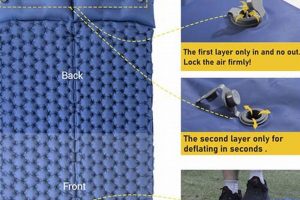
The process of compacting and storing an inflatable sleeping surface, commonly used for temporary bedding, involves removing air and manipulating the material for efficient storage. This action typically follows deflation, preparing the item for placement in a designated storage area. Example: After a guest departs, one may need to undertake this procedure for the item to be neatly put away.
Proper execution of this task yields several advantages, including space conservation within a residence or storage facility. Furthermore, careful manipulation minimizes the potential for material damage, extending the lifespan of the inflatable product. Historically, similar techniques have been employed for various inflatable goods, demonstrating a long-standing need for effective storage solutions.
The following sections will detail the specific steps required to achieve optimal compaction and secure storage. This includes methods for efficiently removing residual air and techniques for minimizing crease formation during the storage process.
Compaction and Storage Guidance
The subsequent guidelines address techniques for optimizing the process of preparing an inflatable sleeping surface for storage. Applying these methods can prolong the item’s usability and preserve storage space.
Tip 1: Maximize Deflation. Ensure thorough air expulsion before initiating the folding process. Utilize the deflation valve and apply manual pressure to facilitate complete air removal. An electric pump with a reverse function can expedite this procedure.
Tip 2: Employ a Flat Surface. Conduct the folding process on a clean, level surface. A flat surface prevents uneven creasing and allows for uniform manipulation of the material.
Tip 3: Fold in Thirds. Begin by folding the item into thirds lengthwise. This method promotes a compact shape and minimizes the surface area exposed to potential damage.
Tip 4: Roll Tightly. After folding lengthwise, initiate a tight rolling motion from one end to the other. This compresses the remaining air and creates a cylindrical form suitable for storage.
Tip 5: Secure with Straps. Employ straps or bungee cords to secure the rolled item. This prevents it from unfurling and maintains its compact shape during storage or transport.
Tip 6: Store in a Dry Environment. Select a storage location that is dry and temperature-controlled. Exposure to moisture and extreme temperatures can compromise the integrity of the inflatable material.
Tip 7: Protect from Sharp Objects. Ensure the storage area is free from sharp objects that could puncture or damage the item. Consider using a protective bag or case for added security.
Effective implementation of these techniques will contribute to the longevity of the inflatable sleeping surface and streamline the storage process. Adherence to these guidelines minimizes the risk of damage and ensures readiness for future use.
The final section will summarize the preceding information and provide concluding remarks on the proper care and maintenance of inflatable sleeping surfaces.
1. Deflation Thoroughness
Deflation thoroughness represents a critical prerequisite for efficient compression and subsequent storage of inflatable sleeping surfaces. Incomplete air removal directly impedes the ability to reduce the overall volume of the item, thereby requiring increased storage space and complicating the folding process. The residual air also contributes to uneven pressure distribution within the folded material, potentially leading to creases and stress points that accelerate material degradation. For instance, if an air mattress is not fully deflated, it will be difficult to roll tightly, and the resulting bulky shape will be more susceptible to damage during storage and transport. This scenario highlights the cause-and-effect relationship between deflation thoroughness and the successful execution of the folding procedure.
Achieving optimal deflation requires more than simply opening the primary valve. Supplementing passive air release with active measures, such as applying body weight to expel remaining air or utilizing an electric pump with a reverse function, significantly enhances the effectiveness of the deflation process. This is particularly crucial for larger inflatable sleeping surfaces, where substantial air volumes can persist even after initial valve opening. The practical application of this understanding is evident in the reduced effort required to fold a thoroughly deflated mattress, as well as the decreased risk of material stress during the folding and storage phases. Failure to ensure adequate deflation can result in a poorly compacted and unstable package that is prone to unfolding and requires a disproportionately large storage footprint.
