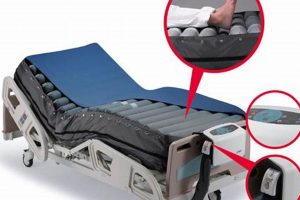
Determining the presence and location of escaping air from an inflatable sleeping surface is a necessary step to maintain its functionality. Identifying the source of deflation ensures the continued usability and comfort of the air mattress.
Locating these faults is important for extending the lifespan of the product and avoiding the cost of replacement. Historically, methods have ranged from simple auditory checks to more involved submersion techniques. Successfully pinpointing the source enables users to implement appropriate repairs and maintain the bed’s intended purpose.
The following sections will outline several techniques employed to identify these compromises, ranging from simple visual inspections to more involved methods requiring water and soapy solutions. These will address both small, hard-to-detect leaks and larger, more easily identifiable punctures.
Techniques for Identifying Air Escape Points
The following strategies provide systematic methods for pinpointing areas where air is escaping from an air mattress.
Tip 1: Auditory Inspection: Inflate the mattress fully in a quiet environment. Listen closely for hissing sounds, especially near seams, valves, and the mattress’s surface. This is most effective for larger leaks.
Tip 2: Visual Examination: Carefully inspect the entire surface of the mattress. Look for any visible punctures, tears, or abrasions. Pay close attention to areas that appear worn or stressed.
Tip 3: Soapy Water Test: Mix a solution of mild dish soap and water. Apply the solution to the surface of the inflated mattress using a sponge or spray bottle. Air escaping will create bubbles at the leak’s location.
Tip 4: Submersion Method: If feasible and the mattress is small enough, submerge it in a bathtub or large container of water. Observe for air bubbles rising from the mattress, indicating the leaks location.
Tip 5: Pressurized Inspection: With the mattress inflated, apply firm pressure to different sections. This may help force air out of smaller, less obvious leaks, making them easier to detect using auditory or soapy water methods.
Tip 6: Valve Integrity Check: Ensure the valve is tightly closed and functioning correctly. Test the valve’s seal by applying soapy water around its perimeter to check for escaping air.
Tip 7: Sectional Approach: Divide the mattress into smaller, manageable sections. Systematically inspect each section using the methods above. This approach ensures thorough coverage and improves the chances of finding smaller leaks.
These techniques are designed to provide a structured approach to pinpointing the source of air leaks, thus enabling more effective repair efforts.
The successful identification of these points allows for informed decisions regarding repair or replacement of the air mattress.
1. Auditory detection
Auditory detection serves as a primary method in establishing whether an air mattress is compromised. The principle relies on the physics of air escaping from a pressurized environment through a small opening, generating an audible hissing or whistling sound. This sound, even if faint, indicates the presence of a breach in the air mattress’s structure. The effectiveness of auditory detection is contingent upon the size of the leak and the ambient noise level. In a quiet environment, even minute perforations can be identified through the subtle sound of escaping air. Larger punctures will produce louder and more readily detectable sounds.
The implementation of auditory detection typically involves fully inflating the air mattress and systematically listening near seams, valves, and the surface material. Proximity is key; moving closer to the mattress surface enhances the ability to discern faint sounds. Real-world examples include locating slow leaks that gradually deflate a mattress over several hours, which might be missed by visual inspection alone. A small puncture caused by a pet’s claw, for instance, may produce a barely audible hiss, detectable only through careful listening. The success of this method also depends on the user’s auditory acuity and their ability to differentiate the sound of escaping air from other ambient noises.
In conclusion, auditory detection represents a straightforward, cost-effective initial step in identifying air leaks in mattresses. Its efficacy is limited by the size of the leak and ambient noise, often necessitating its combination with other methods like soapy water tests. Despite its limitations, it remains a valuable diagnostic tool, facilitating early detection and enabling timely repairs, ultimately extending the lifespan of the inflatable product.
2. Visual inspection
Visual inspection constitutes a fundamental step in determining the location of air leaks within an inflatable mattress. Its effectiveness stems from the principle that many leaks manifest as physically discernible anomalies on the mattress’s surface. This direct observation offers a non-invasive method for identifying potential breaches before employing more complex diagnostic techniques. The presence of punctures, tears, abrasions, or deformities are directly attributable to the escape of pressurized air, compromising the integrity of the product. The absence of these signs, however, does not negate the presence of a leak, necessitating further investigation through other means.
