A specialized support surface, often utilized in healthcare settings and for home care, is designed to redistribute pressure and reduce the risk of pressure injuries, also known as bedsores. These devices consist of inflatable sections that alternately inflate and deflate, creating a dynamic surface. This alternating pressure minimizes prolonged contact with bony prominences, enhancing blood circulation to susceptible areas.
The significance of such a support system lies in its ability to prevent and manage pressure ulcers, which can lead to significant morbidity and increased healthcare costs. By alleviating pressure points and promoting circulation, it contributes to patient comfort and improved healing. The development of these surfaces represents a considerable advancement in patient care, evolving from simple static mattresses to sophisticated systems equipped with adjustable pressure settings and low air loss features.
The subsequent sections will delve into the different types of these pressure-redistributing surfaces, their specific applications, factors to consider when selecting one, and the proper maintenance procedures to ensure optimal performance and longevity. This includes analysis of the technologies employed, clinical considerations, and practical aspects relevant to both healthcare professionals and patients.
Essential Guidance for Utilizing Pressure-Redistributing Support Surfaces
The following guidelines are provided to ensure the safe, effective, and prolonged use of pressure-redistributing support surfaces. Adherence to these recommendations contributes to optimal patient outcomes and maximizes the lifespan of the equipment.
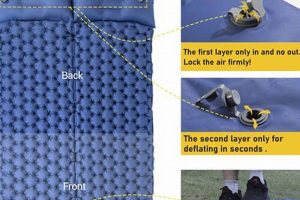
Tip 1: Proper Inflation is Crucial. Ensure the support surface is adequately inflated according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Insufficient inflation diminishes its pressure-redistributing capabilities, potentially increasing the risk of pressure injury development.
Tip 2: Regular Inspection is Necessary. Routinely inspect the surface for any signs of damage, such as punctures, tears, or leaks. Compromised integrity can negate its therapeutic benefits and pose a safety hazard.
Tip 3: Weight Limits Must Be Observed. Adhere strictly to the weight limits specified by the manufacturer. Exceeding these limits can damage the internal components, rendering the support surface ineffective and potentially unsafe.
Tip 4: Appropriate Sheet Usage is Recommended. Use only breathable, moisture-wicking sheets designed for use with pressure-redistributing surfaces. Non-breathable materials can trap heat and moisture, increasing the risk of skin maceration.
Tip 5: Electrical Safety Precautions are Mandatory. Ensure the power cord is properly grounded and protected from damage. Avoid using extension cords unless absolutely necessary, and always follow electrical safety guidelines.
Tip 6: Cleaning and Disinfection Protocols Should Be Followed. Implement a regular cleaning and disinfection schedule using approved cleaning agents. This helps prevent the spread of infection and maintain the hygiene of the support surface.
Tip 7: Pressure Settings Need to Be Adjusted. Adjust pressure settings according to the individual patient’s needs and risk factors. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate settings for optimal pressure redistribution.
Consistent application of these guidelines will significantly enhance the effectiveness and longevity of the support surface, directly contributing to improved patient care and reduced risk of pressure-related complications.
The following section will address common troubleshooting issues and provide further guidance on maintaining optimal performance.
1. Pressure Redistribution
Pressure redistribution is the fundamental principle underlying the therapeutic efficacy of specialized support surfaces. In the context of medical air mattresses, this principle dictates the design and operational characteristics of the device. The primary objective is to minimize concentrated pressure on bony prominences, thereby reducing the risk of tissue ischemia and subsequent pressure ulcer formation.
- Alternating Pressure Therapy
Alternating pressure therapy employs cyclical inflation and deflation of air cells within the mattress. This dynamic redistribution of pressure prevents prolonged compression of tissues. For example, cells beneath the sacrum might deflate while those supporting the thighs inflate, and then alternate. This prevents constant pressure on the sacrum, a common site for pressure ulcers.
- Immersion and Envelopment
These surfaces are designed to immerse and envelop the patients body, increasing the surface area in contact with the mattress. This effectively distributes the patients weight over a larger area, reducing the pressure per unit area. An example is a mattress conforming to the patient’s contours, providing support and minimizing pressure points.
- Microclimate Management
Some mattresses incorporate low air loss (LAL) technology to manage the microclimate at the skin surface. This involves gently circulating air to reduce moisture and heat, further minimizing the risk of skin breakdown. Consider the scenario where a patient perspires; a LAL system will aid in wicking away moisture, preventing skin maceration.
- Material Properties
The material composition of the support surface contributes significantly to pressure redistribution. Materials with high elasticity and low stiffness deform easily under pressure, conforming to the bodys shape and minimizing peak pressure points. Viscoelastic foam, for instance, molds to the patient’s shape and slowly returns to its original form, providing continuous support and redistribution.
