Addressing discoloration caused by bodily fluids on bedding requires prompt and appropriate action. The successful removal of such marks hinges on several factors, including the age of the stain, the type of material affected, and the cleaning agents employed. Failure to address the problem effectively can lead to lasting blemishes and potential fabric damage.
Effective stain removal is paramount for maintaining hygiene and extending the lifespan of the mattress. Left untreated, organic matter can harbor bacteria and create unpleasant odors. Historically, various methods and materials have been utilized to combat staining, ranging from simple household remedies to specialized commercial products.
The following sections will outline proven techniques for tackling blood stains on mattresses, encompassing both readily available solutions and considerations for more stubborn or aged marks. Specific product recommendations and detailed application instructions will be provided to guide the user through the cleaning process.
Mattress Stain Removal Strategies
Effective blood stain removal from a mattress requires a systematic approach, combining appropriate cleaning agents with careful technique. The following strategies will maximize the likelihood of successful stain elimination without damaging the mattress material.
Tip 1: Act Quickly. Fresh stains are significantly easier to remove than older, set-in stains. Immediate attention increases the chances of complete removal.
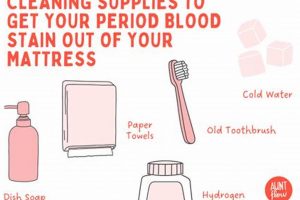
Tip 2: Use Cold Water. Blood proteins coagulate in hot water, setting the stain. Always use cold water when treating blood stains.
Tip 3: Blot, Do Not Rub. Rubbing can spread the stain and damage the fibers of the mattress. Gently blot the stain with a clean cloth, working from the outside in.
Tip 4: Utilize Hydrogen Peroxide. A 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide can be effective at breaking down blood stains. Test in an inconspicuous area first to ensure it does not discolor the mattress.
Tip 5: Employ Baking Soda Paste. A paste of baking soda and water can absorb the stain. Apply the paste, let it dry completely, and then vacuum it up.
Tip 6: Consider Enzyme Cleaners. Enzyme-based cleaners are designed to break down organic matter and can be effective on blood stains. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully.
Tip 7: Vacuum Thoroughly. After using any cleaning solution, vacuum the mattress thoroughly to remove any residue.
By following these methods, one can significantly improve the outcome of blood stain removal from mattresses, restoring cleanliness and preventing lasting damage.
The subsequent section will address persistent stains and professional cleaning options if home remedies prove insufficient.
1. Prompt Action
The efficacy of any method aimed at eliminating blood stains from a mattress is inextricably linked to the immediacy of the response. Delaying intervention allows the blood to penetrate deeper into the mattress fibers, facilitating coagulation and solidifying the bond between the staining agent and the material. This process renders subsequent removal attempts significantly more challenging and increases the likelihood of a permanent, visible mark. Consider, for example, a scenario where a minor nosebleed occurs during sleep. If addressed immediately upon awakening, a simple blotting with cold water might suffice. However, if the stain remains unattended for several hours, or overnight, more aggressive cleaning agents and techniques will invariably be required, with a diminished probability of complete success.
The chemical composition of blood changes over time, further complicating removal. As blood dries, its proteins denature and become more resistant to dissolution. Furthermore, the iron content in blood can oxidize, leading to a more persistent and potentially discolored stain. In a practical setting, this translates to a need for more intensive cleaning solutions, potentially containing enzymes or bleaching agents, and increased physical effort in the form of scrubbing or prolonged soaking. This heightened cleaning regime carries an elevated risk of damaging the mattress fabric, leading to discoloration, weakening of fibers, or even structural compromise.
In conclusion, prompt action represents a critical determinant in the success of efforts to eliminate blood stains from mattresses. The immediate application of appropriate cleaning techniques not only simplifies the removal process but also minimizes the potential for lasting damage to the mattress. While effective cleaning solutions and methods exist, their effectiveness is substantially diminished in the absence of a timely response, underscoring the importance of immediate attention to such incidents.
2. Cold Water Only
The principle of using only cold water when addressing blood stains on mattresses is paramount to achieving successful stain removal. This directive stems from the unique properties of blood and its reaction to temperature changes. Understanding this relationship is crucial for preventing permanent staining and maintaining the integrity of the mattress.
