Protective encasements designed to fully enclose mattresses and box springs, often constructed from materials like polyethylene or polypropylene, are specifically engineered to prevent bed bugs from infesting or escaping from bedding. These encasements typically feature airtight zippers and seams, creating a barrier that denies access and restricts movement. A common application involves encasing a mattress suspected of harboring bed bugs to starve the existing population and prevent further spread within a residential or commercial setting.
The employment of these protective coverings offers a non-chemical approach to bed bug management, reducing reliance on pesticides and minimizing potential health risks associated with chemical treatments. Furthermore, utilizing these encasements provides a long-term preventative measure against future infestations, especially beneficial in high-risk environments such as hotels, dormitories, and multi-unit dwellings. Historically, sealing mattresses has been practiced as a basic method for controlling various pests, but the development of specialized, bed bug-resistant encasements has significantly improved efficacy.
The subsequent discussion will elaborate on selecting appropriate sizes and materials, proper installation techniques, maintenance procedures for extended use, and strategies for integrating encasements into a comprehensive bed bug control plan. This also explores potential limitations and alternative solutions when dealing with severe infestations.
Essential Guidance on Encasements
The following tips provide practical information for the effective utilization of mattress and box spring encasements in bed bug management.
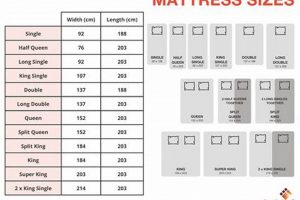
Tip 1: Select the Correct Size: Accurate measurements of the mattress and box spring are crucial. Encasements must fit snugly to prevent gaps where bed bugs can harbor. Consult the manufacturer’s sizing chart to ensure compatibility.
Tip 2: Choose Durable Materials: Opt for encasements constructed from tightly woven fabrics that resist tearing and penetration. Polypropylene or polyethylene materials with a pore size small enough to prevent bed bug passage are recommended.
Tip 3: Inspect Before Installation: Thoroughly examine the mattress and box spring for any existing bed bug activity prior to encasement. Infested items should be treated before being sealed.
Tip 4: Implement Proper Installation: Carefully encase the mattress and box spring, ensuring that all seams and zippers are completely sealed. Use the zipper pull and secure it with a provided fastener to prevent accidental opening.
Tip 5: Regularly Inspect the Encasement: Routinely check the encasement for any signs of damage, such as tears or holes. Promptly repair or replace damaged encasements to maintain their effectiveness.
Tip 6: Maintain Cleanliness: Regularly vacuum the surface of the encasement to remove dust and debris. This helps to identify any potential issues early on.
Tip 7: Incorporate Into a Comprehensive Plan: Encasements are most effective when used in conjunction with other bed bug control measures, such as professional pest control treatments and thorough cleaning of the affected area.
Adhering to these guidelines will maximize the protective benefits and contribute to a more successful bed bug eradication strategy.
The concluding section of this article will further discuss the long-term effectiveness and potential limitations of encasements in different infestation scenarios.
1. Material Integrity
Material integrity is a paramount consideration in the effectiveness of mattress encasements designed to mitigate bed bug infestations. The durability and composition of the encasement material directly influence its ability to prevent bed bug penetration and escape, thereby impacting the success of both preventative and remedial pest control efforts.
- Weave Density
The density of the material’s weave is a primary determinant of its resistance to bed bug passage. Tightly woven fabrics, with minimal spacing between fibers, inhibit the entry and exit of bed bugs, including their eggs. Materials with loose weaves are susceptible to penetration, rendering the encasement ineffective. An example of a tight weave includes fabrics with a pore size less than that required for bed bugs to pass through. This is directly related to the success of containing bed bugs.
- Puncture Resistance
The ability of the material to withstand punctures or tears is crucial for maintaining the encasement’s integrity over time. Materials prone to damage can create entry points for bed bugs. For instance, using a puncture-resistant material such as polypropylene reduces the chance of bed bugs escaping. Polypropylene is a durable option that can last for several years if cared for properly.
- Zipper Quality and Seam Construction
Zippers and seams represent potential weak points in the encasement. High-quality zippers with locking mechanisms and meticulously sealed seams are essential to prevent bed bugs from exploiting these vulnerabilities. If low-quality materials are used, bed bugs may be able to wiggle into these areas. High-quality zippers and seam construction is essential to prevent the bed bugs from exploiting these vulnerabilities.
