage minimizes the disruption to living areas when not in use. Accurate measurement is crucial, as compressed storage can lead to foam deformation over extended periods, affecting the bed’s comfort and lifespan.
- Carrying and Handling Features
Integrated handles, straps, or carrying bags enhance transportability. These features facilitate easy handling, particularly for individuals with limited strength or mobility. The presence of durable carrying mechanisms minimizes strain during relocation, preventing damage to the mattress and promoting user safety.
The interplay between folding design, material selection, storage dimensions, and carrying features determines the practicality in scenarios demanding portability and space efficiency. Selecting one with balanced attributes is critical, particularly when prioritizing ease of movement and minimization of storage space requirements.
3. Material Composition
The materials used in constructing a foam bed that folds directly influence its comfort, durability, support, and overall lifespan. The specific components determine its suitability for various applications and user needs.
- Foam Density and Type
The type of foam employed, be it memory foam, polyurethane, or latex, dictates its feel and support characteristics. Higher density foam provides greater resistance to compression, increasing longevity and support. Memory foam conforms to the body, relieving pressure points, while polyurethane offers a firmer, more resilient surface. The choice impacts the bed’s overall comfort and suitability for different sleep preferences.
- Cover Fabric
The fabric encasing the foam core contributes to breathability, temperature regulation, and overall durability. Materials such as cotton, polyester, or blended fabrics offer varying degrees of moisture wicking, stain resistance, and abrasion resistance. A durable, breathable cover enhances comfort and prolongs the mattress’s lifespan. Some covers include hypoallergenic or antimicrobial treatments for added benefits.
- Adhesives and Bonding Agents
The adhesives used to bond the foam layers and attach the cover must be durable and non-toxic. The type and quality of these agents influence the structural integrity and resistance to delamination. Low-quality adhesives can break down over time, leading to separation of the foam layers and reduced support.
- Internal Structure and Support Elements
Some designs incorporate internal support elements, such as springs or reinforced hinges, to enhance durability and stability. These elements provide additional support and prevent sagging, particularly in areas subjected to high stress. The presence and quality of these elements influence the product’s longevity and resistance to wear and tear.
Understanding the interplay between foam type, cover fabric, adhesives, and internal support elements is essential for selecting an appropriate product. The chosen materials impact comfort, durability, and overall suitability for specific needs, ensuring a worthwhile investment.
4. Size and Thickness
The dimensions of a foam bed that folds directly impact its suitability for various users and applications. Size dictates the number of individuals it can comfortably accommodate, while thickness influences the level of support and comfort provided. These factors are critical considerations when selecting a bed of this type.
- Standard Size Categories
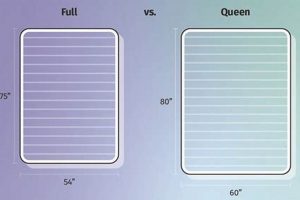
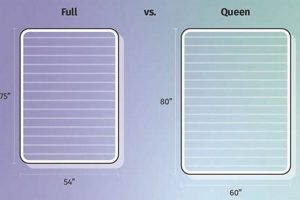
These beds are available in standard mattress sizes, including twin, full, queen, and king. Twin size is suitable for single sleepers, while full size accommodates single adults with more space or couples seeking a compact option. Queen and king sizes offer ample space for couples prioritizing comfort and freedom of movement. The selected size should align with the intended user and available space.
- Thickness and Support Levels
Thickness typically ranges from 3 to 6 inches, influencing the level of support and cushioning. Thinner mattresses offer minimal support, suitable for temporary use or individuals with lower body weights. Thicker mattresses provide enhanced support and pressure relief, accommodating a wider range of body weights and sleeping positions. The ideal thickness depends on individual needs and preferences.
- Folded Dimensions and Portability
The size and thickness influence the folded dimensions, impacting portability and storage convenience. Larger and thicker mattresses generally have larger folded dimensions, requiring more storage space. Smaller and thinner mattresses are more compact when folded, facilitating easier transport and storage. The folded dimensions should align with available storage space and transportation capabilities.
- Weight Capacity Considerations
Size and thickness affect the bed’s weight capacity, determining the maximum weight it can support without compromising support or durability. Larger and thicker mattresses typically have higher weight capacities, accommodating heavier individuals or multiple sleepers. Exceeding the weight capacity can lead to sagging, reduced support, and premature wear and tear.
The interplay between size and thickness determines the overall comfort, support, portability, and durability. Selecting the appropriate dimensions ensures it meets the intended user’s needs, aligning with available space and storage capabilities, and providing optimal comfort and support for restful sleep.
5. Durability and Lifespan
The long-term utility of a foam bed that folds is intrinsically linked to its inherent resistance to wear and tear and the expected duration of serviceable use. These factors are influenced by material selection, construction techniques, and usage patterns, collectively determining the product’s overall value proposition.
