Addressing discoloration and marks resulting from perspiration on a sleeping surface requires specific cleaning techniques. These blemishes, often yellowed or darkened, are caused by the interaction of bodily fluids and oils with mattress materials over time. Successfully removing these requires understanding the stain’s composition and the appropriate cleaning agents to dissolve and lift it without damaging the underlying fabric and padding.
Maintaining a clean sleeping environment is crucial for hygiene and comfort. The removal of these blemishes extends the life of the mattress, prevents the buildup of allergens and bacteria, and contributes to a more sanitary and pleasant sleep experience. Historically, methods for addressing mattress stains have evolved from simple airing and sun-bleaching to the utilization of specialized cleaning solutions and techniques.
The subsequent sections will detail practical methods for tackling these marks on a mattress, encompassing preparation, cleaning solutions, application techniques, and preventative measures to minimize future occurrences. The procedures outline safe and effective approaches applicable to various mattress types and stain severities.
Tips for Eliminating Perspiration Marks on Mattresses
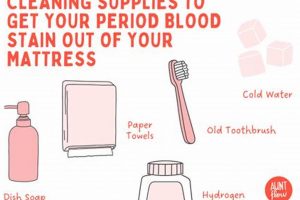
Effectively removing perspiration marks from a mattress requires a methodical approach and the application of appropriate cleaning agents. The following tips provide guidance on achieving optimal results while minimizing potential damage to the mattress.
Tip 1: Immediate Action: Address fresh perspiration as quickly as possible. Blot the affected area with a clean, dry cloth or towel to absorb as much moisture as possible before it penetrates deeper into the mattress fibers.
Tip 2: Baking Soda Application: Liberally apply baking soda to the stained area. Baking soda is a natural deodorizer and absorbent, helping to draw out moisture and odors. Allow it to sit for several hours, preferably overnight, before vacuuming thoroughly.
Tip 3: Hydrogen Peroxide Solution: For stubborn stains, mix a solution of hydrogen peroxide (3%), water, and a small amount of dish soap. Lightly spray the solution onto the stain, ensuring not to oversaturate the mattress. Allow it to sit for 20-30 minutes, then blot with a clean, damp cloth.
Tip 4: Enzyme Cleaner Utilization: Enzyme-based cleaners are effective at breaking down organic matter, including perspiration. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully when applying, and test the cleaner on an inconspicuous area of the mattress first.
Tip 5: Steam Cleaning: Steam cleaning can help to lift stains and sanitize the mattress. Use a steam cleaner with an upholstery attachment and move it slowly over the stained area. Ensure the mattress is thoroughly dry after steam cleaning to prevent mold growth.
Tip 6: Vinegar Solution: White vinegar, diluted with water, can be used as a natural cleaning agent. Apply the solution to the stain, let it sit for a few minutes, and then blot with a clean cloth. Vinegar also helps to neutralize odors.
Tip 7: Sun Exposure: Whenever possible, expose the mattress to direct sunlight after cleaning. Sunlight has natural bleaching and disinfecting properties, which can further help to remove stains and odors. However, prolonged exposure to direct sunlight can damage some mattress materials.
These tips offer a range of methods to address and eliminate perspiration marks. Consistent and prompt attention to spills, coupled with regular cleaning and mattress protection, will significantly contribute to maintaining a clean and hygienic sleep environment.
The final section will address preventative measures to minimize future staining, thereby prolonging the life and cleanliness of the mattress.
1. Absorption
Absorption constitutes a fundamental first step in mitigating the impact of perspiration on a mattress. The prompt removal of moisture prevents deeper penetration into the mattress fibers, minimizing stain formation and potential odor development. The longer perspiration remains unaddressed, the more firmly it binds to the mattress materials, complicating subsequent cleaning efforts. A timely response utilizing absorbent materials such as clean cloths or towels is crucial for limiting the extent of the stain and facilitating easier removal in the long run. For example, immediately blotting a spill with a dry towel greatly reduces the amount of liquid that soaks into the mattress compared to leaving it unattended.