- Hypoallergenic Properties
While primarily focused on bed bug control, material integrity also extends to hypoallergenic considerations. Individuals with sensitivities may require encasements constructed from materials that minimize allergic reactions. The hypoallergenic properties include properties that will not cause harm to the skin. This consideration ensures that the encasement provides a barrier against allergens and reduces any allergic reactions.
In conclusion, material integrity is not merely a characteristic but a fundamental attribute that dictates the performance of mattress encasements. The selection of materials with appropriate weave density, puncture resistance, zipper quality, seam construction, and hypoallergenic properties is essential for the successful control and prevention of bed bug infestations. Failure to address these material aspects compromises the encasement’s functionality and, consequently, the effectiveness of the overall bed bug management strategy.
2. Secure Enclosure
Secure enclosure represents a critical functional aspect of mattress encasements designed for bed bug management. The primary purpose of these encasements is to completely isolate the mattress and box spring, creating an impenetrable barrier that prevents both the ingress and egress of bed bugs. A compromised enclosure negates the effectiveness of the encasement, regardless of other material properties. This section will explore key facets of secure enclo
sure and their implications for successful bed bug control.
- Airtight Zippers
The zipper constitutes a potential weak point in the encasements integrity. Airtight zippers, typically featuring fine teeth and a locking mechanism, are essential to prevent bed bugs from squeezing through minute gaps. For example, a standard zipper may allow the passage of bed bug nymphs, while an airtight zipper will not. The selection of an airtight zipper directly impacts the level of protection afforded by the encasement.
- Sealed Seams
Seams, where different sections of the encasement material are joined, require meticulous sealing to prevent bed bug penetration. Reinforced or taped seams are commonly employed to create a robust barrier. A poorly sealed seam offers a readily exploitable entry point for bed bugs, rendering the encasement vulnerable. This requires a careful sealing process using equipment specific to the material type.
- Zipper Flaps and Closures
An additional layer of protection is often provided by a flap that covers the zipper. This flap prevents bed bugs from directly accessing the zipper teeth and potentially finding a way through. Closures such as Velcro or snaps further secure the flap. Without a flap, bed bugs may congregate around the zipper, increasing the likelihood of infestation.
- Material Durability at Stress Points
Areas around the zipper and seams are subject to increased stress during installation and use. Reinforcing these stress points with durable materials or additional stitching enhances the encasement’s longevity and prevents tearing, which could compromise the secure enclosure. This reinforcement often involves using thicker material or multiple layers of stitching.
In summary, secure enclosure is not simply a feature of mattress encasements but a system of interconnected elements that must function cohesively to provide effective bed bug protection. The integration of airtight zippers, sealed seams, zipper flaps, and reinforced stress points is critical for maintaining the integrity of the encasement and ensuring its long-term effectiveness as a bed bug management tool. Failure to adequately address any of these facets can compromise the entire system, leading to potential infestation and undermining the purpose of the encasement.
3. Correct Sizing
Correct sizing of mattress encasements is paramount to achieving optimal bed bug control. An improperly sized encasement compromises its protective capabilities, rendering it ineffective as a barrier against infestation. Therefore, meticulous attention to dimensional accuracy is essential for successful implementation.
- Accurate Measurement Protocols
Precise measurement of the mattress and box spring dimensions forms the foundation for selecting the appropriate encasement size. Length, width, and depth must be accurately determined to ensure a snug fit. For instance, a mattress measuring 60 inches wide, 80 inches long, and 12 inches deep necessitates an encasement specifically designed for those dimensions. Disregarding precise measurements introduces the risk of an ill-fitting encasement, which can compromise its effectiveness.
- Consequences of Oversized Encasements
An encasement that is too large presents several disadvantages. Excess material can create folds and crevices, providing potential harborage sites for bed bugs. Moreover, an oversized encasement may not fully protect the mattress, leaving vulnerable areas exposed. In practice, an oversized encasement may slide and shift, negating its intended barrier function.
- Consequences of Undersized Encasements
Conversely, an encasement that is too small may be impossible to install or, if forced into place, can place undue stress on the seams and zipper, increasing the risk of tearing. Furthermore, an undersized encasement may not fully enclose the mattress, leaving portions exposed and susceptible to infestation. An undersized encasement often results in premature failure and a compromised barrier.