In summary, deflation thoroughness is not merely a preliminary step but an integral component of the entire compression and storage procedure. Its impact extends beyond simply reducing the volume of the item; it directly influences the ease of folding, the stability of the folded package, and the long-term preservation of the inflatable material. While challenges may arise in achieving complete air removal, particularly in the absence of specialized equipment, prioritizing deflation thoroughness ultimately contributes to a more efficient and sustainable management strategy for inflatable sleeping surfaces, aligning with broader goals of space conservation and resource optimization.
2. Surface Cleanliness
Surface cleanliness directly impacts the condition and longevity of inflatable sleeping surfaces, influencing the effectiveness of any folding technique. Contaminants present on the surface, if not addressed, can become embedded within the material during compression and storage, leading to potential damage and hygiene concerns.
- Abrasive Particle Introduction
The presence of sand, dust, or other abrasive particles on the surface can cause microscopic abrasions to the inflatable material during the folding and rolling process. These abrasions weaken the structural integrity over time, potentially leading to air leaks or tears. For example, folding an air mattress on a carpeted floor without prior vacuuming can embed fibers into the material, creating friction points during compression.
- Mold and Mildew Propagation
Moisture combined with organic matter, such as spilled food or sweat residue, fosters the growth of mold and mildew. When folded, these contaminants become trapped within the layers of the mattress, creating a breeding ground for microorganisms. Prolonged exposure to these organisms can degrade the material and generate unpleasant odors. Leaving a slightly damp air mattress folded in a storage bag provides an ideal environment for such growth.
Staining and Discoloration Dirt and stains can permanently alter the appearance of the inflatable sleeping surface, even after cleaning. Folding a soiled mattress compresses the staining agents deeper into the material, making them more difficult to remove later. For instance, folding an air mattress after outdoor use without removing grass stains can result in permanent discoloration that detracts from its aesthetic value.
- Compromised Hygiene
Folding an unclean air mattress introduces potential allergens and pathogens into the storage environment. Dust mites, pet dander, and other allergens become concentrated within the folded layers, posing a health risk to individuals with sensitivities. Moreover, the presence of bacteria can compromise the overall hygiene of the item, requiring more frequent and thorough cleaning.
Addressing surface cleanliness prior to compression mitigates these risks. Wiping down the surface with a damp cloth and mild detergent removes loose debris and minimizes the potential for contaminant introduction. This preventative measure enhances both the storage conditions and the overall lifespan of the inflatable sleeping surface. Neglecting this crucial step can render even the most meticulous folding techniques ineffective in preserving the item’s integrity.
3. Folding Technique
The applied folding technique directly influences the final dimensions and structural integrity of a compressed inflatable sleeping surface. Deviation from established folding methods can result in inefficient space utilization and increase the risk of material damage during storage or transport. The selection of a specific folding pattern, therefore, constitutes a critical element within the process of preparing an air mattress for storage.
Optimal folding techniques, such as the tri-fold method combined with a tight rolling action, aim to minimize the overall volume of the deflated mattress while distributing pressure evenly across the material. A haphazard or inconsistent folding approach creates irregular stress points, potentially leading to creases, punctures, or accelerated degradation of the inflatable material. For example, attempting to fold an air mattress in a random manner can trap air pockets, resulting in a bulky and unstable form that is difficult to secure. Conversely, a structured folding technique promotes a compact, uniform shape that is more resistant to damage and occupies less storage space. The cause-and-effect relationship between the chosen folding method and the final compressed form underscores the practical importance of selecting an appropriate technique.
In conclusion, the careful selection and execution of a suitable folding technique represent an indispensable component of effectively managing inflatable sleeping surfaces. While challenges may arise in consistently applying these techniques, particularly with larger or less flexible mattresses, prioritizing structured folding methods yields significant benefits in terms of space optimization and material preservation. Ultimately, a well-executed folding technique extends the lifespan of the air mattress and enhances the efficiency of its storage, aligning with the overarching goal of responsible resource management.