- Protein Coagulation Prevention
Blood contains proteins that coagulate when exposed to heat. Hot water accelerates this process, causing the proteins to solidify and bind more tightly to the mattress fibers. This essentially sets the stain, making it significantly more difficult, if not impossible, to remove. Cold water, conversely, helps to keep the proteins in a liquid state, allowing them to be more easily flushed out of the fabric. For example, rinsing a blood-stained garment under cold water will initially remove a significant portion of the stain, while hot water will likely worsen it.
- Fiber Integrity Preservation
Mattress fabrics, particularly those made from natural fibers like cotton or wool, are susceptible to damage from high temperatures. Hot water can cause these fibers to shrink, warp, or weaken, potentially leading to permanent changes in the mattress’s texture and appearance. Using cold water minimizes the risk of such damage, preserving the mattress’s structural integrity and prolonging its lifespan. A scenario might involve attempting to clean a wool mattress cover with hot water, leading to irreversible shrinkage and distortion of the fabric.
- Enzyme Cleaner Efficacy
Many effective blood stain removal products rely on enzymes to break down the organic components of blood. These enzymes function optimally within a specific temperature range, typically cooler temperatures. Hot water can denature these enzymes, rendering them ineffective. By using cold water, the enzymatic cleaning agents retain their ability to digest the blood stain, enhancing the overall cleaning process. Consider an enzyme-based stain remover applied with hot water, which would significantly reduce its effectiveness in breaking down the blood proteins.
- Stain Spread Minimization
Hot water can cause blood to spread further into the mattress fibers, expanding the stained area. This occurs because the heat increases the fluidity of the blood, allowing it to seep deeper and wider into the fabric. Cold water, on the other hand, helps to contain the stain, preventing it from spreading and making it easier to target the affected area. Imagine attempting to clean a small blood spot with hot water, only to find it has expanded into a much larger, more diffuse stain.
In conclusion, the exclusive use of cold water is a fundamental principle in the successful elimination of blood stains from mattresses. By preventing protein coagulation, preserving fiber integrity, maintaining enzyme efficacy, and minimizing stain spread, cold water maximizes the chances of complete stain removal and safeguards the mattress from potential damage. This approach, while seemingly simple, is crucial for achieving optimal results when addressing this common household issue.
3. Blotting Technique
The blotting technique is a cornerstone of effective blood stain removal from mattresses. Its significance lies in minimizing the disruption of mattress fibers while facilitating the absorption of the stain. Unlike rubbing or scrubbing, which can force the stain deeper into the material and damage the fibers, blotting gently lifts the blood from the surface. This method involves using a clean, absorbent cloth or paper towel and pressing it firmly against the stain, allowing the material to soak up the liquid. The action is repeated with clean sections of the cloth until no more blood is transferred. The efficacy of this approach is demonstrably higher than aggressive rubbing, which can lead to a larger, more diffuse stain and potential fabric damage. For instance, attempting to scrub a fresh blood stain on a delicate memory foam mattress can embed the stain and compromise the foam’s structure; however, gentle blotting with a cold, damp cloth will likely yield a significantly better result.
The success of the blotting technique is also contingent on the choice of absorbent material and cleaning agent. A highly absorbent cloth, such as microfiber, is preferable to a coarser material that might abrade the mattress surface. The cleaning agent, whether it is cold water, hydrogen peroxide, or an enzymatic cleaner, should be applied sparingly to the cloth, rather than directly onto the mattress. This controlled application prevents over-saturation and potential damage to the underlying layers. Furthermore, the direction of blotting is important; it should proceed from the outside of the stain inwards, to prevent the stain from spreading outwards. An example of incorrect application would be saturating the stain with a cleaning solution and then aggressively rubbing it with a rough cloth, leading to a larger, more deeply embedded stain and potential discoloration of the mattress fabric.
In summary, the blotting technique is an essential component of successful blood stain removal from mattresses. Its gentle, controlled approach minimizes fiber damage and facilitates effective stain absorption. Coupled with the appropriate cleaning agents and absorbent materials, blotting offers a superior alternative to more aggressive cleaning methods, resulting in a cleaner mattress and a reduced risk of lasting damage. The technique underscores the importance of a delicate and methodical approach to stain removal, prioritizing preservation of the mattress material over brute force.
4. Appropriate Cleaner
The selection of a suitable cleaning agent is paramount to the effective removal of blood stains from mattresses. The efficacy of any method depends significantly on the cleaner’s capacity to break down the components of blood without causing damage to the mattress material. Misapplication of cleaning agents can result in permanent discoloration, fiber degradation, or the setting of the stain, thereby exacerbating the problem. For instance, using a bleach-based cleaner on a colored mattress could lead to irreversible fading, while an overly acidic cleaner could damage the fibers of a natural latex mattress. Thus, a careful assessment of both the stain’s characteristics and the mattress material is critical in selecting the appropriate cleaner.