The effectiveness of subsequent stain removal treatments is directly influenced by the initial absorption efforts. By extracting excess moisture, the concentration of staining agents is reduced, thereby enhancing the efficacy of cleaning solutions and minimizing the potential for lasting discoloration. Moreover, rapid absorption helps prevent the growth of mold and mildew, which thrive in moist environments. Failing to address moisture promptly can lead to embedded stains, persistent odors, and a compromised mattress structure, ultimately necessitating more aggressive cleaning methods or even premature replacement.
In summary, prioritizing absorption as the initial response to perspiration on a mattress is paramount for effective stain management. It reduces the severity of staining, minimizes odor development, and prevents the proliferation of mold and mildew. This proactive approach not only simplifies the cleaning process but also extends the lifespan and hygiene of the mattress. Neglecting absorption can result in more challenging stain removal, potential material damage, and a less sanitary sleeping environment.
2. Disinfection
Disinfection is a crucial aspect of addressing perspiration stains on a mattress. Beyond aesthetic concerns, bodily fluids can harbor microorganisms that pose health risks. Therefore, stain removal should incorporate disinfection protocols to eliminate pathogens and ensure a sanitary sleeping surface.
- Bacterial and Fungal Growth
Perspiration creates a favorable environment for the proliferation of bacteria and fungi. These microorganisms can contribute to unpleasant odors, exacerbate allergies, and potentially cause skin infections. Disinfection eliminates these organisms, preventing these adverse effects. For example, using a disinfecting spray with antifungal properties after stain removal can inhibit fungal growth in the mattress fibers.
- Odor Control
Many malodors associated with sweat stains are caused by bacterial decomposition. Disinfecting agents target these bacteria, effectively neutralizing the source of the odor. Simply masking the smell is insufficient; complete disinfection is necessary for long-term odor control. An example includes using a steam cleaner with a disinfecting solution to penetrate deep into the mattress and eliminate odor-causing bacteria.
- Prevention of Allergen Accumulation
Perspiration can attract dust mites and other allergens. Disinfection helps reduce the population of these allergens, improving air quality and reducing allergic reactions. For example, applying a disinfectant spray specifically formulated to kill dust mites after cleaning can significantly reduce allergen levels.
- Enhancing Hygiene
Disinfection promotes overall hygiene by eliminating pathogens and creating a cleaner sleep environment. This is particularly important for individuals with compromised immune systems or allergies. Ensuring a disinfected mattress reduces the risk of exposure to harmful microorganisms and contributes to better health. A practical example is regularly disinfecting a mattress used by someone recovering from an illness to prevent reinfection.
The multifaceted benefits of disinfection in the context of stain removal extend beyond superficial cleaning. By targeting bacteria, fungi, allergens, and odors, disinfection ensures a thoroughly sanitized mattress, contributing to improved hygiene and a healthier sleeping environment. This holistic approach is essential for effectively “getting rid of sweat stains on mattress” and maintaining long-term mattress hygiene.
3. Odor Neutralization
Odor neutralization is an integral component of eliminating perspiration stains from mattresses. The presence of lingering odors, even after stain removal, can compromise the overall cleanliness and comfort of the sleeping surface. Effective odor neutralization targets the source of these smells, ensuring a truly fresh and hygienic mattress.
- Decomposition Byproducts
Perspiration, when absorbed into mattress fibers, undergoes decomposition, leading to the formation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) responsible for unpleasant odors. Neutralization involves the chemical alteration or absorption of these VOCs to eliminate their scent. For example, baking soda acts as an absorbent, trapping and neutralizing acidic VOCs produced during decomposition.
- Bacterial Odors
Bacteria thrive in the moist environment created by perspiration, producing metabolic waste products that contribute to mattress odors. Neutralizing bacterial odors requires the use of antimicrobial or enzymatic agents that disrupt bacterial activity or break down their byproducts. An example includes using a fabric-safe disinfectant spray that eliminates odor-causing bacteria without damaging the mattress material.
