The process of inflating an Intex air mattress involves introducing air into the mattress’s internal chambers, thereby providing a supportive and comfortable surface for rest or sleep. This procedure typically requires an air pump, either manual or electric, and a nozzle or adapter that fits the mattress’s valve.
Proper inflation is crucial for maximizing the lifespan and comfort of the mattress. An adequately inflated mattress provides optimal support and prevents premature wear and tear. Historically, air mattresses were simpler designs, requiring more manual effort. Modern designs and pumping technologies offer increased convenience and efficiency. The ability to quickly and easily prepare a comfortable sleeping surface is a significant advantage for both home and outdoor use.
The following sections will detail various methods for achieving complete and correct mattress inflation, covering different types of pumps and addressing common issues that may arise during the process. Detailed instructions ensure successful and efficient preparation of the sleeping surface.
Essential Inflation Guidelines
The following guidelines are designed to optimize the inflation process and prolong the lifespan of an Intex air mattress.
Tip 1: Select the Appropriate Pump: Determine the most suitable pump type based on availability of power and desired inflation speed. Electric pumps offer rapid inflation, while manual pumps provide a backup option in the absence of electricity.
Tip 2: Ensure Proper Nozzle Fit: Verify that the pump nozzle is correctly sized for the mattress valve. An ill-fitting nozzle can lead to air leakage and prolong the inflation time.
Tip 3: Avoid Over-Inflation: Monitor the firmness of the mattress during inflation. Over-inflation can stress the seams and potentially cause ruptures. The mattress should feel firm but still have some give when pressed.
Tip 4: Inflate in a Temperature-Controlled Environment: Temperature fluctuations can affect air pressure inside the mattress. Inflate in a location where temperature changes are minimal to prevent pressure imbalances.
Tip 5: Use a Protective Layer: Place a sheet or mattress protector on the air mattress after inflation. This will help protect it from punctures and dirt.
Tip 6: Inspect the Valve Regularly: Check the valve for any signs of damage or leakage. A damaged valve can cause slow deflation and reduce the mattress’s overall lifespan.
Tip 7: Store the Mattress Properly After Deflation: After deflation, ensure the mattress is completely dry before storing. Fold it neatly to prevent creases, and store it in a cool, dry place away from sharp objects or extreme temperatures.
Adhering to these guidelines enhances the durability and user experience of an Intex air mattress, ensuring a comfortable and reliable sleeping surface.
The concluding section will summarize the key points and offer final recommendations for efficient mattress management.
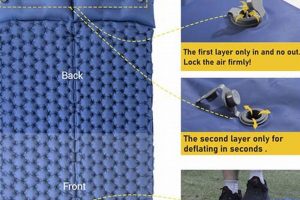
1. Valve Compatibility
Valve compatibility is a foundational element in the process of inflating an Intex air mattress. The valve serves as the interface through which air is introduced into the mattress. Without proper alignment between the pump nozzle and the valve, efficient inflation is impossible. Incompatible connections result in air leakage, significantly prolonging the inflation process and potentially preventing the mattress from reaching its intended firmness. For instance, attempting to use a standard bicycle pump nozzle on a wide-bore Intex valve would be unsuccessful, necessitating the correct adapter or a pump specifically designed for Intex air mattresses. The effect of incompatibility manifests as inefficient use of resources, increased inflation time, and a substandard final product.
The importance of valve compatibility extends beyond the immediate act of inflation. Repeated attempts to force an incompatible nozzle into a valve can damage the valve itself, leading to permanent leaks and rendering the mattress unusable. Furthermore, different Intex mattress models may feature different valve designs, requiring a diverse set of nozzles or adaptors. A practical understanding of valve types and corresponding pump attachments is thus essential for anyone owning or regularly using Intex air mattresses. Specific valve types include Boston valves (double-sealed valves that allow air to go in or out and prevent air leakage), and 2-in-1 valves (valves with extra-wide openings for rapid inflation and deflation).