These facets of pressure redistribution collectively influence the effectiveness of medical air mattresses in preventing and managing pressure ulcers. By understanding the principles of alternating pressure, immersion, microclimate management, and material properties, healthcare providers can make informed decisions regarding the selection and use of appropriate support surfaces for their patients. The goal is to customize the choice to individual patient needs and risk factors.
2. Alternating Inflation
Alternating inflation is a core operational characteristic of specialized medical air mattresses, representing a pivotal advancement in pressure ulcer prevention. This dynamic process cycles air through the mattress’s cells, creating periodic pressure relief and promoting enhanced blood flow in susceptible areas.
- Pressure Relief Cycling
The system inflates and deflates individual air cells in a timed sequence. This cyclical change in pressure prevents prolonged
compression of tissues over bony prominences such as the sacrum, heels, and hips. The duration of each cycle is carefully calibrated to ensure optimal tissue perfusion without compromising patient comfort. A typical cycle might last 10-15 minutes, alternating between inflation and deflation phases for different sets of cells. - Microcirculation Enhancement
Alternating inflation enhances microcirculation to vulnerable tissues. By periodically relieving pressure, blood vessels are allowed to refill, delivering oxygen and nutrients to cells that are at risk of ischemia. This is particularly important for patients with limited mobility, who are unable to reposition themselves and relieve pressure manually. Proper microcirculation reduces the risk of tissue breakdown and ulcer formation.
- Customizable Pressure Settings
These mattresses often feature adjustable pressure settings to accommodate varying patient weights, body types, and risk levels for pressure ulcer development. The healthcare provider can tailor the inflation pressure to ensure adequate support and pressure redistribution without causing discomfort. For instance, a heavier patient may require higher inflation pressure to achieve optimal pressure relief.
- Prevention of Reactive Hyperemia
Reactive hyperemia, the temporary increase in blood flow after a period of ischemia, can itself contribute to tissue damage if it is excessive or prolonged. Alternating inflation is designed to minimize reactive hyperemia by gradually relieving pressure and promoting controlled reperfusion of tissues. This helps to prevent inflammation and cellular injury that can result from sudden changes in blood flow.
The effective implementation of alternating inflation within medical air mattresses relies on precise engineering and clinical expertise. The specific cycle times, pressure settings, and mattress design should be carefully selected based on individual patient needs and assessed risk factors. Proper use can significantly reduce the incidence of pressure ulcers and improve patient outcomes.
3. Patient Comfort
Patient comfort, an essential element of care, is significantly impacted by the characteristics of the support surface utilized. In the context of specialized medical air mattresses, patient comfort is not merely a desirable attribute but a fundamental consideration that directly influences therapeutic outcomes and overall well-being.
- Pressure Soreness Reduction
The primary function of such mattresses, pressure redistribution, directly contributes to patient comfort by minimizing the risk of pressure sore development. Constant pressure on bony prominences can cause significant discomfort and pain. By alternating pressure and distributing weight, these mattresses alleviate concentrated pressure, thereby enhancing comfort. For instance, a patient confined to bed for extended periods experiences less pain and discomfort when using a mattress designed to redistribute pressure effectively.
- Microclimate Control and Skin Integrity
The ability of some mattresses to manage the microclimate at the skin surface contributes significantly to patient comfort. Excessive moisture and heat can lead to skin maceration and discomfort. Mattresses with low air loss (LAL) technology help to regulate temperature and humidity, promoting a more comfortable and dry environment. A practical example includes a patient experiencing reduced sweating and improved skin integrity, leading to a more comfortable rest.
- Noise and Vibration Levels
The operational noise and vibration of the air pump and mattress system can impact patient comfort and sleep quality. Excessive noise can disturb sleep and increase anxiety. Manufacturers strive to minimize noise and vibration through improved pump designs and vibration-dampening materials. A quiet mattress system ensures a restful environment, contributing to overall patient comfort and well-being.
- Adjustability and Customization
The adjustability of pressure settings and the ability to customize the mattress to individual patient needs are crucial for maximizing comfort. Different patients have varying body weights, shapes, and sensitivities. Mattresses with adjustable pressure settings allow healthcare providers to tailor the support surface to the specific needs of each patient. This ensures optimal pressure redistribution and comfort, regardless of the patient’s size or condition. For instance, a lightweight patient may require lower pressure settings to avoid feeling overly supported.
