The uppermost layer designed for placement on a king-size bed is a component intended to enhance comfort and support. This product can be constructed from various materials, including memory foam, latex, or fiberfill, and its dimensions correspond to those of a standard king-size bed frame. An example of its use is layering it over an existing innerspring mattress to modify its feel and provide pressure relief.
These mattress layers serve multiple purposes. They can extend the lifespan of an underlying mattress by protecting it from wear and tear. Furthermore, they offer a customizable sleep surface, allowing individuals to adjust the firmness or softness of their bed according to personal preference. Historically, the concept of layering bedding has been employed to regulate temperature and improve sleep quality, with modern iterations focusing on advanced materials and ergonomic design.
The following sections will delve into the specific types of materials used in these products, factors to consider when selecting one, and proper maintenance techniques for optimal longevity and performance. These considerations will provide a comprehensive understanding of how to choose and care for these bedding additions effectively.
Tips for Selecting a King Size Top Mattress
Choosing a mattress layer for a king-size bed requires careful consideration to ensure optimal comfort, support, and longevity. The following tips provide guidance on making an informed decision.
Tip 1: Material Selection: Evaluate the material composition based on specific needs. Memory foam offers pressure relief and conforms to the body’s shape, while latex provides responsiveness and breathability. Fiberfill options are typically more affordable but may lack the durability of foam or latex.
Tip 2: Thickness Assessment: The thickness significantly impacts the feel and support offered. Thicker options generally provide more cushioning and can significantly alter the overall firmness of the underlying mattress. Consider the existing mattress’s firmness when determining the appropriate thickness.
Tip 3: Density Evaluation: Density, particularly in foam mattress layers, indicates durability and support. Higher density materials tend to resist sagging and maintain their shape over time, although they may also retain more heat.
Tip 4: Firmness Level Consideration: Select a firmness level that complements the existing mattress and aligns with individual sleep preferences. A softer option can add plushness to a firm mattress, while a firmer option can add support to a softer mattress.
Tip 5: Temperature Regulation: If overheating during sleep is a concern, opt for materials known for their breathability and cooling properties. Gel-infused memory foam, latex, and certain fiberfill blends can help regulate temperature.
Tip 6: Size Verification: Confirm that the selected mattress layer is specifically designed for a king-size bed to ensure proper fit and prevent shifting or overhang. Standard king-size dimensions should be verified prior to purchase.
Tip 7: Warranty and Return Policies: Review the manufacturer’s warranty and return policies to ensure protection against defects and dissatisfaction. A trial period allows for assessing the comfort and suitability of the mattress layer before committing to a long-term purchase.
Selecting the appropriate mattress layer involves a thorough evaluation of material, thickness, density, firmness, temperature regulation, size, and warranty. By considering these factors, individuals can enhance their sleep experience and extend the life of their existing mattress.
The subsequent sections will explore specific product recommendations and maintenance guidelines to further refine the decision-making process.
1. Material Composition
The material composition of a king-size mattress layer directly influences its performance characteristics and suitability for various sleep preferences. The choice of material determines factors such as pressure relief, temperature regulation, motion isolation, and overall durability. For example, a memory foam layer, composed of viscoelastic polyurethane foam, conforms closely to the body, distributing weight and reducing pressure points. This characteristic is particularly beneficial for individuals experiencing joint pain or seeking enhanced spinal alignment. Conversely, latex, derived from rubber trees, offers a more resilient and breathable sleep surface. Its inherent elasticity provides responsive support, preventing excessive sinking and promoting airflow to dissipate heat. The material dictates the product’s lifespan and the user’s comfort.
Consider a scenario where an individual experiences night sweats. A memory foam layer, despite its pressure-relieving qualities, may exacerbate the issue due to its tendency to retain heat. In this case, a layer composed of natural latex or a fiberfill blend with cooling properties would be more appropriate. Another relevant example involves couples who are sensitive to movement during sleep. A mattress layer constructed of high-density memory foam or a specifically designed motion-isolating material can minimize the transfer of movement, allowing for undisturbed rest. The internal architecture, like convoluted designs, can augment airflow irrespective of material.
In summary, the material composition of a king-size mattress layer is a critical determinant of its functional properties and user satisfaction. The relationship is causal: the material selected dictates the performance attributes of the product. A thorough understanding of material characteristics is essential for selecting a layer that aligns with individual sleep needs and preferences. While advancements in material technology continue to emerge, the fundamental principles of pressure relief, temperature regulation, and support remain paramount when evaluating these bedding components.
