Locating the source of escaping air from an inflatable sleeping surface is a necessary step in maintaining its functionality and prolonging its lifespan. This process involves a systematic approach to identify the precise point from which air is being expelled, allowing for targeted repair.
Identifying the precise point of air leakage is crucial because it prevents further deflation during use, ensuring a comfortable and supportive sleeping surface. Addressing these leaks promptly preserves the integrity of the mattress material and saves resources by avoiding the need for premature replacement. Traditionally, submersion in water was a common method; modern techniques leverage soapy water solutions and auditory detection.
Several methodologies can be employed to pinpoint the exact location of the breach. These include visual inspection, auditory detection, the application of soapy water, and, in some cases, the use of specialized leak detection devices. The following sections will detail these methods, offering a step-by-step guide for effectively locating and addressing the source of air loss.
Tips for Air Leak Detection in Inflatable Mattresses
Effective identification of air egress points in inflatable mattresses requires a systematic approach. Employing the following techniques will enhance the likelihood of successfully locating and repairing the source of deflation.
Tip 1: Conduct a Thorough Visual Examination: Begin by meticulously inspecting the entire surface of the mattress, paying particular attention to seams, valves, and areas prone to stress. Look for visible punctures, tears, or abrasions which may indicate the source of air loss.
Tip 2: Listen Carefully: In a quiet environment, inflate the mattress fully and listen closely for the sound of escaping air. Slowly move the ear across the surface, concentrating on areas identified during the visual inspection. The hissing sound can help pinpoint the general vicinity of the leak.
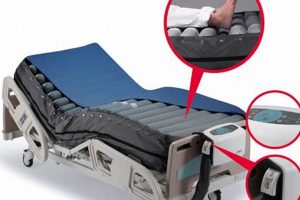
Tip 3: Utilize Soapy Water Solution: Mix a small amount of liquid dish soap with water in a spray bottle. Inflate the mattress and lightly spray the soapy water solution onto suspected areas. The formation of bubbles indicates the presence of an air leak.
Tip 4: Submerge in Water (When Feasible): For smaller mattresses, or sections thereof, submersion in water can be an effective method. Slowly submerge the inflated mattress and observe for rising air bubbles, which will identify the leak’s location. Ensure proper drying after submersion to prevent mold growth.
Tip 5: Check the Valve Assembly: The valve is a common source of leaks. Inspect the valve for proper seating and tightness. Apply soapy water around the valve area to check for leaks originating from the valve itself or its connection to the mattress material.
Tip 6: Focus on Seams and Edges: Seams and edges are often subject to increased stress and wear. Pay particular attention to these areas during visual inspection, auditory detection, and soapy water testing.
Tip 7: Divide and Conquer: For larger mattresses with suspected leaks in multiple areas, divide the mattress into sections and systematically inspect each section using the methods described above. This will help narrow down the search area and improve efficiency.
Implementing these strategies systematically increases the probability of pinpointing the air leakage point, facilitating effective repair and extending the service life of the inflatable mattress.
Following the identification of the leak, appropriate repair techniques, such as patching or sealing, should be implemented to restore the mattress to its functional state.
1. Visual Inspection
Visual inspection serves as the foundational step in the process of locating air egress points in inflatable mattresses. It provides an initial assessment of the mattress’s integrity and directs subsequent, more focused diagnostic efforts.
- Identifying Obvious Damage
The primary objective of visual inspection is to detect any readily apparent physical damage, such as punctures, tears, cuts, or abrasions. These are frequently the source of air leakage. Examples include punctures caused by sharp objects, tears resulting from excessive stretching, or abrasions due to friction against rough surfaces. Locating these visible flaws immediately pinpoints the leak’s location.
- Assessing Seam Integrity
Mattress seams are points of inherent weakness and are susceptible to separation or failure over time. Visual inspection should focus on scrutinizing the seam lines for any signs of unraveling, splitting, or adhesive breakdown. A compromised seam allows air to escape, leading to deflation. Any discoloration or unevenness along the seam indicates potential issues. Careful examination of this area directly relates to locating a source of the leakage.
- Examining Valve Condition
The valve assembly is a critical component responsible for maintaining air pressure within the mattress. Visual inspection of the valve involves checking for cracks, deformities, or loose connections. The valve cap should be securely in place, and the valve stem should appear undamaged. A malfunctioning or improperly sealed valve results in continuous air loss. Detecting valve flaws visually helps pinpoint the leak’s origin.
- Evaluating Surface Degradation
Over time, the mattress material can degrade due to exposure to UV light, chemicals, or extreme temperatures. Visual inspection includes assessing the overall condition of the mattress surface for signs of hardening, cracking, or discoloration. Degraded areas are more prone to developing leaks. Identifying signs of material degradation provides insight into potential leak sites and aids in determining the mattress’s overall lifespan.
In summary, visual inspection constitutes the initial and often most direct method for addressing the question of “how to find air mattress leak.” By systematically examining the mattress for visible damage, seam integrity, valve condition, and surface degradation, individuals can effectively identify the source of air loss and proceed with appropriate repair measures, therefore prolonging the functionality and comfort of the inflatable mattress.
