The process of filling an Intex air mattress with air is a fundamental step in preparing it for use. This involves using a pump, either manual, electric, or battery-operated, to introduce air into the mattress’s internal chambers until the desired firmness is achieved. Proper inflation ensures optimal comfort and support during use.
A correctly inflated air mattress provides a temporary sleeping surface, useful for accommodating guests, camping trips, or as a temporary bed solution during relocation or home renovations. The ability to quickly establish a comfortable sleeping space enhances convenience and improves the overall experience in situations where conventional beds are unavailable. Air mattresses also offer a portable and storable solution, contributing to space-saving advantages.
The subsequent sections will detail the various methods and considerations involved in achieving proper inflation, addressing pump selection, inflation techniques, and troubleshooting common issues encountered during the inflation process. This will ensure the air mattress reaches its optimal performance and longevity.
Inflation Best Practices
Optimizing the inflation process of an Intex air mattress involves several key practices to ensure proper functionality and longevity.
Tip 1: Select the Appropriate Pump: The choice of pump depends on the availability of power and desired inflation speed. Electric pumps offer convenience and speed, while manual pumps provide a backup solution in the absence of electricity. Battery-operated pumps offer a balance of portability and efficiency.
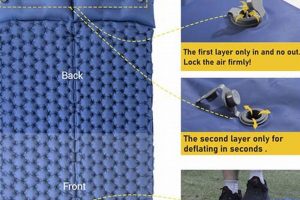
Tip 2: Locate the Inflation Valve: Familiarize yourself with the type of valve present on the Intex air mattress. Common valve types include Boston valves and standard pinch valves. Ensure the correct nozzle or adapter is used for a secure connection and to prevent air leakage.
Tip 3: Prevent Overinflation: Overinflating the mattress can strain the seams and potentially lead to punctures or ruptures. Inflate the mattress until it is firm but still has some give when pressed. Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for recommended pressure levels, if available.
Tip 4: Monitor Inflation Progress: Periodically check the firmness of the mattress during inflation. This allows for adjustments and prevents accidental overinflation. Ensure even distribution of air within the mattress chambers.
Tip 5: Ensure Valve Security: After inflation, ensure the valve is securely closed to prevent air leakage. For Boston valves, tightly screw the cap in place. For pinch valves, ensure the valve is properly sealed.
Tip 6: Consider Ambient Temperature: Temperature fluctuations can affect air pressure inside the mattress. In colder environments, the air may contract, requiring additional inflation. Conversely, in warmer environments, the air may expand, potentially leading to overinflation.
Tip 7: Inspect the Mattress Surface: Before inflation, thoroughly inspect the mattress surface for any sharp objects or debris that could cause punctures. Place the mattress on a smooth, clean surface to minimize the risk of damage.
By adhering to these best practices, the inflation process becomes more efficient, minimizing potential issues and maximizing the lifespan of the Intex air mattress.
The following section will address common troubleshooting steps related to air mattress inflation and maintenance.
1. Pump Selection
The selection of an appropriate pump directly determines the efficiency and ease with which an Intex air mattress can be inflated. The type of pump chosen dictates the speed of inflation, the effort required, and the accessibility to inflate the mattress in various locations. Mismatched or inadequate pump selection leads to prolonged inflation times, potential damage to the mattress valve, or the inability to inflate the mattress at all. For example, attempting to inflate an Intex air mattress with a Boston valve using a standard bicycle pump without the correct adapter will prove ineffective. Conversely, an electric pump designed for high-volume, low-pressure inflation is generally more effective than a manual foot pump for rapidly inflating a large air mattress.
Practical implications of pump selection extend to portability and power requirements. A battery-operated pump is advantageous for camping or situations where access to mains electricity is limited. Manual pumps offer a reliable backup when power sources are unavailable, though they necessitate greater physical exertion. Electric pumps, while offering convenience, require access to an electrical outlet, restricting their use in certain environments. Selecting a pump with adjustable pressure settings allows for customized firmness levels, optimizing comfort and preventing overinflation, a common cause of air mattress damage.
In conclusion, pump selection is a foundational element in the procedure to inflate an Intex air mattress. The appropriate choice significantly impacts inflation speed, convenience, and the overall lifespan of the mattress. Understanding the characteristics and limitations of different pump types enables informed decisions that minimize inflation challenges and maximize user satisfaction. Failure to consider pump selection increases the risk of damage or inadequate inflation, undermining the utility of the air mattress.