- Material Degradation and Resistance
The constituent materials, particularly the foam core and cover fabric, are susceptible to degradation over time. Foam can compress, lose elasticity, or crumble with repeated use and exposure to environmental factors such as humidity and temperature fluctuations. The cover fabric may tear, fade, or pill due to abrasion and repeated folding. Selecting high-quality, durable materials mitigates these risks, extending the bed’s lifespan. For instance, high-density foam resists compression better than low-density alternatives, and tightly woven, abrasion-resistant fabrics withstand wear and tear more effectively.
- Structural Integrity of Folding Mechanisms
The hinges and seams that facilitate folding are critical points of potential failure. Repeated folding and unfolding can stress these areas, leading to tearing, separation, or breakage. Reinforced hinges and durable stitching enhance the structural integrity of the folding mechanism, prolonging its functional lifespan. The design of the folding mechanism, whether employing metal hinges or fabric seams, impacts its long-term reliability.
- Impact of Usage Patterns and Storage Conditions
The frequency of use and the manner in which the bed is stored significantly influence its lifespan. Regular use subjects the mattress to continuous compression and stress, accelerating wear and tear. Improper storage, such as folding the mattress tightly or storing it in humid conditions, can damage the foam and fabric, reducing its lifespan. Proper storage, such as folding loosely and storing in a dry, well-ventilated area, minimizes these risks.
- Maintenance and Cleaning Protocols
Regular cleaning and maintenance can extend the bed’s lifespan by preventing the accumulation of dirt, dust, and allergens that can degrade the materials over time. Vacuuming the surface regularly, spot-cleaning spills promptly, and using a mattress protector can prevent stains and damage. Following manufacturer-recommended cleaning protocols preserves the integrity of the foam and fabric, prolonging the bed’s usable life.
The combined effect of material quality, structural design, usage patterns, and maintenance practices determines the long-term durability. Investing in a well-constructed product and adhering to recommended care guidelines maximizes its lifespan, providing long-term value and minimizing the need for frequent replacement.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding the selection, usage, and maintenance of this specific type of bedding.
Question 1: What is the typical lifespan of a full trifold foam mattress?
The lifespan is generally between 3 to 5 years with regular use, varying according to foam density, construction quality, and care provided. Higher density foam and durable cover materials contribute to extended longevity.
Question 2: Is a full trifold foam mattress suitable for everyday use?
While designed for temporary sleeping arrangements, certain models constructed with high-density foam and adequate thickness can provide sufficient support for everyday use. However, a traditional innerspring or hybrid mattress is often preferable for consistent, long-term comfort.
Question 3: How should a full trifold foam mattress be properly stored to prevent damage?
It should be stored in a dry, well-ventilated area, ideally in its folded configuration. Avoid prolonged compression or exposure to direct sunlight, as these conditions can degrade the foam and fabric over time. Consider using a mattress bag to protect it from dust and moisture.
Question 4: What is the recommended method for cleaning a full trifold foam mattress?
Spot cleaning with a mild detergent and water is generally recommended. Avoid harsh chemicals or excessive moisture, which can damage the foam. Allow the mattress to air dry completely before folding or storing.
Question 5: What factors should be considered when selecting a full trifold foam mattress for individuals with back pain?
Firmness and support are paramount. A higher density foam offers greater spinal alignment and pressure relief. Individuals should assess the product’s firmness level in relation to their sleeping position and preferred level of support. Consulting a healthcare professional may provide further guidance.
Question 6: Are there any specific safety concerns associated with full trifold foam mattresses?
Ensure the product meets relevant safety standards regarding flammability and chemical emissions. Look for certifications such as CertiPUR-US, indicating the foam has been tested for harmful substances. Proper ventilation is important, especially when new, to dissipate any residual odors.
Proper selection and care are essential for maximizing the usability of this product. The considerations outlined above provide a comprehensive overview of key factors influencing performance and longevity.
The subsequent section will summarize the key benefits of using it.
Conclusion
This exploration of the full trifold foam mattress has encompassed its design, material composition, size considerations, durability, and practical applications. The analysis has underscored the importance of balancing portability with comfort and support, highlighting factors such as foam density, cover material, and folding mechanisms. Furthermore, it has emphasized the significance of proper maintenance and storage to maximize product lifespan.
Ultimately, the selection of a full trifold foam mattress represents a trade-off between convenience and long-term sleeping comfort. Potential purchasers are encouraged to carefully weigh the presented considerations against their individual needs and intended use cases to make an informed decision. Continued advancements in material science and design may lead to future iterations that further enhance both portability and sleep quality.





![Best Full Size Daybed with Mattress [Deals] Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Best Full Size Daybed with Mattress [Deals] | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-2863-300x200.jpg)