2. Thickness dimension
The thickness dimension of a king-size mattress layer directly impacts its comfort and support characteristics, influencing the overall sleep experience. Thicker mattress layers provide a greater degree of cushioning and can significantly alter the feel of the underlying mattress. For instance, a thin, one-inch memory foam layer will primarily offer minimal contouring, while a four-inch layer will dramatically soften the sleep surface and enhance pressure relief. The selection of an appropriate thickness is contingent upon the condition and firmness of the existing mattress, as well as individual preferences for sleeping position and firmness level. Thicker layers also contribute to improved motion isolation, reducing disturbance from a sleeping partner.
Consider a scenario where an individual seeks to extend the lifespan of a firm, older king-size mattress. A thicker mattress layer, typically three to four inches, can effect
ively mask the underlying mattress’s stiffness and provide a more comfortable sleep surface. Conversely, if the existing mattress is relatively new and already provides adequate support, a thinner mattress layer, perhaps one to two inches, can offer a subtle enhancement without significantly altering the overall feel. The weight of the sleeper should also be factored in, as heavier individuals may require a thicker layer to prevent bottoming out and ensure adequate support. The thickness dimension impacts not only comfort but also the longevity of both the layer and the underlying mattress.
In conclusion, the thickness dimension is a critical consideration when selecting a king-size mattress layer. It directly affects the degree of comfort, support, and motion isolation provided. The appropriate thickness depends on the existing mattress’s condition, individual sleep preferences, and body weight. Understanding the relationship between thickness and performance allows for a more informed decision, ultimately contributing to improved sleep quality. The challenge lies in balancing the added comfort with potential drawbacks, such as increased heat retention or difficulty in fitting existing bedding. Future innovations may focus on optimizing thickness in conjunction with advanced materials to address these limitations.
3. Density rating
The density rating of a king-size mattress layer is a crucial specification indicating the material’s mass per unit volume. This metric directly correlates with the layer’s durability, support, and overall performance. A higher density generally signifies greater resistance to compression, deformation, and wear over time. Therefore, understanding density ratings is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
- Support and Longevity
Higher density materials offer enhanced support, preventing premature sagging and maintaining their shape longer. For instance, a high-density memory foam layer will provide more consistent support across the surface of a king-size bed, accommodating varying body weights and sleeping positions. Low-density options, conversely, may compress rapidly and fail to provide adequate support, leading to discomfort and reduced lifespan.
- Pressure Relief
While high density primarily indicates durability, it also affects pressure relief. A balance between density and material composition is critical. For example, a high-density latex layer offers excellent support and responsiveness, but its firmness may need to be tempered with a comfort layer to optimize pressure relief. Conversely, a low-density memory foam layer may provide initial plushness, but its lack of support can compromise spinal alignment over time.
- Heat Retention
Density can influence temperature regulation. Denser materials tend to retain more heat, which can be problematic for individuals who sleep hot. Conversely, lower density materials may allow for greater airflow and dissipate heat more effectively. The addition of cooling technologies, such as gel infusions or open-cell structures, can mitigate heat retention in denser mattress layers.
- Cost and Value
Density often correlates with the cost of the mattress layer. Higher density materials typically require more resources and complex manufacturing processes, resulting in a higher price point. However, the increased durability and longevity of high-density options can provide better long-term value compared to lower-density alternatives that require more frequent replacement.
The density rating serves as a fundamental indicator of a king-size mattress layer’s quality and performance. While high density generally implies superior support and longevity, it’s crucial to consider other factors such as material composition, pressure relief, and heat retention to determine the optimal choice. The selection process should prioritize a balanced approach that aligns with individual sleep needs and preferences, ensuring a comfortable and supportive sleep environment.
4. Firmness level
Firmness level, when discussing a king-size mattress layer, denotes the degree of resistance to compression experienced by the sleeper. This characteristic fundamentally influences comfort, support, and spinal alignment, thus playing a critical role in sleep quality.
- Subjective Comfort and Preference
Firmness is largely subjective, contingent on individual preferences, sleeping positions, and body weight. A side sleeper, for example, generally benefits from a softer mattress layer that allows the shoulder and hip to sink in, maintaining spinal alignment. Conversely, a stomach sleeper typically requires a firmer surface to prevent excessive sinking of the midsection, which can lead to back pain. Individual preference further complicates the issue; some individuals simply prefer a firmer or softer feel, irrespective of biomechanical considerations. The proper selection enhances restfulness, mitigating sleep disturbances associated with discomfort.
