Dimensions of patient support surfaces in healthcare facilities are standardized to ensure compatibility with hospital bed frames. These measurements are critical for patient safety and comfort, directly influencing the effectiveness of pressure redistribution and overall therapeutic outcomes. A correctly sized surface prevents gaps that could lead to entrapment or improper support, while also maximizing the benefits of the bed’s adjustable features.
Proper fit is paramount for several reasons. Historically, ill-fitting surfaces have contributed to increased risks of falls and pressure injuries. Adherence to established size standards facilitates efficient inventory management for healthcare providers, enabling them to readily replace or upgrade surfaces without compatibility concerns. Furthermore, standardized dimensions promote inter-facility transfer of patients without requiring changes in their support surfaces, thus maintaining continuity of care.
The subsequent discussion will elaborate on specific measurement standards, available material options, and considerations for selecting the appropriate support surface for diverse patient populations and therapeutic needs. This includes analysis of width, length, and depth variations, and their impact on patient positioning and pressure management protocols.
Guidance on Selecting a Patient Support Surface
The following considerations are vital when specifying dimensions for patient support surfaces within a healthcare environment. Careful attention to these points can mitigate risk and optimize patient care.
Tip 1: Adhere to Standard Dimensions: Verify compatibility with the bed frame by confirming adherence to established standards for length and width. Incompatibility may compromise patient safety and support surface function.
Tip 2: Account for Bed Frame Articulation: Consider how the surface will perform when the bed is articulated into various positions. Some surfaces may compress or buckle if not properly sized for the bed’s range of motion.
Tip 3: Evaluate Surface Depth: Surface depth affects ease of patient transfer and fall risk. A depth that is either too high or too low relative to the bed frame can create challenges for both patients and caregivers.
Tip 4: Consider Patient Weight Capacity: Ensure the selected surface is rated to support the patient’s weight. Exceeding the weight capacity can lead to premature surface failure and compromised patient safety.
Tip 5: Verify Material Compatibility: Select materials that are compatible with hospital-grade cleaning solutions and infection control protocols. Durability and ease of cleaning are essential in a healthcare environment.
Tip 6: Assess Pressure Redistribution Properties: Choose a surface with appropriate pressure redistribution characteristics based on the patient’s risk for pressure injuries. Different materials and designs offer varying levels of pressure relief.
Tip 7: Confirm Fire Safety Standards: Ensure the chosen surface meets all applicable fire safety standards for healthcare facilities. Flammability testing and certification are critical for patient safety.
Following these guidelines will contribute to the selection of an appropriate patient support surface that promotes patient safety, comfort, and optimal therapeutic outcomes.
The subsequent section will examine emerging trends and technological advancements in patient support surface design, including the integration of sensor technology and smart surface capabilities.
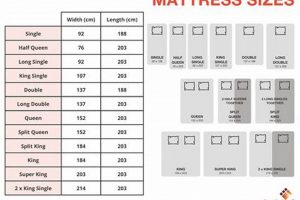
1. Standard width dimensions and Mattress Size for Hospital Bed
Standard width dimensions are a critical factor in determining the appropriate support surface for a hospital bed. These dimensions influence patient comfort, safety, and the overall functionality of the bed within a healthcare setting.
- Lateral Patient Support
The width of the surface directly affects lateral support provided to the patient. Insufficient width can lead to instability and an increased risk of falls, particularly for patients with limited mobility. Standard widths generally range from 35 to 42 inches, accommodating a diverse range of body types.
- Caregiver Accessibility
Surface width impacts caregiver access for tasks such as repositioning, wound care, and hygiene. An excessively wide surface can hinder these activities, increasing caregiver strain and potentially compromising patient care. Optimal width balances patient support with caregiver accessibility.
- Bed Frame Compatibility
The width must be compatible with the hospital bed frame to ensure secure placement and prevent gaps that could pose a safety hazard. Improper fit can lead to surface displacement and potential entrapment issues. Adherence to established industry standards is crucial for compatibility.
- Pressure Redistribution Considerations
The effective area for pressure redistribution is directly influenced by the width. A wider surface can distribute pressure over a larger area, reducing the risk of pressure injuries. However, this must be balanced with the overall size constraints of the bed and the patient’s needs.