4. Rolling Tightness
Rolling tightness is integrally connected to effective compression within the process of preparing an inflatable sleeping surface for storage. The degree to which an air mattress is tightly rolled directly influences its final packed size and its resistance to unfolding during storage or transport. Inadequate rolling tightness results in a larger, less stable package, while optimal tightness maximizes space efficiency and minimizes the risk of damage.
The practical significance of rolling tightness can be illustrated through comparison: an air mattress loosely rolled will occupy significantly more volume than one rolled tightly, potentially exceeding available storage space. Furthermore, a loosely rolled mattress is more likely to unravel, exposing the material to potential punctures or abrasions. Conversely, a tightly rolled mattress maintains its compressed form, protecting the material and reducing the overall footprint. This is achieved by expelling remaining air pockets and distributing pressure evenly across the surface, preventing localized stress points. Applying straps or fasteners subsequently reinforces the compressed state. The challenge lies in achieving sufficient tightness without excessively straining the material, requiring a balance of pressure and technique.
In summary, rolling tightness is not merely a superficial aspect of preparing an inflatable sleeping surface; it constitutes a fundamental component that directly impacts storage efficiency and product durability. Addressing this factor contributes to both space conservation and the preservation of the item’s structural integrity. Mastering the appropriate level of rolling tightness, alongside other compression techniques, is essential for optimizing the management of inflatable sleeping surfaces.
5. Securing Method
The application of a reliable securing method represents a critical final step in the process of compacting and storing an inflatable sleeping surface. This procedure directly influences the long-term integrity of the folded unit and its ease of handling. Without adequate securing measures, the compressed air mattress is prone to unfurling, negating the benefits of careful folding and potentially exposing the material to damage.
- Retention of Compressed Form
The primary function of a securing method is to maintain the tightly rolled or folded configuration achieved through prior compression techniques. This prevents the expansion of trapped air and the loosening of the compacted material, ensuring that the air mattress occupies minimal storage space. For instance, utilizing ratchet straps around a tightly rolled mattress prevents it from expanding over time, unlike relying solely on the inherent friction of the folded material. The long-term retention of the compressed form directly correlates with the effectiveness of the securing method.
- Protection Against Environmental Factors
A robust securing method can also provide a degree of protection against environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and pests. Securing straps or a fitted storage bag can act as a barrier, preventing contaminants from penetrating the folded material. This is particularly relevant in damp storage environments, where unsecured air mattresses are susceptible to mold and mildew growth. A zippered storage bag, for example, offers a more effective barrier than simple tie straps.
- Enhanced Portability and Handling
A well-secured air mattress is significantly easier to transport and handle. Straps or a fitted bag provide convenient handholds or attachment points for carrying or moving the item. This is particularly important for larger mattresses, where an unsecured package is cumbersome and difficult to maneuver. A mattress secured with multiple straps, forming a carrying harness, allows for safer and more efficient transportation than a loose, unwieldy bundle.
The possibility of accidental unfurling poses a risk to both the stored air mattress and its surroundings. An unsecured mattress can suddenly expand, potentially causing damage to nearby objects or presenting a tripping hazard. A reliable securing method minimizes this risk by preventing the unintentional release of the compressed material. Securing clips, for example, provide a secondary layer of protection against accidental strap slippage.
In conclusion, the securing method is an indispensable element of the “how to fold up an air mattress” process. Its function extends beyond simply containing the folded unit; it contributes to long-term storage efficiency, environmental protection, and ease of handling. The selection of an appropriate securing method, therefore, requires careful consideration of the storage environment, the size of the mattress, and the desired level of protection.
6. Storage Environment
The ambient conditions under which a compressed inflatable sleeping surface is maintained significantly impact its longevity and readiness for future use. The storage environment encompasses a range of factors that directly influence the material’s structural integrity and its susceptibility to degradation. These factors, when not properly managed, can undermine the effectiveness of even the most meticulous folding and securing techniques.