- Impact on Spinal Alignment
A king-size mattress layer’s firmness directly affects spinal alignment. An inappropriately firm layer for a side sleeper can create pressure points, while an insufficiently firm layer for a back or stomach sleeper can lead to spinal curvature. Maintaining proper spinal alignment is crucial for minimizing musculoskeletal stress and preventing chronic pain. The choice of firmness should therefore prioritize the maintenance of a neutral spinal posture during sleep.
- Influence on Pressure Distribution
The firmness level determines how weight is distributed across the sleep surface. A softer layer allows for greater surface area contact, reducing pressure points in areas such as the hips and shoulders. A firmer layer distributes weight more evenly but may create concentrated pressure points for some individuals. Proper pressure distribution is essential for promoting circulation and preventing discomfort caused by prolonged pressure on specific areas of the body. Certain conditions, such as arthritis, necessitate a carefully chosen firmness level to mitigate joint pain.
- Correlation with Body Weight
Body weight significantly influences the perception of firmness and the support provided by a king-size mattress layer. A heavier individual will typically require a firmer layer to prevent excessive sinking, while a lighter individual may find a softer layer more comfortable. This relationship underscores the importance of considering body weight when selecting a mattress layer. Failure to do so can result in inadequate support, compromised spinal alignment, and diminished comfort.
The interplay between firmness level and a king-size mattress layer directly determines the quality of sleep, spinal health, and overall comfort. Selection requires careful consideration of individual preferences, sleeping positions, body weight, and existing musculoskeletal conditions to optimize the sleep experience and promote long-term well-being. Different compositions and designs will change the impression of comfort from Firmness level.
5. Temperature regulation
Temperature regulation constitutes a critical performance aspect of any king-size mattress layer. The ability of a mattress layer to effectively manage heat dissipation directly impacts sleep quality and overall comfort. Overheating during sleep can disrupt sleep cycles, leading to restlessness and diminished restorative rest. A mattress layer that facilitates airflow and wicks away moisture can mitigate these issues. Material composition plays a significant role in this process; for instance, memory foam, known for its pressure-relieving properties, often retains heat, necessitating design modifications such as gel infusions or open-cell structures to enhance breathability. Conversely, natural latex and materials like wool or cotton offer inherent temperature-regulating properties.
The design and construction of a king-size mattress layer can further influence temperature regulation. Convoluted surfaces or channeled designs promote airflow, while moisture-wicking fabrics draw perspiration away from the body. Consider an individual residing in a warm climate. A mattress layer that retains heat will exacerbate discomfort, leading to fragmented sleep. In contrast, a breathable layer will create a cooler sleep environment, facilitating restful sleep. Similarly, individuals experiencing night sweats can benefit from a layer designed to manage moisture and promote evaporation, reducing sleep disturbances. The practical significance lies in the demonstrable impact on sleep efficiency and the mitigation of factors contributing to insomnia or other sleep disorders. Technological advancements such as phase-change materials are being incorporated to provide dynamic temperature regulation, adapting to changes in body temperature throughout the night.
Effective temperature regulation in a king-size mattress layer is thus a multi-faceted characteristic reliant on material science, design, and construction. While inherent properties of materials like latex contribute to breathability, modifications to material structure can offset shortcomings associated with materials like memory foam. Achieving optimal temperature regulation presents ongoing challenges, particularly in balancing comfort and support with thermal management. Ultimately, a well-designed mattress layer contributes directly to improved sleep quality and overall well-being, emphasizing the importance of understanding the interplay between material properties and thermal regulation.
6. Size specifications
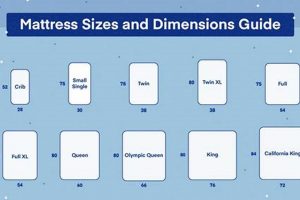
Precise size specifications are paramount when selecting a mattress layer intended for use on a king-size bed. Deviations from standard dimensions can compromise comfort, support, and the aesthetic appearance of the bedding ensemble. The following outlines critical facets relating to size and their implications.
- Standard Dimensions and Tolerances
A standard king-size mattress measures approximately 76 inches in width and 80 inches in length. Mattress layers designed for king-size beds must adhere to these dimensions within a narrow tolerance range, typically 0.5 inches. Variations exceeding this range can result in overhang or insufficient coverage, impacting sleep quality and the longevity of the underlying mattress. For example, a layer that is too narrow may shift during sleep, exposing the underlying mattress to wear and tear. A layer that is too wide may bunch up, creating uneven pressure distribution.