In summary, standard width dimensions are integral to the safe and effective use of support surfaces within healthcare environments. Careful consideration of lateral support, caregiver accessibility, bed frame compatibility, and pressure redistribution needs ensures appropriate selection and optimal patient outcomes. Deviations from standard widths should be carefully evaluated to mitigate potential risks.
2. Length accommodations
Length accommodations are a critical aspect of patient support surface selection, directly impacting patient comfort, safety, and the efficacy of care interventions. Appropriate length is essential for proper anatomical support and preventing potential complications arising from insufficient or excessive surface dimensions.
- Full Body Support
Adequate length ensures the entire body is supported, from head to heels. A surface that is too short can result in pressure points at the heels or sacrum, increasing the risk of pressure injuries. Conversely, excessive length can create tripping hazards during patient transfers.
- Articulation Considerations
Hospital beds often articulate into various positions, such as Fowler’s or Trendelenburg. The surface length must accommodate these movements without causing the patient to slide or experience undue pressure at specific points. Dynamic surfaces may adjust their length to compensate for bed articulation.
- Patient Height V
ariancePatient height varies significantly; therefore, length accommodations are crucial. Standard hospital bed surfaces typically range from 80 to 84 inches to accommodate most adult patients. Bariatric surfaces may require additional length to provide adequate support for larger individuals.
- End of Bed Protrusion Mitigation
Excessive length can cause the surface to protrude beyond the end of the bed frame, creating a potential obstruction or tripping hazard for staff. Careful consideration of the bed frame dimensions and surface length is essential to prevent such issues.
Proper length accommodations within patient support surfaces are paramount for promoting patient well-being and minimizing risks associated with improperly sized surfaces. By addressing full body support, articulation considerations, patient height variance, and end of bed protrusion, healthcare facilities can ensure optimal surface selection for diverse patient populations and care settings.
3. Thickness considerations
Thickness significantly contributes to the overall functionality of patient support surfaces. Its relationship to dimensional parameters influences pressure redistribution, patient access, and compatibility with bed frames, thereby directly impacting therapeutic outcomes.
- Pressure Redistribution Capabilities
Surface thickness plays a pivotal role in pressure redistribution. Thicker surfaces, often incorporating multiple layers of foam or air cells, can more effectively distribute pressure away from bony prominences, reducing the risk of pressure injuries. Conversely, excessively thin surfaces may offer inadequate pressure relief, particularly for patients with limited mobility or those at high risk for skin breakdown. The optimal thickness must balance pressure reduction with patient stability and ease of movement.
- Patient Transfer Height
The thickness influences the height of the surface relative to the bed frame, affecting patient transfer ease and safety. Excessive thickness can increase the transfer height, posing challenges for patients and caregivers, and potentially increasing the risk of falls. Conversely, insufficient thickness can make transfers more difficult and may not provide adequate support for the patient’s weight and anatomical contours. Careful consideration of patient mobility and caregiver capabilities is essential when determining optimal thickness.
- Bed Frame Compatibility
Surface thickness must be compatible with the hospital bed frame to ensure proper fit and prevent instability. An overly thick surface may not fit securely within the bed frame, compromising safety and potentially damaging the bed’s mechanisms. Insufficient thickness can result in gaps between the surface and the frame, creating potential entrapment hazards. Compliance with established industry standards is critical for ensuring compatibility and minimizing risks.
- Surface Material Composition
Thickness often dictates the types of materials that can be incorporated into the support surface. Thicker surfaces may accommodate more complex layering of foams, gels, or air cells, allowing for advanced pressure redistribution and microclimate management. Conversely, thinner surfaces may be limited to simpler material compositions, potentially reducing their therapeutic effectiveness. The selection of materials should align with the patient’s specific needs and the desired therapeutic outcomes.
In summation, thickness is a crucial parameter that intricately links to the overarching dimension. Optimal thickness promotes pressure injury prevention, facilitates safe patient transfers, ensures bed frame compatibility, and enables the integration of advanced surface materials. Careful consideration of these factors is essential for selecting appropriate support surfaces that meet the unique needs of diverse patient populations.