2. Valve Compatibility
Valve compatibility represents a crucial element within the operational procedures to inflate an Intex air mattress. The successful introduction of air into the mattress hinges upon the precise alignment between the inflation device’s nozzle and the mattress’s designated valve. A mismatch in valve types renders the inflation process either significantly less efficient or entirely impossible. For example, an Intex air mattress equipped with a Boston valve necessitates the use of an adapter or pump nozzle specifically designed to interface with this valve type. Attempting to use a standard pinch valve adapter on a Boston valve will result in air leakage and a failure to inflate the mattress to its optimal pressure.
The implication of valve incompatibility extends beyond mere inconvenience. Forcible attempts to connect mismatched valve types can damage the valve mechanism, leading to irreversible air leakage and rendering the mattress unusable. In emergency situations, such as providing temporary bedding during a power outage or natural disaster, the inability to inflate the mattress due to valve incompatibility can have significant practical consequences. Air mattress manufacturers provide various valve designs, including Boston valves, pinch valves, and newer proprietary systems. Identifying the valve type present on the mattress and procuring the corresponding pump or adapter represents a necessary preparatory step before initiating the inflation proce
ss.
In summation, valve compatibility is not merely a peripheral detail, but a fundamental pre-requisite for inflating an Intex air mattress successfully. Overlooking this aspect introduces the risk of damage, inefficient inflation, and, ultimately, the failure to utilize the air mattress for its intended purpose. Emphasizing the correct matching of valve types and adapters guarantees an efficient and reliable inflation process, maximizing the utility and lifespan of the inflatable mattress.
3. Inflation Technique
The method employed to inflate an Intex air mattress, termed here as “inflation technique,” directly dictates the outcome of the process. Incorrect technique leads to inefficient inflation, potential damage to the mattress, or failure to achieve the desired firmness. For example, rapidly introducing air at maximum pressure can overstress seams and internal baffles, increasing the risk of rupture. Conversely, a slow, uneven inflation process can result in uneven support and reduced comfort. The specific steps taken during inflation are therefore not arbitrary but rather critical determinants of both immediate usability and long-term durability.
Practical implementation of appropriate technique involves several considerations. Monitoring the mattress’s expanding volume and firmness prevents overinflation, a common error. Applying consistent pressure from the pump without sudden bursts ensures even distribution of air within the internal chambers. Regularly checking the valve seal for leaks minimizes air loss during the inflation process. Furthermore, the angle at which the pump nozzle is inserted into the valve impacts airflow efficiency. Suboptimal nozzle placement can restrict airflow, prolonging the inflation period. Therefore, an understanding of these elements is essential for achieving optimal results.
In summary, the “inflation technique” is inextricably linked to the successful utilization of an Intex air mattress. Mastering the correct procedures, monitoring pressure, and ensuring proper valve sealing translates directly to a more comfortable and durable sleeping surface. Disregard for proper technique increases the risk of mattress damage, reduced lifespan, and compromised user experience, underscoring the importance of understanding and implementing the correct inflation process.
4. Pressure Monitoring
Pressure monitoring is an integral component of inflating an Intex air mattress to its optimal state. The internal air pressure directly influences the mattress’s firmness, support, and overall comfort. Failure to monitor the pressure during inflation can result in overinflation or underinflation, both detrimental to the mattress’s lifespan and the user’s experience. Overinflation stresses the seams and internal structures, increasing the risk of rupture, while underinflation leads to inadequate support and an uncomfortable sleeping surface. Therefore, pressure monitoring during inflation is not a mere suggestion but a practical necessity for proper air mattress usage. A real-life example illustrates this: imagine inflating an air mattress on a hot day without monitoring the pressure. As the air inside heats up, it expands, potentially leading to overinflation and subsequent seam failure if the user does not periodically release some air.
Various methods exist for pressure monitoring, ranging from simple manual checks to the use of pressure gauges. Manual checks involve pressing down on the mattress surface to assess its firmness, a subjective method that relies on the user’s experience and judgment. More precise methods involve using a separate pressure gauge or a pump with an integrated pressure gauge. These devices provide objective readings, allowing the user to inflate the mattress to a specific pressure level recommended by the manufacturer. Furthermore, ambient temperature and altitude should be considered during pressure monitoring. Air density changes with temperature and altitude, affecting the internal pressure of the mattress. The practical application of this understanding means that the user should adjust the inflation level based on the prevailing environmental conditions to achieve the desired firmness and support.
