The typical mass of a queen-sized bed covering can vary considerably, primarily influenced by the materials used in its construction. A basic innerspring model may present a different figure than a memory foam or latex variant. For example, a simpler coil design might register a lower value, while a denser, multi-layered foam construction will usually present a higher figure.
Understanding the physical properties is crucial for several reasons. Practical considerations such as moving, rotating, or replacing the item are directly affected by its heaviness. Additionally, structural implications for bed frames and bedroom flooring need to be addressed based on the distributed pressure. Historically, advancements in materials and construction techniques have steadily altered the standards. This has lead to variations found in older versus newer models.
The following sections will delve into specific factors influencing these figures, common materials, weight ranges, and considerations for transport and support.
Weight Management Strategies for Queen Size Mattresses
The following are actionable recommendations for mitigating challenges associated with handling and supporting queen-size bed coverings.
Tip 1: Assess Frame Capacity: Before purchasing, verify that the bed frame can adequately support the anticipated mass. Frame specifications typically list a maximum bearing capacity; exceeding this may lead to structural failure.
Tip 2: Employ Proper Lifting Techniques: When moving, avoid back strain by lifting with the legs. Maintain a straight back and utilize assistance when available. Consider using furniture dollies for transport over longer distances.
Tip 3: Consider Material Composition: Different materials contribute differently to the overall measurement of the object. Memory foam and latex tend to be heavier than traditional innerspring models. Evaluate material options based on individual needs and tolerance for handling heavier items.
Tip 4: Reinforce Flooring as Needed: In older homes or structures with less robust flooring, consider reinforcing the area beneath the bed frame. This may involve adding shims or consulting with a structural engineer.
Tip 5: Utilize Professional Movers: For difficult moves or when physical limitations are a concern, engage professional moving services. These services possess the necessary equipment and experience to safely transport large and cumbersome items.
Tip 6: Regularly Rotate the Item: Periodic rotation can help distribute pressure evenly, potentially extending its lifespan. However, exercise caution when rotating; utilize proper lifting techniques or enlist assistance.
Tip 7: Inspect Support Slats: If the bed frame uses slats for support, regularly inspect these slats for signs of wear or damage. Replace any compromised slats to maintain adequate support and prevent premature failure.
By following these strategies, individuals can minimize potential risks and optimize the lifespan of their queen-size sleeping platform and associated support structures.
The subsequent sections will discuss selecting the ideal model based on individual needs and lifestyle.
1. Material Density
Material density is a primary determinant of a queen-size mattress’s overall measurement. Density, defined as mass per unit volume, varies significantly across different mattress materials. High-density materials, such as memory foam and latex, contribute proportionally more than lower-density materials like traditional innerspring coils. The direct causal relationship is evident: an increase in material density, given a constant volume, will inevitably lead to an increase in the mattress’s heaviness.
The composition of a queen-size mattress frequently involves layering various materials, each possessing a distinct density. For instance, a hybrid mattress combining a high-density memory foam comfort layer with a low-density innerspring core will exhibit an intermediate figure. The relative proportions of high-density and low-density materials within the overall structure dictate the aggregate value. Understanding these distinctions allows consumers to anticipate the effort required for handling and supporting the sleeping platform. For example, a fully latex queen-size mattress, known for its high density, may necessitate reinforced bed frames and additional assistance during relocation, unlike a lightweight innerspring counterpart.
In conclusion, material density is a foundational factor influencing the overall heft. Its importance lies in predicting transport and installation challenges, ensuring proper support from bed frames and flooring, and informing long-term investment decisions. While the precise composition varies among models, the principle remains consistent: denser materials translate to a heavier sleeping platform, requiring careful consideration of logistical and structural implications.
2. Core Construction
The internal architecture is a significant determinant of the mass of a queen-size mattress. The core, serving as the primary support structure, contributes substantially to the overall measurement. Variations in materials, design, and construction techniques directly influence the mattress’s heaviness.
- Innerspring Coil Count and Gauge
The number of coils within an innerspring core, coupled with the gauge (thickness) of the steel wire used, directly affects the total mass. Higher coil counts and lower gauge numbers (thicker wire) generally indicate a heavier core. For example, a mattress with 800 individually wrapped coils of 13-gauge steel will typically exhibit a greater measurement than a mattress with 600 coils of 15-gauge steel.
- Foam Density and Composition
Foam core construction, often found in all-foam or hybrid mattresses, relies on the density and composition of the foam materials. Higher-density foams, such as memory foam or latex, will invariably contribute more than lower-density polyurethane foams. A queen-size mattress featuring a high-density memory foam core is usually heavier than one utilizing a polyfoam core of similar dimensions.
- Hybrid Construction and Material Combinations
Hybrid mattresses combine innerspring and foam elements, creating a more complex relationship between core construction and overall heaviness. The relative proportions of each material directly influence the total value. A hybrid model with a substantial innerspring system and a thin layer of high-density foam may measure differently than one with a lower-density innerspring system and a thick layer of high-density foam.
- Support Layers and Edge Reinforcement
Additional support layers and edge reinforcement systems within the core contribute incrementally to the overall measurement. These elements, often constructed from dense foam or reinforced steel, provide structural integrity and edge support, but also add to the heaviness of the mattress. The inclusion of a high-density foam edge support system around the perimeter of an innerspring core will invariably increase the overall mass.