- pH Imbalance Correction
Perspiration can alter the pH balance of mattress materials, creating conditions that favor odor development. Neutralizing agents often work by restoring the natural pH of the fibers, inhibiting odor-causing reactions. For instance, a diluted vinegar solution can neutralize alkaline residues from sweat, restoring the material’s natural acidity and reducing odor.
- Encapsulation and Masking
While not true neutralization, encapsulation involves trapping odor molecules within a compound, preventing their release into the air. Masking, on the other hand, uses stronger, more pleasant scents to overwhelm the original odor. These methods offer temporary relief but do not address the underlying source of the odor. An example of encapsulation is using a fabric refresher spray that contains cyclodextrins to trap odor molecules. Masking includes using heavily scented fabric sprays that only cover up the smell of sweat.
The successful elimination of perspiration stains from a mattress necessitates a comprehensive approach that incorporates both stain removal and odor neutralization. Addressing the underlying causes of odors, such as decomposition byproducts and bacterial activity, is essential for long-term freshness. While masking agents may provide temporary relief, true odor neutralization requires agents that chemically alter or absorb odor-causing molecules, contributing to a cleaner, healthier, and more comfortable sleep environment. By addressing each odor from a sweat stain, your “how to get rid of sweat stains on mattress” approach is further enhanced.
4. Material Compatibility
Material compatibility is a critical consideration when addressing perspiration stains on a mattress. The diverse composition of mattresses, ranging from natural fibers to synthetic foams, necessitates a careful selection of cleaning agents and techniques to prevent damage and ensure effective stain removal. Incompatibility can lead to discoloration, degradation of materials, and a reduction in the mattress’s overall lifespan.
- Fiber Sensitivity
Natural fibers, such as cotton and wool, exhibit varying degrees of sensitivity to different cleaning agents. Harsh chemicals can strip natural oils, leading to brittleness, shrinkage, or discoloration. Synthetic fibers, like polyester and memory foam, may be more resistant to some chemicals but susceptible to damage from excessive heat or abrasive cleaning methods. For instance, using bleach on a wool mattress can permanently damage the fibers, while a mild enzymatic cleaner may be more suitable.
- Foam Degradation
Mattresses incorporating foam layers, including memory foam and latex, are particularly vulnerable to degradation from certain cleaning solutions. Solvents and harsh detergents can break down the foam structure, causing it to crumble or lose its supportive properties. Water saturation can also lead to mold growth within the foam. As an example, excessive application of water-based cleaners to a memory foam mattress can result in trapped moisture and subsequent mold formation.
- Color Fastness
The color fastness of mattress fabrics is another factor to consider. Some dyes are susceptible to fading or bleeding when exposed to certain cleaning agents. Testing a small, inconspicuous area of the mattress before applying any cleaning solution to the entire stain is crucial to avoid widespread discoloration. An example of this is when using a colored cleaning solution on white fabric resulting in the dye transferring from the solution to the material.
- pH Levels
The pH level of cleaning solutions can significantly impact mattress materials. Highly acidic or alkaline cleaners can damage fibers and foams. Opting for pH-neutral or mildly acidic solutions is generally safer. For instance, using undiluted vinegar (highly acidic) on certain mattress fabrics can cause damage, while a diluted vinegar solution may be appropriate for odor neutralization without harming the materials.
The effective elimination of perspiration stains from mattresses requires a thorough understanding of material composition and sensitivity. Selecting compatible cleaning agents and methods is essential to prevent damage, maintain the mattress’s integrity, and ensure a safe and hygienic sleep environment. Ignoring material compatibility can lead to irreversible damage and a reduced lifespan of the mattress.
5. Preventative Measures
The effectiveness of “how to get rid of sweat stains on mattress” is intrinsically linked to the implementation of preventative measures. These actions serve to minimize or eliminate the direct contact of perspiration with the mattress, thereby reducing the frequency and severity of staining. By addressing the root cause of the problem bodily fluids reaching the mattress proactive strategies lessen the reliance on stain removal techniques and contribute to a longer lifespan for the sleeping surface. For instance, the use of a waterproof mattress protector acts as a physical barrier, preventing sweat from penetrating the mattress layers and causing stains. This simple intervention reduces the need for aggressive cleaning methods that can degrade mattress materials over time.