In summary, valve compatibility is not merely a minor detail but a critical precondition for successful mattress inflation. Addressing the issue of valve compatibility upfront minimizes potential frustration, prevents damage to the mattress, and ensures the user can efficiently achieve the desired level of firmness. Selecting the correct pump and nozzle combination is thus a foundational step in air mattress preparation, connecting directly to the user’s overall experience and satisfaction.
2. Pump Selection
The selection of an appropriate pump directly influences the efficiency and success of inflating an Intex air mattress. Different pump types offer varying levels of power, convenience, and suitability for specific circumstances. The choice of pump should align with the intended use of the mattress and the availability of power sources.
- Electric Pumps
Electric pumps provide rapid inflation, significantly reducing the time and effort required to inflate a mattress. They are particularly suitable for home use or locations where access to electricity is readily available. A drawback is their dependence on a power source, rendering them unusable in remote locations or during power outages. For example, a user preparing a guest room would find an electric pump convenient, while a camper would need an alternative.
- Manual Pumps
Manual pumps, such as foot pumps or hand pumps, offer a portable and independent solution for inflation. While they require more physical effort, they are invaluable in situations where electricity is unavailable. Manual pumps are often more compact and lightweight than electric models, making them ideal for travel and outdoor activities. The trade-off is a slower inflation rate, demanding more time and exertion. A camper, for instance, might prioritize a foot pump for inflating a mattress in a remote location.
- Battery-Operated Pumps
Battery-operated pumps bridge the gap between electric and manual options, offering the convenience of electric power without the need for a direct electrical connection. They are particularly useful for scenarios where portability is important, but manual effort is undesirable. The limitation lies in battery life and the need for replacement or recharging.
A user setting up a mattress at a picnic might choose a battery-operated pump for its balance of convenience and portability. - Built-In Pumps
Some Intex air mattresses come equipped with integrated electric pumps. These built-in systems offer maximum convenience, as they eliminate the need to locate and attach a separate pump. The primary advantage of this design is streamlined operation; however, a failure of the integrated pump renders the entire mattress unusable until the pump is repaired or replaced. A homeowner might prefer a model with a built-in pump for its ease of use, but would need to consider potential repair challenges.
The optimal pump selection hinges on a balance of factors, including the environment in which the mattress will be used, the user’s physical capabilities, and the importance of speed versus portability. Carefully considering these factors ensures that the selected pump effectively and efficiently facilitates mattress inflation, contributing directly to user satisfaction and comfort.
3. Inflation Pressure
Inflation pressure is a critical determinant of comfort, support, and durability in inflatable mattresses. Correctly managing pressure during the inflation process is paramount for achieving optimal performance and prolonging the lifespan of the product. Proper inflation ensures the mattress provides adequate support without risking damage to its internal structure.
- Achieving Optimal Firmness
The goal of inflation is to reach a level of firmness that provides adequate support while remaining comfortable. Over-inflation leads to a rigid surface that can be uncomfortable and increase the risk of seam rupture. Under-inflation, conversely, results in a sagging mattress that fails to provide adequate support, potentially causing discomfort and improper spinal alignment. The user must monitor the inflation process, periodically testing the firmness by applying manual pressure to the surface. The mattress should feel firm but allow for slight compression under pressure. For example, a mattress used for camping may require a slightly firmer inflation to compensate for uneven ground surfaces, while a mattress used indoors may benefit from a softer inflation for enhanced comfort.
- Impact of Environmental Factors
Ambient temperature influences the pressure within an air mattress. Colder temperatures cause the air to contract, leading to a decrease in pressure and a potentially softer mattress. Warmer temperatures cause the air to expand, increasing the pressure and firmness. To maintain consistent comfort and support, the inflation pressure may need to be adjusted based on the surrounding environment. For instance, inflating a mattress indoors at room temperature and then moving it outdoors on a cold night may require adding air to compensate for the temperature drop.