In conclusion, pressure monitoring constitutes a fundamental step in the process of inflating an Intex air mattress. It dictates both the immediate comfort and the long-term durability of the product. While challenges exist in achieving perfectly consistent pressure due to environmental factors and subjective assessments, the effort to monitor and adjust pressure during inflation results in a significantly improved user experience and a prolonged lifespan for the air mattress. A conscious consideration of pressure parameters transcends the mere act of inflating the mattress, signifying an informed approach to maximizing the utility of the product.
5. Leak Prevention
Leak prevention forms a critical consideration in the procedures for successfully filling an Intex air mattress with air. Sustaining the desired inflation level and maintaining structural integrity depend significantly on minimizing air leakage throughout the mattress’s lifespan. Proactive measures taken to prevent leaks contribute directly to the air mattress’s utility, comfort, and longevity. Addressing potential leak sources is therefore an integral aspect of ensuring optimal performance.
- Surface Inspection and Preparation
Prior to inflation, meticulous inspection of the mattress’s surface is paramount. Sharp objects, abrasive materials, and uneven surfaces pose a significant threat. Removal of debris and placement of the mattress on a smooth, clean surface reduces the risk of punctures or abrasions. Failure to undertake this inspection can result in immediate or gradual air loss, negating the inflation effort.
- Valve Integrity and Maintenance
The inflation valve represents a common point of air leakage. Ensuring the valve is clean, free from obstructions, and correctly sealed is essential. Over-tightening or cross-threading valve caps can damage the valve mechanism, leading to leaks. Proper valve maintenance, including periodic cleaning and lubrication (if recommended by the manufacturer), sustains the valve’s sealing effectiveness. For example, grains of sand trapped in the valve threads of a Boston valve prevent a tight seal, causing air loss.
- Seam Reinforcement and Protection
The seams where the mattress’s material is joined represent vulnerable areas. Excessive stress or pressure on these seams can lead to separation and air leakage. Avoidance of overloading the mattress beyond its stated weight capacity and prevention of sharp impacts to the seams mitigates this risk. Reinforcing seams with specialized adhesive patches can further enhance their durability and prevent leaks in areas prone to stress.
- Temperature Considerations and Storage Protocols
Temperature fluctuations affect air pressure within the mattress, potentially exacerbating existing leaks. Storage of the mattress in a cool, dry environment, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures, minimizes pressure-induced stress on seams and valves. Proper folding and storage techniques preven
t creases and abrasions that can compromise the mattress’s airtight integrity. Avoid storing heavy objects on top of a folded air mattress, as this can create stress points and lead to leaks.
Effective implementation of leak prevention strategies minimizes air loss, ensuring the air mattress maintains its intended firmness and support. These measures contribute directly to the user’s comfort, extending the mattress’s operational lifespan. Integrating leak prevention practices into the inflation and maintenance routines of an Intex air mattress ensures sustained performance and optimal utilization.
6. Environmental Factors
Environmental conditions exert considerable influence on the inflation process and sustained performance of an Intex air mattress. Ambient temperature, altitude, and humidity levels directly affect air pressure and material properties, necessitating adjustments to inflation techniques and maintenance protocols. Understanding these environmental factors is crucial for optimal usage and longevity of the air mattress.
- Temperature Variation
Temperature fluctuations significantly impact air density within the mattress. As temperature increases, air expands, leading to higher internal pressure. Conversely, colder temperatures cause air contraction, resulting in reduced pressure and firmness. This necessitates adjustments during inflation: on warmer days, less air is needed to achieve the desired firmness, while colder days may require additional inflation. Failure to account for temperature variation can lead to overinflation (in warm conditions, potentially causing seam stress) or underinflation (in cold conditions, resulting in inadequate support). For example, an air mattress inflated to optimal firmness indoors at room temperature may become significantly softer when used outdoors on a cold night.
- Altitude Effects
Atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing altitude. At higher elevations, the lower external pressure causes air inside the mattress to expand relative to its original volume at sea level. This phenomenon requires adjusting the inflation volume to compensate for the pressure difference. An air mattress inflated at sea level and subsequently transported to a high-altitude location will exhibit increased firmness due to the reduced external pressure. Conversely, an air mattress inflated at high altitude will appear less firm when brought to sea level. Users must account for these altitude-related pressure variations to maintain optimal comfort and prevent overinflation or underinflation.