Beyond the immediate prevention of stains, these measures offer additional benefits. Many mattress protectors also provide a barrier against dust mites and allergens, contributing to a healthier sleep environment. Regular washing of these protectors removes accumulated sweat and debris, further reducing the potential for staining and odor development. Furthermore, the choice of breathable bedding materials, such as cotton or linen sheets, can promote airflow and reduce the amount of perspiration that comes into contact with the mattress. As a practical example, individuals prone to night sweats can benefit significantly from using moisture-wicking sheets and a waterproof, breathable mattress protector, effectively mitigating the risk of staining.
In conclusion, preventative measures represent a proactive and cost-effective approach to maintaining mattress hygiene. While stain removal techniques address existing blemishes, preventative strategies minimize the occurrence of staining, reducing the need for aggressive cleaning and extending the life of the mattress. The understanding and application of these strategies are, therefore, integral to a comprehensive approach to “how to get rid of sweat stains on mattress” and ensuring a clean and comfortable sleep environment over the long term.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions and answers address common concerns regarding the removal of perspiration stains from mattresses. This information aims to provide clarity and guidance on best practices.
Question 1: Is professional mattress cleaning necessary for all perspiration stains?
Professional cleaning is not always required. Minor, recent stains can often be addressed with appropriate DIY methods. However, deep-set, extensive, or long-standing stains may necessitate professional intervention to ensure thorough cleaning and prevent damage to the mattress.
Question 2: Can baking soda alone effectively remove perspiration stains?
Baking soda primarily functions as an odor absorbent and mild cleaner. It is effective for neutralizing odors and drawing out some surface-level moisture. However, for more stubborn stains, baking soda should be combined with other cleaning agents or techniques to achieve optimal results.
Question 3: How often should a mattress protector be washed to prevent perspiration stains?
A mattress protector should be washed at least every one to two months. More frequent washing may be necessary for individuals who perspire heavily or those with allergies. Regular washing prevents the accumulation of sweat, oils, and allergens within the protector, minimizing the risk of stains and odors.
Question 4: Are enzyme cleaners safe for all types of mattresses?
Enzyme cleaners are generally safe for most mattress types, but testing the cleaner on an inconspicuous area is always recommended before applying it to the entire stain. Some enzyme cleaners may be too harsh for delicate materials or cause discoloration. Careful adherence to the manufacturer’s instructions is essential.
Question 5: Will exposing a mattress to direct sunlight completely remove perspiration stains?
Sunlight possesses natural bleaching and disinfecting properties, which can help to fade stains and eliminate odors. However, sunlight alone may not completely remove deep-set or severe perspiration stains. It is most effective when used in conjunction with other cleaning methods.
Question 6: Can neglecting perspiration stains lead to health problems?
Neglecting perspiration stains can contribute to the growth of mold, mildew, and bacteria within the mattress, potentially exacerbating allergies, triggering asthma, and causing skin irritations. Maintaining a clean and hygienic mattress is crucial for promoting overall health and well-being.
Proper stain management, incorporating the strategies outlined above, contributes significantly to the longevity and hygiene of the mattress.
The following section will provide a summary, emphasizing the critical points about “how to get rid of sweat stains on mattress.”
Conclusion
Effective management of perspiration stains requires a multifaceted approach, emphasizing immediate action, appropriate cleaning agents, and preventative measures. From initial absorption to disinfection and odor neutralization, each step plays a critical role in restoring and maintaining mattress hygiene. Material compatibility must be prioritized to prevent damage during the cleaning process, while consistent preventative actions such as mattress protectors minimize future occurrences. The integrated application of these principles ensures a cleaner and healthier sleep environment.
The proactive approach to “how to get rid of sweat stains on mattress” extends the lifespan of the sleeping surface and contributes significantly to overall well-being. By prioritizing cleanliness and employing effective strategies, individuals can safeguard their health and preserve the integrity of their mattresses, ensuring a comfortable and sanitary sleep experience for years to come. Continuous vigilance and adherence to best practices are essential for long-term success.