- Corner Radius and Edge Consistency
The corner radius of the mattress layer should align with that of the underlying mattress to ensure a seamless fit. Inconsistent edges or improperly rounded corners can create gaps or protrusions, leading to discomfort and aesthetic issues. A mattress layer with sharp, unrounded corners may also pose a safety hazard, particularly in households with young children. Accurate corner radius specifications are therefore essential for ensuring both comfort and safety.
- Thickness and its Impact on Bedding Fit
While not strictly a dimensional specification in the same sense as width and length, the thickness of the mattress layer directly affects the fit of bedsheets and other bedding accessories. A thicker layer may necessitate the purchase of deep-pocket sheets to accommodate the increased mattress height. Failure to account for the layer’s thickness can result in ill-fitting sheets that are prone to slipping off, compromising both comfort and aesthetics. The selected layer’s thickness impacts the selection of compatible bedding.
- Weight Distribution and Surface Area
Accurate size specifications ensure uniform weight distribution across the mattress surface. A mattress layer that is too small will concentrate weight in certain areas, leading to uneven wear and potential sagging. Conversely, a layer that is too large may not be adequately supported by the bed frame, resulting in instability and reduced support. Proper surface area coverage is therefore critical for maintaining consistent support and extending the lifespan of both the mattress layer and the underlying mattress.
The preceding facets demonstrate that size specifications transcend mere measurements; they encompass critical functional considerations. Deviations from standard king-size dimensions can compromise comfort, support, and the longevity of the sleep system. Therefore, verifying dimensions prior to purchase is essential for ensuring a satisfactory and long-lasting sleep experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries pertaining to king-size mattress layers, providing factual information to assist in making informed purchasing and usage decisions.
Question 1: What is the typical lifespan of a king size top mattress?
The lifespan varies depending on the material composition, density, and usage patterns. High-density memory foam or latex layers can last up to 8-10 years with proper care. Lower-density materials may only last 3-5 years before exhibiting significant wear.
Question 2: How does a king size top mattress impact the firmness of the underlying mattress?
A mattress layer alters the surface feel of the existing mattress. A softer layer will reduce the overall firmness, while a firmer layer will increase it. The extent of change depends on the layer’s thickness and material density.
Question 3: Can a king size top mattress alleviate back pain?
A properly selected mattress layer can provide pressure relief and improve spinal alignment, potentially reducing back pain. However, it is not a guaranteed solution and may not address underlying medical conditions.
Question 4: How should a king size top mattress be cleaned?
Cleaning methods vary depending on the material. Most can be spot-cleaned with a mild detergent and water. Some may require professional cleaning. Avoid harsh chemicals or excessive moisture.
Question 5: What is the ideal thickness for a king size top mattress?
The ideal thickness depends on individual preferences and the condition of the underlying mattress. A 2-4 inch layer is generally sufficient for most users. Those seeking significant change in firmness may opt for a thicker layer.
Question 6: Are there specific king size top mattress options for hot sleepers?
Yes, options incorporating cooling technologies, such as gel-infused memory foam or open-cell structures, are available. Latex and natural fiber layers also tend to offer better breathability than traditional memory f
oam.
In summary, understanding the properties of mattress layers and their impact on sleep quality is crucial for making informed decisions. Material composition, density, thickness, and care practices all contribute to the overall performance and longevity of the product.
The following sections will explore specific product recommendations and maintenance guidelines to further refine the decision-making process.
King Size Top Mattress
This exploration has elucidated the multifaceted considerations surrounding the selection and utilization of a king size top mattress. Material composition, density rating, firmness level, and size specifications each exert a distinct influence on the resultant sleep experience. Understanding these parameters enables a discerning consumer to make an informed decision, optimizing comfort and promoting spinal health.
The informed selection of a king size top mattress represents a tangible investment in well-being. Prioritizing research, objective assessment, and alignment with individual needs will yield the most favorable outcome. As technology advances, further refinements in material science and design are anticipated, promising even greater customization and performance in this critical component of the sleep environment.


![Best King Size Split Mattress [Guide] For Couples! Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Best King Size Split Mattress [Guide] For Couples! | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-8339-300x200.jpg)



![Ultimate Tempur-Pedic Split King Mattress [Guide] Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Ultimate Tempur-Pedic Split King Mattress [Guide] | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-8335-300x200.jpg)