- Humidity Levels
High humidity can affect the material properties of the air mattress. Increased moisture content in the air can penetrate the mattress material, leading to potential mold growth and degradation of the internal structure over time. Moreover, humidity affects the accuracy of pressure gauges, as moisture can interfere with their functionality. In humid environments, it is advisable to use a dehumidifier in the storage area and regularly inspect the mattress for signs of moisture damage. Proper ventilation during inflation and deflation can also help mitigate the effects of humidity.
- Surface Conditions and Stability
The surface on which the air mattress is placed impacts its stability and susceptibility to damage. Uneven or abrasive surfaces can cause stress points and potential punctures. Sharp objects and debris can easily compromise the mattress’s integrity. Placement on a smooth, level surface minimizes these risks. Furthermore, the surface material’s thermal properties can influence the mattress’s temperature. For example, placing an air mattress directly on a cold concrete floor can draw heat away from the mattress, affecting the air pressure and requiring adjustments. Therefore, selecting an appropriate surface and using a protective barrier can significantly enhance the mattress’s performance and longevity.
In conclusion, environmental factors play a vital role in determining the proper inflation and maintenance of an Intex air mattress. Temperature, altitude, humidity, and surface conditions all contribute to the overall performance and lifespan of the product. Consideration of these elements allows users to adapt their inflation techniques and storage practices, maximizing comfort and preventing damage caused by environmental variables.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding the procedure of inflating an Intex air mattress, providing clarity on various aspects of the process and offering solutions to potential challenges.
Question 1: What constitutes the most efficient method for inflating an Intex air mattress?
The efficiency of the inflation process is contingent upon the pump type used. Electric pumps, designed for high-volume, low-pressure inflation, generally offer the quickest and most convenient solution, provided a power source is available. Manual pumps, while requiring physical exertion, provide a reliable alternative when electricity is inaccessible.
Question 2: Is it possible to overinflate an air mattress to the point of damage?
Overinflation poses a significant risk. Exceeding the mattress’s maximum pressure capacity can stress the seams and internal baffles, potentially leading to ruptures or leaks. It is essential to inflate the mattress to a firm but not rigid state, monitoring pressure and adhering to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
Question 3: How can one prevent air leakage from the mattress valve following inflation?
Proper valve sealing is critical. For Boston valves, ensure the cap is tightly screwed on. For pinch valves, verify the valve is fully sealed. Inspect the valve for debris or damage that may compromise its sealing ability. Periodic cleaning and maintenance of the valve mechanism can also prevent leaks.
Question 4: What role does ambient temperature play in maintaining air pressure within the mattress?
Temperature fluctuations affect air density. Colder temperatures cause air to contract, reducing internal pressure. Warmer temperatures lead to air expansion, increasing pressure. It is advisable to adjust the inflation level based on the prevailing temperature to maintain the desired firmness.
Question 5: Are specific tools or accessories required for inflating certain types of Intex air mattresses?
Valve compatibility is essential. Different Intex air mattress models utilize varying valve types, such as Boston valves and pinch valves. Ensuring the pump nozzle or adapter corresponds to the mattress’s valve type is necessary for successful inflation. Incorrect adapters will result in air leakage.
Question 6: What constitutes the recommended procedure for storing an air mattress to prolong its lifespan?
Proper storage contributes to longevity. Ensure the mattress is fully deflated and clean. Fold it neatly to minimize creases and stress points. Store it in a cool, dry environment, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Avoid placing heavy objects on top of the folded mattress, as this can cause damage.
The preceding questions and answers provide essential guidance for the proper inflation and maintenance of Intex air mattresses. Adherence to these principles will contribute to optimal comfort, sustained performance, and extended product lifespan.
The subsequent section will address troubleshooting common issues encountered during air mattress inflation and usage.
Conclusion
The process to inflate an Intex air mattress involves a multifaceted approach, encompassing pump selection, valve compatibility, inflation technique, pressure monitoring, leak prevention, and consideration of environmental factors. Each element contributes directly to achieving optimal firmness, comfort, and long-term durability. A thorough understanding of these aspects is critical for successful utilization of the air mattress.
Mastery of the presented methods equips individuals with the knowledge to efficiently prepare an Intex air mattress for use, ensuring a comfortable and reliable temporary sleeping solution. Consistent application of these principles will maximize the lifespan of the product, providing sustained value and minimizing potential complications. The effort invested in learning and applying these techniques reflects a commitment to responsible and informed product usage.