- Preventing Over-Inflation
Over-inflation is a common cause of air mattress failure. Excessive pressure can stress the seams and internal baffles, leading to leaks or even complete rupture. Avoid continuous inflation without periodically checking the firmness. Furthermore, consider that air pressure will increase as the air inside the mattress warms up. To prevent over-inflation, it is advisable to slightly under-inflate the mattress initially, allowing for natural expansion as the air temperature equilibrates. A preventative measure is to never use an air compressor designed for tires, as it is likely to over-inflate the mattress rapidly, leading to irreversible damage.
- Deflation for Storage
Prior to storage, the air mattress needs to be fully deflated. Complete deflation prevents the material from stretching or weakening over time due to prolonged air pressure. Deflation allows the mattress to be folded and stored in a compact manner, minimizing storage space requirements. However, deflation should only occur when the mattress is dry and clean, to avoid trapping moisture inside. Prior to deflation, any sources of heat or cold should be removed to return the mattress to its original state.
The nuances of managing inflation pressure are integral to the overall experience of using an Intex air mattress. These details directly affect the user’s comfort, the product’s longevity, and the overall efficiency of the inflation process. Careful attention to inflation pressure, considering environmental factors and implementing preventative measures, ultimately maximizes the benefits and minimizes the potential drawbacks of utilizing an air mattress as a temporary or portable sleeping solution.
4. Leak Prevention
Leak prevention is integral to the successful and sustained inflation of an Intex air mattress. Addressing potential leaks proactively minimizes the need for frequent re-inflation and extends the usable lifespan of the mattress. Preventing air leakage requires a multi-faceted approach, focusing on valve integrity, seam strength, and protection from external punctures.
- Valve Inspection and Maintenance
The valve is a primary point of vulnerability for air leakage. Routine inspection for cracks, debris, or improper sealing is essential. Debris obstructing the valve seal can be removed with compressed air or a soft brush. Ensuring the valve is properly tightened after inflation is equally important. A damaged or improperly sealed valve necessitates replacement or repair to maintain air pressure within the mattress. A neglected valve can cause a steady decrease in mattress firmness, necessitating frequent re-inflation.
- Seam Integrity and Reinforcement
The seams of an air mattress are susceptible to stress and separation, leading to gradual air loss. Avoiding excessive weight or pressure on specific areas of the mattress can mitigate seam stress. Reinforcement of weak seams using specialized repair kits designed for inflatable products can prevent further degradation. Regular visual inspection of the seams allows for early detection of potential issues. Ignoring seam weaknesses results in progressive air leakage and eventual mattress failure.
- Puncture Protection and Surface Preparation
Protecting the mattress from punctures is crucial for maintaining inflation. Using a mattress protector or placing the mattress on a smooth, debris-free surface minimizes the risk of sharp objects penetrating the material. Regular inspection of the sleeping area for potential hazards, such as splinters or sharp edges, is a preventative measure. Promptly addressing any punctures with appropriate patching materials is essential to contain air leakage. Failure to protect against punctures leads to immediate and often significant air loss.
- Proper Inflation and Deflation Techniques
Employing correct inflation and deflation techniques minimizes stress on the mattress’s internal structure and reduces the risk of leaks. Over-inflation stretches the material and weakens the seams, while rapid deflation can cause stress points. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines for inflation pressure and using a pump designed for air mattresses can help prevent these issues. Similarly, ensuring complete and gentle deflation before storing the mattress prevents trapped air from causing damage. Neglecting proper inflation and deflation protocols increases the likelihood of leaks and structural failure
s.
Effective leak prevention ensures that the efforts invested in inflating the mattress are not undermined by subsequent air loss. Adhering to these practices maintains the integrity of the mattress, optimizes its performance, and extends its useful life, thereby maximizing the investment in the product and minimizing the inconvenience of recurring inflation.
5. Storage Readiness
Storage readiness, the process of preparing an Intex air mattress for extended storage, is inextricably linked to how to pump up the mattress. The immediate precursor to storage is complete deflation, which directly affects the mattress’s longevity and subsequent ease of inflation. A mattress stored with residual air is more susceptible to material stretching and seam weakening, which can compromise its ability to hold air during future inflation cycles. The initial inflation process, therefore, necessitates a thorough understanding of how to fully deflate the mattress for optimal storage conditions.