- Temperature Fluctuations
Extreme temperature variations can cause expansion and contraction of the inflatable material, leading to stress and potential weakening of seams and valves. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can accelerate material degradation, while freezing temperatures may render the material brittle and prone to cracking. Storing an air mattress in an uninsulated attic or garage, where temperature swings are substantial, exemplifies this issue. Such conditions can compromise the airtight seal and shorten the lifespan of the product.
- Humidity Levels
Elevated humidity promotes the growth of mold and mildew, particularly within the folded layers of the mattress where air circulation is limited. These microorganisms can degrade the material, produce unpleasant odors, and trigger allergic reactions. Conversely, excessively dry conditions can cause the material to become brittle and prone to cracking. Storing an air mattress in a damp basement or a poorly ventilated storage unit creates an ideal environment for microbial growth. The control of humidity levels is, therefore, essential for maintaining the integrity of the stored item.
- Exposure to Ultraviolet Radiation
Prolonged exposure to direct sunlight or other sources of ultraviolet (UV) radiation can cause fading, discoloration, and weakening of the inflatable material. UV radiation degrades the polymers that constitute the mattress, reducing its flexibility and increasing its susceptibility to tears. Storing an air mattress near a window or in an outdoor location without adequate protection exposes it to harmful UV rays. Shielding the stored item from direct sunlight is crucial for preventing material degradation.
- Physical Obstructions and Pests
The presence of sharp objects or pests within the storage environment poses a direct threat to the integrity of the inflatable material. Sharp objects can puncture or tear the mattress, while rodents and insects can gnaw or burrow into the material, causing irreparable damage. Storing an air mattress in a cluttered storage space or an area prone to pest infestation increases the risk of physical damage. Ensuring a clean and pest-free storage area is essential for protecting the stored item from external threats.
These environmental considerations, when integrated into the “how to fold up an air mattress” process, extend beyond mere compression and securing. The selection of an appropriate storage location, characterized by stable temperature, controlled humidity, UV protection, and freedom from physical hazards, is paramount. Neglecting these factors can negate the benefits of even the most meticulous folding techniques, leading to premature degradation and rendering the air mattress unusable. Therefore, the storage environment must be viewed as an integral component of a comprehensive strategy for managing inflatable sleeping surfaces.
7. Puncture Prevention
The safeguarding of inflatable sleeping surfaces against punctures constitutes a critical aspect of long-term maintenance and storage. Integrating puncture prevention strategies into the process of compacting and stowing these items extends their lifespan and ensures their readiness for future use.
- Surface Inspection Prior to Folding
A thorough visual and tactile inspection of the air mattress surface, conducted prior to folding, identifies potential puncture hazards embedded within the material or adhering to its exterior. Small debris, such as pebbles, shards of glass, or metallic fragments, can inflict damage during the compression process. Removing these foreign objects mitigates the risk of punctures that would otherwise compromise the airtight seal. For example, sweeping the floor before deflating the air mattress reduces the likelihood of trapping debris during folding.
- Protective Layer Implementation
The utilization of a protective layer, such as a durable fabric sheet or a specialized storage bag, provides a physical barrier against abrasive surfaces and sharp objects present in the storage environment. This layer minimizes direct contact between the air mattress material and potential puncture hazards. For instance, encasing the deflated and folded air mattress within a heavy-duty canvas bag shields it from rough surfaces and accidental impacts during handling and storage. This preventative measure is particularly relevant in environments with limited control over surface conditions.
- Controlled Compression Techniques
Employing controlled compression techniques during the folding and rolling process prevents the creation of concentrated pressure points that could lead to punctures. Uneven distribution of force can stress the material, increasing its susceptibility to tears or pinholes, especially in areas weakened by prior use or environmental exposure. Implementing a deliberate and systematic folding method, combined with even pressure application during rolling, minimizes the risk of localized stress concentrations. Deliberate, even pressure application, as opposed to forced or abrupt movements, is essential for preventing material strain.