The interplay between these facets underscores the importance of considering patient comfort when selecting and utilizing medical air mattresses. A well-designed and appropriately configured mattress system not only prevents pressure sores but also enhances the patient’s overall experience and promotes a more conducive environment for healing and recovery. A direct link exists between comfort, reduced pain, and improved compliance with prescribed treatment regimens.
4. Ulcer Prevention
Ulcer prevention stands as a central goal in the utilization of specialized support surfaces, namely medical air mattresses. The incidence of pressure ulcers, also known as bedsores, represents a significant healthcare challenge, leading to patient morbidity, increased treatment costs, and prolonged hospital stays. The design and implementation of medical air mattresses are directly predicated on their capacity to mitigate the risk of ulcer development.
- Pressure Redistribution Efficiency
The core mechanism by which specialized support surfaces prevent ulcers is the redistribution of pressure away from bony prominences. Prolonged pressure on these areas, such as the sacrum, heels, and hips, compromises blood flow, leading to tissue ischemia and subsequent ulcer formation. Medical air mattresses achieve pressure redistribution through alternating inflation and deflation of air cells, effectively shifting the load and relieving pressure points. For instance, a mattress that sequentially inflates and deflates cells beneath the sacrum will prevent sustained pressure on this area, preserving tissue perfusion.
- Microclimate Management Contribution
The microclimate at the skin surface plays a pivotal role in ulcer prevention. Excessive moisture, often caused by perspiration or incontinence, can macerate the skin, rendering it more susceptible to breakdown. Some medical air mattresses incorporate low air loss (LAL) technology to circulate air and wick away moisture, maintaining a dry and healthy skin environment. Consider the scenario where a patient experiences perspiration; the LAL system works to reduce moisture levels, preventing skin maceration and minimizing the risk of ulcer development.
- Early Intervention Strategy
The use of specialized support surfaces is often implemented as part of an early intervention strategy for patients at high risk of developing pressure ulcers. Factors such as immobility, compromised nutritional status, and impaired sensory perception increase the likelihood of ulcer formation. Proactive application of a medical air mattress can mitigate these risks by providing continuous pressure relief and promoting circulation. For example, in the case of a patient wi
th limited mobility due to a spinal cord injury, a medical air mattress can serve as a preventative measure, reducing the potential for ulcer development. - Adjunctive Therapy Enhancement
Medical air mattresses are most effective when integrated into a comprehensive pressure ulcer prevention program. This includes regular skin assessments, proper nutritional support, and meticulous attention to hygiene. While the mattress provides a physical barrier to pressure, adjunctive therapies address underlying risk factors and promote overall skin health. For instance, a patient receiving adequate protein intake and undergoing frequent repositioning will benefit synergistically from the pressure-redistributing properties of the mattress.
These multifaceted aspects highlight the critical role of medical air mattresses in preventing pressure ulcers. By effectively redistributing pressure, managing the skin microclimate, serving as an early intervention strategy, and enhancing adjunctive therapies, these support surfaces significantly reduce the incidence and severity of pressure ulcers, ultimately improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs. The selection and implementation of appropriate medical air mattresses should be based on a thorough assessment of individual patient risk factors and adherence to established clinical guidelines.
5. Air Circulation
Air circulation, facilitated through integrated systems within specialized support surfaces, constitutes a critical element in mitigating the risks associated with prolonged immobility. In the context of medical air mattresses, directed airflow serves to regulate both temperature and moisture at the interface between the patient’s skin and the support surface. This functionality minimizes the potential for maceration and pressure injury formation, stemming from prolonged exposure to excessive humidity and heat. The cause and effect relationship is evident: insufficient air circulation leads to increased moisture and temperature, which, in turn, elevates the risk of skin breakdown. This underscores the importance of effective air circulation as a core component of these mattresses. An example is the use of low-air-loss (LAL) technology, where a continuous, gentle flow of air permeates the mattress surface, drawing away moisture and dissipating heat. This results in a drier, cooler environment that is less conducive to bacterial growth and skin compromise.
Further analysis reveals practical applications extending beyond moisture control. Air circulation assists in reducing the risk of hyperthermia or hypothermia, particularly in patients with impaired thermoregulation. The constant airflow helps maintain a more stable body temperature, minimizing the need for additional interventions. Moreover, the subtle massage effect of the circulating air can stimulate superficial blood vessels, improving circulation in areas prone to pressure damage. The practical significance of this understanding lies in the ability to optimize mattress settings based on individual patient needs, considering factors such as ambient temperature, humidity levels, and the patient’s physiological status. Effective implementation involves regular monitoring of skin condition and adjustment of air circulation parameters to maintain optimal conditions.