- Impact on Zipper Functionality
Correct sizing directly influences the ease of zipper operation. An encasement that is appropriately sized allows the zipper to be smoothly closed without excessive force or strain. Undersized encasements place undue stress on the zipper, increasing the risk of breakage. Correct sizing helps ensure long-term durability of the zipper, maintaining a secure closure.
In summation, the relationship between correct sizing and effective bed bug control via mattress encasements is undeniable. Accurate measurements, awareness of the pitfalls associated with both oversized and undersized encasements, and the impact on zipper functionality are all critical considerations. Proper sizing ensures that the encasement fulfills its intended purpose: creating an impenetrable barrier against bed bugs, thereby safeguarding the mattress and box spring from infestation.
4. Regular Inspection
The prolonged effectiveness of mattress encasements for bed bug control hinges significantly on the implementation of regular inspection protocols. While these encasements create a physical barrier against infestation, they are not impervious to damage or wear. Regular inspection serves as a critical component in maintaining the integrity of this barrier, preventing potential breaches that could compromise its protective function. The absence of routine inspections can lead to undetected tears, zipper failures, or seam separations, negating the encasement’s efficacy and allowing bed bugs to establish infestations within the enclosed bedding. For example, consider a hotel that invests in encasements but neglects to incorporate regular inspections into its housekeeping procedures. Undetected damage to an encasement in even a single room could facilitate the spread of bed bugs to other areas, undermining the initial investment and creating a larger infestation problem.
Specifically, inspection should focus on areas prone to wear and tear, such as seams, zippers, and corners. A visual examination for any signs of damage, including tears, punctures, or zipper malfunctions, is essential. Tactile inspection can also reveal subtle issues, such as seam separation or thinning of the material. Early detection of these issues allows for timely repair or replacement of the encasement, preventing a potential infestation. Moreover, regular vacuuming of the encasement’s surface, while not strictly an inspection technique, aids in the detection of bed bugs or their shed skins, indicating a potential breach or infestation originating from an external source.
In conclusion, regular inspection is not merely an ancillary task but an integral component of a successful bed bug management strategy utilizing mattress encasements. Its proactive nature allows for the timely identification and correction of potential vulnerabilities, preserving the encasement’s integrity and preventing costly and disruptive infestations. Failure to prioritize regular inspection can render even the highest-quality encasement ineffective, highlighting the importance of integrating this practice into a comprehensive pest management program.
5. Proper Installation
The effectiveness of encasements in mitigating bed bug infestations is fundamentally linked to proper installation techniques. Even the highest quality encasement will fail to provide adequate protection if installed incorrectly. Adherence to specific procedures is essential to ensure a complete and secure barrier against these pests.
- Complete Enclosure
A core requirement of proper installation involves fully encasing the mattress and box spring. This necessitates ensuring that all surfaces are covered, leaving no exposed areas where bed bugs could harbor. For example, failing to fully zip the encasement leaves a clear entry point. The efficacy of the encasement relies on its capacity to function as an impervious barrier on all sides.
- Zipper Security
The zipper represents a potential weak point in the encasement’s defense. Proper installation includes ensuring that the zipper is fully closed and secured, often with a provided zip tie or other locking mechanism. If the zipper is left partially open, or the locking mechanism is not engaged, bed bugs can readily infiltrate or escape. This act of securing the zipper represents the last step to ensuring that the bed bugs are contained within the encasement.
- Seam Integrity
While high-quality encasements feature reinforced seams, proper installation requires careful handling to avoid stressing these areas. Avoid excessive pulling or stretching during installation, as this can weaken or tear the seams. A torn seam compromises the integrity of the barrier, allowing bed bugs to traverse the encasement. The durability of the seam integrity is of utmost importance.
- Accurate Alignment
Proper alignment of the encasement during installation is crucial for preventing wrinkles and folds, which can create harborage sites for bed bugs. The encasement should fit snugly against the mattress and box spring, minimizing any loose fabric. These folds can occur with improper alignment, so this element is crucial for preventing any further infestation.
In conclusion, the relationship between proper installation and the effectiveness of encasements is inseparable. A meticulous approach to enclosure, zipper security, seam integrity, and accurate alignment is essential for realizing the full protective potential of these tools in the fight against bed bugs. Any deviation from these best practices can undermine the entire strategy, rendering the encasement ineffective and leaving the bedding vulnerable to infestation.