2. Auditory Detection
Auditory detection represents a supplementary technique employed in the process of locating air egress points from inflatable mattresses. Its efficacy hinges on discerning the sound of escaping air within an environment free of extraneous noise. This technique is particularly effective for identifying leaks that are too small to be readily visible or easily detected through other methods.
- Amplifying Subtle Sounds
The fundamental principle behind auditory
detection lies in amplifying the subtle hissing or whistling sounds generated by air escaping through a breach in the mattress material. This often necessitates a quiet setting where ambient noise is minimized to maximize the audibility of the leak. Examples include turning off appliances, closing windows, and ensuring the absence of conversation. In the context of locating air loss, this careful attention to auditory cues increases the likelihood of identifying the source, particularly when other methods prove inconclusive. - Systematic Scanning of the Mattress Surface
Effective auditory detection involves a systematic scanning of the mattress surface while paying close attention to potential leak locations. The ear should be positioned close to the mattress, moving slowly and deliberately across its entirety. Areas of particular interest include seams, valves, and any regions exhibiting signs of wear or stress. This method is most helpful when one uses a deliberate process to examine the mattress surface.
- Utilizing Acoustic Enhancement Tools
While not always necessary, the effectiveness of auditory detection can be enhanced through the use of simple acoustic tools. A length of tubing, held close to the ear at one end and directed towards the mattress surface at the other, can amplify the sound of escaping air, making it easier to pinpoint the leak’s origin. This is a simple example, but it demonstrates ways the method may be improved. More sophisticated devices, such as electronic stethoscopes, can be employed for more precise sound amplification and localization.
- Limitations and Complementary Use
Auditory detection, while valuable, possesses limitations. It may be ineffective in noisy environments or for detecting extremely small leaks that produce minimal sound. Therefore, it is most effectively employed as a complementary technique in conjunction with visual inspection and soapy water testing. Combining these methods increases the overall probability of accurately locating and addressing sources of air loss from inflatable mattresses. Using the other methods increases the utility of the aural method.
In summary, while it is limited by the necessity of a quiet environment, auditory detection can be a very useful tool in identifying the precise source of the air egress from an inflatable mattress. Its value is heightened when combined with other leak detection methods, such as soapy water application and visual inspection, providing a comprehensive approach to maintaining the functionality and lifespan of the mattress.
3. Soapy water
The application of soapy water forms a crucial component in the systematic process of identifying sources of air leakage from inflatable mattresses. This technique leverages the principle that escaping air, when forced through a thin film of soapy water, creates visible bubbles. These bubbles serve as definitive indicators of the leak’s precise location, allowing for targeted repair efforts. The creation of bubbles shows a direct connection between escaping air and leak location. The absence of bubbles at a given location suggests integrity of the mattress at that location.
The practical significance of employing soapy water stems from its ability to detect even minute leaks that might otherwise go unnoticed through visual or auditory inspection. For instance, a pinhole puncture, too small to see, will nevertheless produce a stream of bubbles when exposed to the soapy water solution. The solution is prepared by mixing a mild liquid detergent with water, creating a low-surface-tension fluid that readily forms bubbles. This solution is then applied to the inflated mattress, with particular attention paid to seams, valves, and areas suspected of damage. Real-world examples show the usefulness of this leak detection method. This also applies to other inflatable object. The presence of bubbles signals the need for repair at that specific point.
In summary, the use of soapy water as a leak detection method is practical. It offers a reliable, cost-effective, and readily accessible means of pinpointing air leaks. Its primary challenge lies in ensuring thorough coverage of the mattress surface and differentiating between legitimate leak indications and residual bubbles caused by surface tension. Despite these challenges, the strategic application of soapy water remains an integral part of effectively locating and repairing leaks in inflatable mattresses, contributing to their extended lifespan and continued usability.
4. Valve Check
The integrity of the valve assembly is paramount in maintaining the air retention capabilities of inflatable mattresses. A comprehensive valve check forms an indispensable part of effectively determining the location of air leakage, as a compromised valve constitutes a frequent source of deflation.
- Valve Seating Assessment
The valve must be properly seated within its housing to create an airtight seal. A misaligned or improperly seated valve permits air to escape, irrespective of the valve’s internal mechanism. An example would be a valve dislodged due to impact, preventing a complete seal. This relates directly to locating the source of air loss.
- Internal Valve Mechanism Examination
Many valves incorporate internal mechanisms, such as flapper valves or spring-loaded plungers, designed to prevent air from escaping once inflated. The functionality of these mechanisms should be assessed. A malfunctioning mechanism, such as a broken spring, compromises the valve’s ability to retain air, resulting in leakage. Therefore, identifying a faulty valve mechanism directly indicates the leak’s origin.
- Thread Integrity and Tightness
Valves typically utilize threaded connections to secure them to the mattress material. The integrity of these threads is critical for maintaining an airtight seal. Damaged or stripped threads prevent the valve from being adequately tightened, leading to air leakage. Inspecting the threads on both the valve and the mattress interface is important. Valve tightness impacts air retention capabilities.