The importance of visual inspection is amplified by its efficiency as an initial assessment tool. For instance, a visible tear resulting from contact with a sharp object immediately points to the leak’s location, enabling swift repair. Similarly, areas exhibiting unusual wear or discoloration can indicate potential weak points susceptible to air escape. Furthermore, the seams, valve areas, and regions subjected to frequent folding or compression are prime candidates for visual scrutiny due to the elevated likelihood of stress-induced damage. Systematic examination, involving a focused scan of the entire surface, is crucial for identifying even minute imperfections. Practical applications range from pre-emptive maintenance checks to addressing immediate deflation issues, where a clear puncture necessitates patching. This method can be used in conjunction with leak detection tools.
In summary, visual inspection serves as a cost-effective and readily accessible diagnostic tool in the process of detecting air leaks. The ability to detect punctures or abrasions enables efficient and targeted repairs, improving the lifespan of the air mattress. While not a foolproof solution in isolation, it is an essential component of a comprehensive leak detection strategy, facilitating early identification and minimizing the need for more resource-intensive methods.
3. Soapy solution
The application of a soapy solution represents a highly effective and widely adopted method for pinpointing air leaks in inflatable mattresses. This technique leverages the principle of surface tension reduction. A soap-water mixture, when applied to a pressurized surface, decreases the surface tension of the water. As air escapes through a leak, it encounters this soapy film, causing the formation of visible bubbles at the point of egress. The size and frequency of these bubbles directly correlate with the magnitude of the leak. Therefore, the appearance of bubbles directly indicates the presence and location of escaping air.
The importance of a soapy solution as a component in locating leaks stems from its ability to detect even minute perforations that may be undetectable by auditory or visual inspection alone. For example, a pinhole puncture caused by friction or a small, almost invisible abrasion will likely not produce an audible hiss. However, when coated with the soapy solution, even the slightest air escape will generate a bubble cluster, immediately highlighting the compromise. Practical application involves mixing a mild dish soap with water, typically in a ratio of one part soap to five parts water, and applying it liberally to the inflated mattress surface using a sponge or spray bottle. Focus should be given to seams, valve areas, and any regions showing signs of wear. The observation of bubble formation facilitates precise leak identification and enables targeted repair efforts.
In summary, the implementation of a soapy solution constitutes a crucial step in effectively locating air leaks in mattresses. Its ability to amplify even the smallest air escapes through visible bubble formation provides a means of pinpointing damage. The method is cost-effective, easy to implement, and enhances the overall accuracy of leak detection, thus informing appropriate repair decisions and extending the usable lifespan of the mattress.
4. Submersion
Submersion represents a reliable technique for locating air leaks, particularly in smaller inflatable mattresses. It leverages the principle that escaping air, when forced to travel through water, becomes readily visible as a stream of bubbles. This method is especially effective for identifying multiple or subtle leaks that may evade detection by other means.
- Bubble Visualization
The primary function of submersion is to render air leaks visible. Immersion forces escaping air to create distinct bubble trails emanating from the point of puncture. The presence and frequency of these bubbles provide a direct indication of the leak’s severity. For example, a steady stream suggests a larger breach, while intermittent small bubbles point to a less significant imperfection.
- Detection of Multiple Leaks
Submersion allows for the simultaneous detection of multiple leaks. Unlike methods that focus on a localized area, immersion provides a holistic view of the mattress’s surface. If several punctures exist, each will generate its own distinct stream of bubbles, facilitating comprehensive damage assessment. An instance could be an old air mattress with several pinholes that are undetectable except when submerged.
- Precise Leak Localization
Submersion provides an accurate means of pinpointing leak locations. The origin point of the bubble stream directly corresponds to the site of the puncture. This precision enables targeted repair efforts, minimizing the area requiring patching. It simplifies the process compared to methods where the leak’s location is less defined. For example, the precise location of the leak can be marked with a permanent marker on the mattress itself.
- Limitations and Considerations
While effective, submersion has limitations. It’s best suited for smaller mattresses due to the impracticality of submerging larger items. Additionally, the process requires a sufficiently large container and access to water. Immersion may not be appropriate for mattresses with electronic components or those susceptible to water damage. A further consideration is drying the mattress thoroughly after submersion to prevent mold or mildew growth.
In summary, submersion provides a valuable method for discovering air leaks, especially in smaller air mattresses. The visual clarity offered by bubble formation allows for precise leak localization and comprehensive damage assessment. Consideration of its limitations, however, is crucial for ensuring its appropriate and effective application in the process of leak detection.