The connection between inflation and storage readiness is evident in practical scenarios. For example, an individual preparing an air mattress for seasonal storage must ensure all air is expelled before folding and stowing it. Failure to do so may result in the mattress losing its shape and elasticity, potentially requiring more effort and air volume to achieve the desired firmness during the next inflation. This can translate to a longer pumping time or even the need for a more powerful pump. Furthermore, proper drying after use but before deflation is essential. Trapped moisture can lead to mold and mildew growth within the mattress, degrading the material and impacting its ability to maintain air pressure over time. Consequently, the initial inflation is implicitly linked to the long-term integrity of the mattress through proper storage practices.
In summary, storage readiness is not merely an afterthought but an integral component of the overall air mattress usage cycle. Effective deflation, cleaning, and storage practices, initiated after the initial inflation, directly influence the mattress’s durability and its capacity to be efficiently inflated in the future. By understanding and implementing proper storage protocols, users can maximize the lifespan of their Intex air mattresses and ensure consistent, hassle-free inflation experiences over time. The careful attention to these post-inflation steps ultimately preserves the value and functionality of the inflatable product.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the inflation of Intex air mattresses, providing concise and authoritative answers to ensure proper usage and maintenance.
Question 1: What is the correct inflation pressure for an Intex air mattress?
The appropriate inflation pressure is achieved when the mattress is firm to the touch but still allows for slight compression. Over-inflation can damage the seams, while under-inflation provides inadequate support. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines or inflate incrementally, testing firmness periodically.
Question 2: Can any type of pump be used to inflate an Intex air mattress?
No, it is essential to use a pump with a nozzle that is compatible with the mattress valve. Incompatible nozzles can lead to air leakage and inefficient inflation. Electric pumps, manual pumps, and battery-operated pumps are all suitable, provided they have the correct adapter.
Question 3: How does temperature affect the inflation of an Intex air mattress?
Temperature fluctuations influence air pressure within the mattress. Cold temperatures cause air to contract, reducing pressure, while warm temperatures cause air to expand, increasing pressure. Adjust inflation as needed to compensate for temperature changes.
Question 4: What should be done if the Intex air mattress is losing air?
Inspect the valve for proper closure and potential damage. Check the seams and surface for punctures. If a leak is found, use a patch kit designed for inflatable products to repair the affected area. A valve replacement may be necessary if the valve is faulty.
Question 5: Is it safe to use an air compressor designed for tires to inflate an Intex air mattress?
It is generally not recommended. Tire compressors often deliver air at high pressure, which can easily over-inflate and damage the mattress. If a tire compressor must be used, exercise extreme caution and monitor the inflation process closely, using short bursts of air.
Question 6: How should an Intex air mattress be stored after use?
Ensure the mattress is completely deflated, clean, and dry before storing. Fold it neatly to prevent creases and store it in a cool, dry place away from sharp objects and extreme temperatures. Storing the mattress in its original packaging or a storage bag is recommended.
In summary, careful attention to inflation pressure, pump compatibility, temperature effects, leak detection, and proper storage ensures the longevity and optimal performance of an Intex air mattress.
The concluding section will provide final thoughts and summarize best practices for using Intex air mattresses.
Conclusion
This exploration of how to pump up intex air mattress has outlined the crucial elements for effective and sustained inflation. Key points include selecting a compatible pump, managing inflation pressure with environmental factors in mind, and implementing proactive measures for leak prevention. Proper storage readiness, involving complete deflation and cleanliness, extends the mattress’s lifespan and optimizes future inflation experiences.
Adherence to these guidelines ensures user satisfaction, minimizes potential inconveniences, and maximizes the investment in inflatable sleeping solutions. Consistent application of these principles safeguards the functional integrity of the air mattress, contributing to its reliable performance as a temporary or portable sleeping surface.