In summary, the integration of air circulation within medical air mattresses offers a significant benefit in pressure injury prevention by regulating temperature and moisture. Challenges remain in ensuring consistent and even airflow across the entire surface, particularly in larger or more complex mattress designs. This understanding directly contributes to the broader theme of providing comprehensive and patient-centered care, emphasizing the importance of creating an environment that supports skin integrity and promotes healing. Continued research and technological advancements are focused on refining air circulation systems to further enhance their efficacy and reliability.
6. Weight Capacity
Weight capacity is a critical parameter governing the safe and effective operation of specialized medical air mattresses. This specification defines the maximum weight of a patient the mattress can support while maintaining its structural integrity and therapeutic properties. Exceeding the stated weight capacity can compromise the mattress’s ability to redistribute pressure effectively, potentially leading to increased risk of pressure ulcer formation and equipment failure. For instance, a mattress rated for a maximum weight of 300 pounds, when subjected to a load of 400 pounds, may exhibit compromised pressure distribution, resulting in concentrated pressure points on bony prominences. This directly negates the primary benefit of the mattress.
Further analysis reveals a direct correlation between weight capacity and mattress longevity. Consistent overloading can accelerate wear and tear on internal components, such as air bladders, pumps, and support structures, leading to premature failure. Moreover, exceeding the weight limit can affect the mattress’s inflation and deflation cycles, disrupting the alternating pressure therapy intended to stimulate circulation. In a practical setting, the healthcare provider must meticulously verify the patient’s weight and compare it to the manufacturer’s specified weight capacity before initiating the use of the mattress. This ensures that the mattress functions as intended, providing optimal pressure relief and support. Adherence to weight capacity guidelines is not merely a safety precaution; it is an integral component of maintaining the therapeutic efficacy of the device.
In summary, weight capacity represents a fundamental safety and performance consideration for medical air mattresses. Neglecting this specification can have adverse consequences, undermining the therapeutic benefits and potentially endangering the patient. While technological advancements continue to refine mattress designs and enhance pressure redistribution capabilities, adherence to weight capacity limits remains a non-negotiable aspect of responsible and effective patient care. This understanding directly contributes to the broader goal of minimizing pressure ulcer incidence and improving patient outcomes. Regular reviews of patient weight and mattress specifications are essential to ensure ongoing compliance and optimal performance.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Medical Air Mattresses
The following questions address common concerns and provide essential information regarding the use, maintenance, and selection of medical air mattresses. These answers aim to offer clarity and promote informed decision-making.
Question 1: What is the primary purpose of a medical air mattress?
The primary purpose is to redistribute pressure and reduce the risk of pressure ulcers, also known as bedsores, in patients with limited mobility or those confined to bed for extended periods.
Question 2: How does a medical air mattress achieve pressure redistribution?
Pressure redistribution is achieved through alternating inflation and deflation of air cells within the mattress, cyclically shifting pressure away from bony prominences.
Question 3: Are there different types of medical air mattresses?
Yes, there are various types, including alternating pressure mattresses, low air loss mattresses, and hybrid models that combine both features. The app
ropriate type depends on the patient’s individual needs and risk factors.
Question 4: What are the key considerations when selecting a medical air mattress?
Key considerations include the patient’s weight, risk level for pressure ulcer development, level of mobility, and any specific medical conditions. It is also important to consider the mattress’s weight capacity, adjustability, and ease of cleaning.
Question 5: How should a medical air mattress be properly maintained?
Proper maintenance includes regular inspection for damage, adherence to cleaning and disinfection protocols, ensuring proper inflation levels, and following the manufacturer’s instructions for use. The air pump should be regularly checked and maintained.
Question 6: Are there any contraindications for using a medical air mattress?
While generally safe, certain conditions may warrant caution. Individuals with unstable spinal fractures or those requiring rigid support may not be suitable candidates. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine appropriateness.
These FAQs provide a foundation for understanding the functionality and proper utilization of medical air mattresses. However, professional consultation should always be sought for specific medical advice.
The next section will provide a summary encompassing the key benefits and applications of specialized support surfaces.
Medical Air Mattress
This article has explored various facets of the medical air mattress, emphasizing its pivotal role in pressure redistribution, patient comfort, and ulcer prevention. The significance of alternating inflation, air circulation, and adherence to weight capacity specifications has been underscored. These elements collectively contribute to improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
The integration of the medical air mattress into comprehensive patient care protocols remains essential. Continued research and technological advancements hold the potential for further enhancing the effectiveness and user-friendliness of these support surfaces, promoting a future with fewer pressure-related complications. Healthcare professionals are encouraged to stay informed and advocate for the utilization of appropriate support surfaces to ensure optimal patient well-being.