4. Weight capacity limits
Weight capacity limits are inextricably linked to the dimensions of patient support surfaces in healthcare settings. These limits dictate the maximum load a support surface can safely bear, a critical consideration directly impacting patient safety and the functional integrity of the equipment.
- Surface Material Integrity
The materials used in construction are selected, in part, based on the anticipated load. Exceeding the specified limit risks structural failure, potentially leading to patient falls or compromised pressure redistribution. For example, a wider surface designed for bariatric use must employ materials capable of supporting the increased weight without deformation.
- Frame Stress and Stability
The frame must withstand the combined weight of the surface and the patient. An oversized surface may distribute weight unevenly, increasing stress on certain frame components and potentially destabilizing the bed. Matching surface dimensions to the frame’s weight capacity is crucial for maintaining structural integrity.
- Pressure Redistribution Effectiveness
The intended function of the surface hinges on maintaining proper weight distribution. Exceeding limits can compress support layers, negating the pressure-redistributing properties and increasing the risk of pressure injuries. Surface selection must align with patient weight to ensure effective pressure management.
- Long-Term Durability
Consistent overloading accelerates material degradation and reduces the lifespan of the surface. Adherence to weight limits not only safeguards patients but also protects the investment in medical equipment by prolonging its usability. Regular inspections and adherence to manufacturer guidelines are essential for maintaining long-term performance.
The interplay between weight capacity and dimensional parameters demands meticulous evaluation during surface selection. A comprehensive approach, considering both patient size and weight, ensures that support surfaces provide optimal safety, comfort, and therapeutic benefit within healthcare environments.
5. Frame compatibility
The dimensional congruence between a hospital bed frame and the patient support surface it houses is paramount for both patient safety and therapeutic efficacy. Incompatibility can lead to a range of adverse outcomes, underscoring the criticality of adherence to standardized dimensions and rigorous compatibility assessments.
- Dimensional Alignment and Entrapment Risk
Mismatched dimensions can create gaps between the surface and the frame, posing a significant entrapment hazard for patients. Extremities or even the entire body can become lodged in these spaces, leading to injury or, in extreme cases, fatality. Precise dimensional alignment, ensured through adherence to industry standards, minimizes this risk. Regular inspections are vital to identify and rectify any deviations that may arise due to wear or equipment malfunction.
- Support Surface Stability and Patient Falls
Incompatible dimensions compromise the stability of the support surface within the frame. An improperly sized surface may shift or slide during patient repositioning or bed articulation, increasing the risk of falls. Proper fit ensures the surface remains securely positioned, providing a stable and predictable environment for the patient. The use of locking mechanisms or surface retention systems further enhances stability.
- Bed Functionality and Therapeutic Effectiveness
Dimensional incompatibility can impede the proper functioning of the bed’s adjustable features. Articulation, height adjustments, and other specialized functions may be compromised if the surface does not conform to the frame’s design specifications. This can negatively impact therapeutic interventions, such as pulmonary drainage or pressure redistribution, reducing their effectiveness. Verification of compatibility across all functional parameters is essential.
- Load Distribution and Structural Integrity
Mismatched surface dimensions can lead to uneven load distribution across the bed frame, increasing stress on specific components and potentially compromising its structural integrity. Over time, this can lead to premature wear, component failure, and reduced overall lifespan of the equipment. Correct surface sizing ensures load is distributed evenly, promoting long-term durability and reliability of the bed frame.
These facets underscore the importance of meticulous attention to dimensional compatibility when selecting and installing support surfaces within hospital beds. By adhering to industry standards and conducting thorough compatibility assessments, healthcare facilities can mitigate risks, optimize therapeutic outcomes, and ensure the safe and effective operation of vital medical equipment.
6. Pressure redistribution needs
The dimensions of a patient support surface significantly influence its ability to address pressure redistribution needs. A correctly sized surface maximizes contact area, thereby minimizing pressure concentration on bony prominences. Conversely, an inadequately sized surface, whether too narrow, short, or thin, concentrates pressure, elevating the risk of pressure injuries. For instance, a patient requiring a wider surface due to their body mass will experience compromised pressure redistribution on a standard-sized surface, leading to increased tissue compression and potential skin breakdown. The dimensions, therefore, are not arbitrary but directly related to the mitigation of pressure-related complications.