5. Valve integrity
The integrity of an air mattress valve is paramount to its ability to maintain inflation. Compromised valve functionality can lead to gradual or rapid air loss, necessitating accurate identification as a potential leak source.
- Valve Seal Inspection
The primary role of a valve is to create an airtight seal, preventing air escape. Inspection involves visually examining the valve for cracks, deformities, or debris that may compromise its sealing capabilities. A deformed or damaged valve will allow air to escape through the imperfect contact it makes with the mattress material. Example: A small piece of debris lodged within the valve’s mechanism can prevent complete closure, causing a slow leak.
- Soapy Water Test on the Valve
Similar to leak detection on the mattress surface, a soapy water solution can be applied around the valve perimeter and the valve opening itself to identify escaping air. Bubble formation indicates an imperfect seal, suggesting valve damage or improper closure. For example, applying soapy water to a screw-type valve that is not fully tightened will cause bubbles, pinpointing the valve as the leak source.
- Valve Core Examination and Tightening
Certain valves, particularly those found on higher-end air mattresses, incorporate a removable core. The valve core can loosen over time or become damaged. A specialized tool can be employed to tighten or replace the valve core, potentially resolving slow leak issues. For example, similar to bicycle tire valves, an air mattress valve core can be tightened, re-establishing a secure seal. If tightening fails, the core may need replacement.
- Compatibility and Replacement
If the valve is deemed irreparable, identifying a compatible replacement becomes crucial. The valve must match the thread type and dimensions of the original to ensure a secure and airtight fit. Example: Attempting to install an incompatible valve may result in a loose connection, rendering the mattress unusable. Sourcing a replacement valve with the correct specifications is essential for a successful repair.
Addressing valve integrity directly impacts successful leak identification and resolution. A focus on valve condition alongside mattress surface inspections ensures a comprehensive approach to maintaining air mattress functionality.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common concerns regarding the identification of air leaks in inflatable mattresses.
Question 1: How sensitive must hearing be to effectively detect air leaks audibly?
While excep
tional hearing isn’t mandatory, quiet environments are essential. Background noise significantly hinders the ability to discern faint hissing sounds associated with smaller leaks. The proximity to the mattress and the size of the leak primarily dictate detectability.
Question 2: Can visual inspection reliably identify all types of air leaks?
Visual inspection is more effective for identifying larger punctures, tears, or abrasions. Minute perforations, invisible to the naked eye, may evade detection. Supplemental methods like soapy water tests are advisable for a comprehensive assessment.
Question 3: What is the ideal soap-to-water ratio for an effective soapy water test?
A generally recommended ratio is one part mild dish soap to five parts water. An excessively concentrated solution may produce an overwhelming amount of bubbles, obscuring the precise leak location. Conversely, an insufficiently concentrated solution may not generate enough bubbles for clear identification.
Question 4: Are there risks associated with submerging an air mattress to find leaks?
Submersion is primarily suitable for smaller mattresses. Larger mattresses pose logistical challenges. Furthermore, submersion should be avoided if the mattress contains electronic components or if the material is prone to water damage. Thorough drying post-submersion is imperative to prevent mold or mildew growth.
Question 5: What tools are required to tighten or replace an air mattress valve core?
Air mattress valves with removable cores typically require a valve core tool, similar to those used for bicycle tires. This tool allows for the tightening or removal of the valve core. It is essential to ensure compatibility between the tool and the valve type.
Question 6: Is it always possible to repair an air mattress leak?
The feasibility of repair depends on the size, location, and nature of the damage. Small punctures are often repairable with patching kits. However, extensive tears, valve damage, or material degradation may render the mattress beyond economical repair, necessitating replacement.
These FAQs serve to clarify common concerns and misconceptions associated with discovering air leaks, facilitating more effective and informed troubleshooting.
The following section explores the tools and materials necessary to conduct the repair.
Conclusion
Effective implementation of various detection methodologies is paramount in pinpointing breaches in inflatable mattresses. These methods, including auditory inspection, visual examination, soapy water application, submersion techniques, and valve integrity assessments, each contribute uniquely to the identification process.
The ability to detect such breaches facilitates informed decisions regarding repair or replacement, thereby maximizing the lifespan and utility of the air mattress. Continued vigilance in the implementation of these techniques will ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.