Several cleaning agents are commonly employed for addressing blood stains, each possessing distinct properties and appropriate applications. Cold water alone is effective for fresh stains, especially when combined with prompt blotting. Hydrogen peroxide (3% solution) is a mild oxidizing agent that can break down blood proteins, but it should be tested on an inconspicuous area first to ensure it does not cause discoloration. Enzyme-based cleaners are specifically formulated to digest organic matter and are often effective on older or set-in stains; however, their use requires careful adherence to the manufacturer’s instructions. Ammonia solutions can also be used, but only on mattresses made of materials that are not sensitive to alkaline substances and with extreme caution to avoid inhalation or contact with skin. The inappropriate use of any of these cleaners can lead to adverse effects, highlighting the importance of informed decision-making.
In conclusion, the selection of an appropriate cleaner is an indispensable element in the successful removal of blood stains from mattresses. Factors such as the stain’s age, the mattress material, and the cleaner’s chemical properties must be carefully considered to minimize the risk of damage and maximize the likelihood of complete stain removal. Failure to apply an appropriate cleaner can not only render the cleaning process ineffective but also lead to costly and irreversible damage to the mattress. Therefore, a thorough understanding of available cleaning agents and their suitability for specific situations is essential for maintaining the cleanliness and longevity of mattresses.
5. Thorough Drying
The successful removal of blood stains from a mattress extends beyond the application of cleaning agents; complete and thorough drying of the treated area is a critical, often overlooked, step. Failure to ensure that the mattress is completely dry can lead to consequences that undermine the initial cleaning efforts, potentially causing further damage and rendering the stain removal process ultimately unsuccessful. The residual moisture provides an environment conducive to mold and mildew growth, fostering unpleasant odors and posing potential health risks. This necessitates a re-treatment of the affected area, compounding the initial problem and potentially exacerbating any existing damage to the mattress fibers. A scenario wherein a blood stain is treated, seemingly removed, but then covered before being completely dry can serve as a prime example, leading to the development of a musty odor and the potential appearance of mold within a matter of days.
The method employed for drying the mattress is also important. Air drying in a well-ventilated room is often the most gentle and effective approach, allowing moisture to evaporate naturally. Direct sunlight can also be used, but caution must be exercised to prevent fading or damage to the mattress fabric. The use of fans can accelerate the drying process. Conversely, the application of high heat from a hair dryer or other heating devices should be avoided, as it can potentially set any remaining traces of the stain or damage the mattress fibers. The presence of any remaining dampness allows any remaining hemoglobin or blood components to interact with the mattress materials, potentially leading to the reappearance of the stain over time, even after it initially appeared to have been successfully removed.
In conclusion, thorough drying is an indispensable component of the blood stain removal process on mattresses. It directly influences the long-term success of the cleaning efforts by preventing mold and mildew growth, preserving the integrity of the mattress fibers, and minimizing the risk of stain recurrence. The selection of an appropriate drying method, combined with patience and attention to detail, will ultimately determine whether the mattress is truly free from the stain and the potential adverse effects of residual moisture. Neglecting this crucial step can render the entire cleaning process futile, highlighting the importance of thorough drying as the final, essential stage in the stain removal process.
6. Fabric Sensitivity
The material composition of a mattress directly dictates the suitability of various stain removal techniques. Variations in fabric type, such as cotton, memory foam, latex, or blended materials, necessitate tailored cleaning approaches to prevent damage and ensure effective stain removal. The inherent sensitivity of a fabric to specific cleaning agents and methods forms a critical consideration in any stain removal strategy.
- Reaction to Chemical Cleaners
Different mattress fabrics exhibit varying reactions to chemical cleaning agents. For instance, while hydrogen peroxide may be suitable for certain cotton blends, it can cause discoloration or degradation in sensitive materials like wool or silk. Enzyme-based cleaners, generally considered gentler, may still prove unsuitable for specific synthetic fabrics. A patch test in an inconspicuous area is essential to assess the fabric’s reaction before widespread application. The selection of an inappropriate cleaner can result in irreversible damage, compromising the mattress’s integrity and aesthetic appeal.