Material selection further underscores the importance of dimensional considerations. High-density foam, gel, or air-filled surfaces rely on a specified volume to achieve optimal pressure reduction. A surface compressed beyond its intended thickness due to an inappropriate weight load or inadequate dimensions will lose its pressure-redistributing properties. This necessitates a comprehensive evaluation of patient-specific factors, including weight, body mass index, and risk factors for pressure injuries, when selecting a support surface. The dimensions must accommodate the patient’s characteristics while maintaining the integrity of the pressure-relieving materials. A practical application is seen in bariatric care, where specialized surfaces with increased dimensions and load-bearing capacity are essential to address the unique pressure redistribution needs of this patient population.
In summary, the effectiveness of pressure redistribution is inextricably linked to the surface dimensions. The selection of a surface that does not adequately accommodate the patient’s size and weight undermines its therapeutic benefit and increases the risk of adverse outcomes. Challenges persist in consistently matching patients to appropriate surfaces, particularly in resource-constrained environments. However, a heightened awareness of the dimensional parameters and their impact on pressure redistribution is crucial for improving patient care and minimizing the incidence of pressure-related complications, reaffirming the central role of dimensional specifications within the broader context of patient support surface management.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Patient Support Surface Dimensions
The following addresses common inquiries concerning the selection and utilization of patient support surfaces in healthcare facilities, emphasizing the importance of dimensional accuracy.
Question 1: What are the standard dimensions for a support surface intended for use with a typical hospital bed frame?
Standard dimensions generally fall within a range of 35-36 inches in width and 80-84 inches in length. However, variations exist to accommodate specialized bed frames, such as those used in bariatric or pediatric care.
Question 2: How does support surface thickness affect pressure redistribution?
Thickness influences the capacity for pressure redistribution. Thicker surfaces, particularly those incorporating advanced materials, provide greater immersion and envelopment, thereby reducing pressure concentration on bony prominences.
Question 3: What considerations are pertinent when selecting a support surface for a patient with significant weight?
Weight capacity limits are of primary concern. Surfaces must be rated to safely support the patient’s weight without compromising structural integrity or pressure redistribution effectiveness. Specialized bariatric surfaces are often required.
Question 4: Why is precise dimensional compatibility between the support surface and bed frame so crucial?
Dimensional incompatibility poses a significant risk of patient entrapment. Gaps between the surface and frame can lead to injury or, in extreme cases, fatality. Proper fit is essential for patient safety.
Question 5: How does bed articulation affect the required support surface length?
The surface must accommodate bed articulation without causing the patient to slide or experience undue pressure. Dynamic surfaces that adjust their length during articulation may be necessary in some cases.
Question 6: What role do surface dimensions play in infection control protocols?
The surface must be easily cleanable and compatible with hospital-grade disinfectants. Complex dimensional designs may create areas that are difficult to access and properly sanitize, potentially compromising infection control efforts.
Accurate surface selection involves careful consideration of patient-specific needs, bed frame specifications, and relevant safety standards. Neglecting dimensional parameters can have serious consequences.
The subsequent section will delve into advanced therapeutic options in patient support surfaces, focusing on emerging technologies and clinical applications.
Conclusion
The preceding discussion has elucidated the critical role of dimensional specifications in patient support surfaces. Adherence to established standards for mattress size for hospital bed is not merely a matter of convenience; it directly impacts patient safety, therapeutic efficacy, and operational efficiency within healthcare facilities. Accurate dimensions ensure proper pressure redistribution, minimize entrapment risks, facilitate effective bed articulation, and promote long-term equipment durability. These factors collectively contribute to a higher standard of patient care and a reduction in preventable adverse events.
Healthcare professionals
and procurement specialists must prioritize dimensional accuracy when selecting and implementing patient support surfaces. A continued emphasis on education, rigorous compatibility assessments, and adherence to established guidelines will foster a safer and more effective healthcare environment. Future advancements in surface design and sensor technology hold the promise of further optimizing patient comfort and therapeutic outcomes. The ongoing commitment to precise dimensional control remains a cornerstone of quality patient care.



![Best Toyota Tacoma Bed Air Mattress [Guide] Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions Best Toyota Tacoma Bed Air Mattress [Guide] | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-7271-300x200.jpg)