- Strategic Storage Location Selection
The choice of storage location significantly impacts the risk of puncture damage. Selecting an area free from sharp objects, pests, and excessive weight reduces the potential for accidental damage. Storing the folded air mattress on a smooth, elevated surface, away from potential sources of punctures, such as tools or protruding nails, minimizes the likelihood of compromising the airtight seal. Furthermore, avoiding locations prone to rodent infestation, which can result in gnawing damage to the inflatable material, is crucial for preserving the product’s integrity. The careful selection of a storage location directly contributes to puncture prevention.
These puncture prevention strategies, when
integrated into the established “how to fold up an air mattress” methodology, significantly enhance the long-term viability and usability of inflatable sleeping surfaces. Addressing these considerations proactively minimizes the risk of material damage and ensures that the air mattress remains a reliable and readily available option for temporary bedding needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the proper folding and storage of inflatable sleeping surfaces, emphasizing techniques for maximizing space efficiency and minimizing material degradation.
Question 1: What is the optimal method for removing residual air from an air mattress prior to folding?
Complete air expulsion is essential for compact storage. Utilizing an electric pump with a reverse function expedites this process. Alternatively, applying body weight to the deflated mattress, focusing on areas furthest from the valve, aids in forcing out trapped air. Ensure the valve remains fully open during this procedure.
Question 2: Is a specific folding technique recommended for air mattresses?
A tri-fold method, followed by tight rolling, generally proves effective. Folding the mattress lengthwise into thirds promotes a manageable width for subsequent rolling. The rolling action should commence from the valve end, facilitating further air expulsion. This technique maximizes compactness and minimizes the risk of material stress.
Question 3: What materials are suitable for securing a compressed air mattress?
Durable straps, such as those constructed from nylon or polypropylene, offer reliable compression. Bungee cords can also be employed, but their elasticity may result in gradual loosening over time. Ratchet straps provide adjustable tension for maintaining a secure hold. Avoid using materials that could damage the mattress surface, such as sharp-edged metal clasps.
Question 4: What environmental factors should be considered when selecting a storage location?
A cool, dry environment is paramount. Avoid locations subject to extreme temperature fluctuations or high humidity. Exposure to direct sunlight can degrade the mattress material over time. Pests and sharp objects also pose a threat. A temperature-controlled closet or storage unit, free from potential hazards, is generally suitable.
Question 5: How can the risk of punctures during storage be minimized?
Prior to folding, thoroughly inspect the air mattress surface for any sharp debris. Employ a protective layer, such as a heavy-duty storage bag or a thick fabric sheet, to shield the mattress from abrasive surfaces. Avoid stacking heavy items on top of the compressed unit, as this can create pressure points that may lead to punctures.
Question 6: How frequently should a stored air mattress be inspected?
Periodic inspections, ideally every three to six months, are recommended. Examine the mattress for signs of leaks, material degradation, or pest damage. Re-tighten securing straps as needed and address any environmental concerns, such as moisture accumulation, promptly. Early detection of potential issues prevents more significant problems from developing.
Proper storage and maintenance contribute significantly to the longevity and usability of inflatable sleeping surfaces. Adhering to these guidelines optimizes space efficiency and minimizes the potential for damage during storage.
The subsequent section will provide a comprehensive summary of key recommendations and concluding remarks on the effective management of air mattresses.
Concluding Remarks
The preceding exploration of “how to fold up an air mattress” has illuminated critical techniques for efficient storage and preservation. Key aspects include maximizing deflation, employing structured folding methods, securing the compressed form, selecting appropriate storage environments, and preventing puncture damage. Adherence to these practices contributes directly to the longevity and usability of inflatable sleeping surfaces.
Effective implementation of these strategies requires a proactive and diligent approach. Prioritizing these measures ensures the readiness and integrity of stored air mattresses, optimizing resource utilization and minimizing potential expenses associated with premature replacement. The long-term benefits of proper storage techniques extend beyond mere convenience, contributing to sustainable consumption practices and responsible resource management.



![Best Toyota Tacoma Air Mattress [Sleep Easy!] Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Best Toyota Tacoma Air Mattress [Sleep Easy!] | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-6744-300x200.jpg)