- Water Absorption and Drying Time
Fabric density and fiber structure significantly impact water absorption and drying time. Denser fabrics, such as tightly woven cotton or memory foam, retain moisture for extended periods, increasing the risk of mold or mildew growth if not thoroughly dried. Latex, being naturally water-resistant, requires a different approach to prevent water from pooling beneath the surface. Understanding the fabric’s water absorption characteristics is crucial for selecting appropriate drying methods, such as air drying, blotting, or the use of fans. Inadequate drying can lead to persistent odors and compromise the mattress’s hygienic condition.
- Fiber Strength and Abrasion Resistance
The fiber strength and abrasion resistance of a mattress fabric determine its tolerance to scrubbing and physical manipulation. Delicate fabrics, such as silk or certain types of rayon, are easily damaged by aggressive scrubbing, leading to fiber breakage and pilling. More durable fabrics, like tightly woven cotton or polyester blends, can withstand more rigorous cleaning methods. The choice of cleaning technique, whether gentle blotting or light scrubbing, should be guided by the fabric’s inherent strength and resistance to abrasion. Improper technique can result in visible wear and tear, reducing the mattress’s lifespan.
- Colorfastness and Dye Stability
The colorfastness of a mattress fabric indicates its resistance to fading or color bleeding when exposed to cleaning agents or water. Fabrics with poor colorfastness are prone to discoloration, especially when treated with harsh chemicals. Darker-colored fabrics are generally more susceptible to color bleeding than lighter-colored ones. When treating blood stains on colored mattresses, it is crucial to use color-safe cleaning agents and avoid excessive rubbing to minimize the risk of discoloration. Patch testing is particularly important for colored fabrics to ensure that the cleaning agent does not cause fading or color transfer.
In summary, fabric sensitivity plays a crucial role in how blood stains are addressed. A comprehensive understanding of the mattress material’s properties is essential for selecting appropriate cleaning agents and techniques that effectively remove stains without causing damage. Failure to consider fabric sensitivity can result in irreversible damage, discoloration, or reduced lifespan of the mattress. Therefore, a cautious and informed approach is paramount to successful stain removal.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the removal of blood stains from mattresses, providing factual information and practical guidance.
Question 1: Why is it important to act quickly when dealing with blood stains on mattresses?
Prompt action prevents the blood from penetrating deeper into the mattress fibers, making subsequent removal efforts significantly more challenging and potentially leading to a permanent stain.
Question 2: Is hot water an effective cleaning agent for blood stains on mattresses?
No. Hot water causes the proteins in blood to coagulate, setting the stain and making it more difficult to remove. Cold water is the recommended approach.
Question 3: What is the significance of blotting, rather than rubbing, a blood stain on a mattress?
Blotting minimizes fiber disruption and prevents the stain from spreading further into the mattress material, whereas rubbing can embed the stain and damage the fibers.
Question 4: Can hydrogen peroxide be used safely on all mattress types to remove blood stains?
Hydrogen peroxide can be effective, but it should be tested on an inconspicuous area first to ensure it does not cause discoloration. Certain fabrics may be sensitive to its oxidizing properties.
Question 5: What are the potential consequences of not thoroughly drying a mattress after blood stain removal?
Residual moisture can create an environment conducive to mold and mildew growth, leading to unpleasant odors, potential health risks, and the possible reappearance of the stain.
Question 6: Are professional mattress cleaning services necessary for all blood stains?
While many stains can be addressed with home remedies, persistent or extensive stains may require professional intervention to ensure complete removal and prevent further damage to the mattress.
In summary, successful blood stain removal from mattresses requires prompt action, appropriate cleaning agents, gentle techniques, and thorough drying. Understanding these key factors can help maintain the cleanliness and longevity of the mattress.
The subsequent section will delve into professional cleaning options and preventative measures to safeguard mattresses from future staining incidents.
Conclusion
This exploration of “how to get rid of blood stains from mattress” has detailed various methods, emphasizing the critical factors that influence success. Prompt action, the exclusive use of cold water, careful blotting techniques, appropriate cleaner selection based on material sensitivity, and thorough drying were identified as essential steps. The information presented underscores the importance of a methodical approach in addressing these often-challenging stains.
Effective management of blood stains on mattresses is vital for maintaining a clean and hygienic sleep environment. The diligent application of the techniques described can extend the life of the mattress and prevent potential health hazards. Should home remedies prove insufficient, professional cleaning services offer a viable alternative. Prioritizing mattress care through preventative measures, such as mattress protectors, remains the most effective strategy for mitigating the occurrence of blood stains and preserving the integrity of this essential household item.