6. Preventative Measure
Encasements serve as a proactive barrier against bed bug infestations, functioning as a key preventative measure. The primary cause of bed bug infestations often stems from the introduction of these pests via luggage, clothing, or used furniture. By encasing mattresses and box springs, a physical barrier is established, preventing bed bugs from establishing a colony within the bedding. This is of particular importance in environments with high turnover, such as hotels, dormitories, and apartment complexes, where the risk of introduction is elevated. A practical example can be seen in student housing, where students moving in and out frequently may unknowingly carry bed bugs. Encasements in this setting can significantly reduce the likelihood of widespread infestation.
The importance of preventative measures in bed bug control cannot be overstated. Once an infestation is established, eradication can be costly, time-consuming, and disruptive. Chemical treatments, while effective, may pose health risks and require extensive preparation and follow-up. Encasements, as a non-chemical preventative measure, offer a safe and sustainable alternative, minimizing the need for more aggressive interventions. Furthermore, the use of encasements allows for early detection of bed bug activity. If bed bugs are present, they will be confined to the exterior of the encasement, making them easier to identify and treat. This early detection is crucial in preventing the infestation from spreading to other areas of the home or building.
In summary, the use of mattress and box spring encasements as a preventative measure is a cornerstone of effective bed bug management. By creating a physical barrier, encasements significantly reduce the risk of infestation, minimize the need for chemical treatments, and facilitate early detection. While not a standalone solution in the event of an existing infestation, encasements play a crucial role in preventing future outbreaks and maintaining a bed bug-free environment. The challenge lies in consistent implementation and proper maintenance of the encasements to ensure their long-term effectiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the use of mattress encasements in the context of bed bug prevention and management. The information provided aims to clarify key aspects and address potential misconceptions.
Question 1: Are all mattress encasements effective against bed bugs?
Not all mattress encasements offer adequate protection against bed bugs. Encasements must be specifically designed and certified as bed bug-proof, constructed from tightly woven materials with secure zippers. Standard mattress protectors may not provide the necessary barrier.
Question 2: Can bed bugs live inside a mattress encasement?
Bed bugs cannot establish a new infestation inside a properly installed and maintained encasement. However, existing bed bugs may be trapped within the encasement if the mattress was infested prior to encasement. Therefore, treatment of the mattress is crucial prior to sealing.
Question 3: How often should mattress encasements be inspected for damage?
Mattress encasements should be inspected regularly, ideally during routine linen changes. Inspect for tears, punctures, and zipper malfunctions. Any damage compromises the encasement’s protective capabilities.
Question 4: Do mattress encasements eliminate the need for professional pest control?
Mattress encasements are a valuable component of a bed bug management strategy but may not eliminate the need for professional pest control, particularly in cases of established infestations. Encasements primarily serve as a preventative measure and containment tool.
Question 5: How long do mattress encasements last?
The lifespan of a mattress encasement depends on its quality, material, and usage. High-quality encasements, properly maintained, can last for several years. However, regular inspection and prompt replacement of damaged encasements are essential.
Question 6: Are mattress encasements effective against dust mites and allergens?
Many bed bug-proof mattress encasements also provide a barrier against dust mites and other allergens. This dual functionality makes them a beneficial investment for individuals with allergies or asthma.
The information presented emphasizes the importance of selecting appropriate encasements, proper installation, and regular maintenance for effective bed bug control. A comprehensive approach involving multiple strategies remains the most effective method for managing bed bug infestations.
The subsequent section will explore the economic implications of using mattress encasements in bed bug management programs.
Concluding Remarks on Mattress Bags for Bed Bugs
This ex
position has underscored the critical role of mattress bags for bed bugs in both preventing and managing infestations. The effectiveness hinges on material integrity, secure enclosure, correct sizing, regular inspection, and proper installation. Employing these protective encasements represents a proactive strategy, minimizing reliance on chemical interventions and reducing the potential for widespread infestations, especially in high-risk environments.
The long-term success of bed bug management programs is contingent upon consistent implementation of best practices and ongoing vigilance. The strategic use of mattress bags for bed bugs offers a sustainable approach to safeguarding bedding and contributing to a healthier living environment. Continued research and development in encasement technology will likely enhance their effectiveness and durability, further solidifying their place as a vital tool in integrated pest management strategies.



![Best Toyota Tacoma Bed Air Mattress [Guide] Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Best Toyota Tacoma Bed Air Mattress [Guide] | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-7271-300x200.jpg)