- Soapy Water Application around the Valve
Applying a soapy water solution around the perimeter of the valve and its connection point is a direct method for detecting subtle leaks. The formation of bubbles indicates that air is escaping from the valve assembly, confirming its role as the source of deflation. This approach provides visual confirmation of valve leakage, directing repair efforts accordingly.
The facets highlight the significance of thorough valve evaluation when diagnosing air loss from inflatable mattresses. The valve’s operational condition, seating, thread integrity, and reaction to a soapy water check can effectively help determine the cause of leakage and the need for repair or replacement.
5. Seam Scrutiny
Seam scrutiny constitutes a critical phase in the process of identifying air leakage sources in inflatable mattresses. Mattress seams, being points of connection between separate material sections, often represent inherent weaknesses and potential failure points. Careful examination of the
se areas is therefore essential to determine whether a seam compromise is the origin of air loss. The process involves a detailed visual and tactile inspection, coupled with other diagnostic techniques, focused specifically on the seams’ integrity. When the mattress exhibits rapid deflation, it becomes more important to inspect seems with great details.
The correlation between seam integrity and air retention is direct. Substandard adhesion, material fatigue, or physical damage to the seam directly results in air escape. Visual signs of seam compromise include separation of the joined materials, fraying of the seam edges, or discoloration, which suggests adhesive breakdown. Tactile examination may reveal areas where the seam has become weakened or detached, even if visual signs are not immediately apparent. Application of soapy water along the seam can further highlight air leakage, as bubbles form at the precise location of the breach. For example, a mattress used frequently will see seams stretched, causing the seams to open and cause a leak. The same example can be observed when the mattress is exposed to different weather conditions.
In summation, thorough seam scrutiny is instrumental in the effort to effectively locate sources of air leakage in inflatable mattresses. This process necessitates meticulous visual and tactile inspection, supplemented by techniques such as soapy water testing, to reveal any compromise in the seam’s integrity. Addressing identified seam weaknesses through appropriate repair methods prolongs the mattress’s lifespan and ensures its continued utility. Without the seam scrutiny, one may miss a leak that is very close to being invisible.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the identification of air leaks in inflatable mattresses, providing concise and informative answers to facilitate effective leak detection.
Question 1: What is the initial step when suspecting an air leak in an inflatable mattress?
The initial step is conducting a thorough visual inspection of the entire mattress surface. Pay close attention to seams, valves, and areas showing signs of wear or damage. This allows for the quick identification of obvious punctures, tears, or abrasions.
Question 2: How effective is auditory detection in locating air leaks?
Auditory detection can be effective in a quiet environment, allowing for the detection of the hissing sound of escaping air. However, its effectiveness is limited in noisy environments or for extremely small leaks that produce minimal sound. It is best used in conjunction with other methods.
Question 3: What is the principle behind using soapy water to find an air leak?
Soapy water creates a thin film over the mattress surface. Escaping air passing through this film generates visible bubbles, indicating the precise location of the leak. This method is effective for detecting even very small leaks.
Question 4: Why is it important to specifically check the valve when looking for a leak?
The valve is a common source of air leaks due to improper seating, damage to the valve mechanism, or loose connections. A thorough valve check is crucial to rule out or confirm the valve as the cause of air loss.
Question 5: Are seams more susceptible to leaks than other parts of the mattress?
Yes, seams often represent inherent weaknesses in the mattress construction, making them more prone to leaks. Therefore, careful scrutiny of the seams is an important part of the leak detection process.
Question 6: What should be done after a leak has been located?
After a leak has been located, the next step is to repair it using appropriate methods such as patching or sealing. The specific method will depend on the size and nature of the leak, as well as the mattress material.
Effective leak detection is crucial for maintaining the functionality and prolonging the lifespan of inflatable mattresses. Combining visual inspection, auditory detection, soapy water application, and a thorough valve and seam check ensures a comprehensive approach to identifying and addressing air leaks.
Having addressed common questions, the following section will discuss methods of repairing identified leaks.
Conclusion
Effective determination of “how to find air mattress leak” necessitates a systematic methodology. This encompasses visual inspection, auditory detection, application of soapy water, and thorough examination of both the valve and seams. Each method contributes unique insights into the potential sources of air egress, and their combined application maximizes the probability of accurate leak localization.
Mastery of these techniques equips individuals with the ability to prolong the lifespan of inflatable mattresses, promoting resource conservation and minimizing the need for premature replacement. Consistent and conscientious application of these principles ensures sustained comfort and utility. The skill is also useful in locating leaks for other inflatables.





![Best Pickup Truck Air Mattress [Guide] Camping Ready! Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Best Pickup Truck Air Mattress [Guide] Camping Ready! | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-6772-300x200.jpg)
![Best Minivan Air Mattress [Comfort & Travel] Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Best Minivan Air Mattress [Comfort & Travel] | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-6771-300x200.jpg)