Ultimately, the core construction serves as a foundational element determining the heaviness of queen-size bedding. The choice of materials, coil counts, foam densities, and support systems collectively dictate the final measurement, impacting logistical considerations during transportation, installation, and long-term use. Therefore, understanding these elements is crucial for making informed decisions regarding mattress selection and support requirements.
3. Layer Composition
Layer composition within a queen-size mattress exerts a direct and measurable influence on its overall heaviness. Each layer, whether composed of foam, fiber, or other materials, contributes incrementally to the total mass. The specific materials used and their respective thicknesses determine the aggregate contribution. For instance, a queen-size mattress featuring multiple layers of high-density memory foam will inherently exhibit a greater figure than a comparable mattress with fewer or thinner layers of the same material. Similarly, the inclusion of a substantial pillow top layer, often containing a blend of fibers and foam, adds measurably to the final heaviness. Thus, the number of layers and the characteristics of those layers are key determinants.
The practical significance of understanding layer composition lies in predicting handling and support requirements. A mattress with a complex layer structure, incorporating various densities and thicknesses of foam and fiber, necessitates careful consideration of bed frame capacity and moving procedures. Real-world examples underscore this connection: individuals attempting to move a queen-size mattress with a thick, multi-layered construction frequently encounter greater difficulty compared to handling a simpler, thinner mattress. Moreover, the long-term structural integrity of a bed frame depends on its ability to adequately support the weight contributed by the mattress’s composite layers. Retail specifications often indicate the composition, allowing for informed decision-making.
In summary, layer composition constitutes a critical factor in determining the weight of a queen-size mattress. The selection of materials and their arrangement directly impact the effort required for handling, the demands placed on support structures, and the overall longevity of both the mattress and the bed frame. Recognizing the influence of layer composition allows for proactive management of potential challenges associated with heavy bedding, ultimately ensuring a more comfortable and sustainable sleep environment.
4. Support Systems
The inclusion of robust support systems within a queen-size mattress contributes measurably to its overall heaviness. These systems, designed to enhance structural integrity, edge support, and motion isolation, often incorporate high-density materials and complex engineering, consequently increasing the total measurement. The cause-and-effect relationship is direct: strengthening the internal framework through additional materials elevates the mattress’s weight. The significance lies in ensuring longevity, preventing sagging, and maximizing sleep quality, but at the expense of increased mass. Examples include reinforced edge supports, typically composed of high-density foam or steel, and zoned support systems, where varying densities of foam are strategically placed to provide targeted support. These features, while beneficial for sleep ergonomics, contribute to the overall heaviness.
Practical applications stemming from this understanding are numerous. Retailers and consumers must account for the added weight when considering bed frame compatibility. Lightweight frames may prove inadequate for supporting a heavy mattress with extensive support systems, leading to premature wear or structural failure. Furthermore, the heaviness impacts transportation and handling logistics. Moving a mattress with robust support systems may require additional personnel or specialized equipment to prevent injury or damage. Manufacturers must also balance the benefits of enhanced support with the logistical challenges associated with producing and distributing heavier products.
In summary, support systems are integral to a queen-size mattress’s functionality and longevity, but their inclusion inevitably increases its weight. This necessitates careful consideration of bed frame compatibility, handling logistics, and potential physical strain during transportation. While manufacturers continually seek to optimize support systems while minimizing weight, the fundamental relationship remains: enhanced support often translates to a heavier mattress, requiring informed decision-making on the part of both retailers and consumers.
5. Dimensional Variance
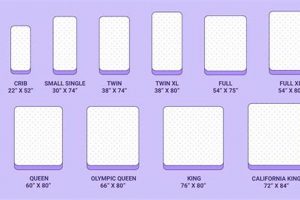
Dimensional variance, although seemingly minor, exerts a discernable influence on a queen size mattress’s weight. The standardized dimensions for a queen-size mattress are generally accepted as 60 inches in width and 80 inches in length. However, manufacturing tolerances and design variations can lead to subtle deviations from these norms. While these variations might only amount to fractions of an inch, they contribute to changes in volume, directly impacting the total mass. A larger volume, given consistent material density, inevitably results in a higher figure. Therefore, dimensional variances represent a contributing factor, though not always a dominant one, in the overall spectrum of a queen-size mattress’s measurements.
The practical implications of dimensional variance extend to fitting sheets and bed frames. A mattress significantly exceeding the standardized dimensions may not fit properly within a designated frame or be compatible with standard queen-size sheets. Consequently, consumers may encounter difficulties in securing the mattress or experience discomfort due to ill-fitting bedding. Conversely, a mattress falling short of the expected dimensions could leave unsightly gaps between the mattress and the bed frame, potentially compromising support and aesthetics. In some cases, the cumulative effect of these variances across multiple production batches can lead to inconsistencies in average statistics reported by manufacturers.
In conclusion, dimensional variance, while often overlooked, warrants consideration when evaluating a queen-size mattress. Its impact on the overall figure, though typically marginal, contributes to challenges related to sheet fitting and bed frame compatibility. While adherence to standardized dimensions remains a priority, acknowledging the existence of dimensional variances enables informed decision-making and preemptive mitigation of potential fitment problems. Future manufacturing advancements aimed at minimizing these deviations could further enhance consistency in statistics across different models.
6. Foundation Impact
The mass of a queen-size mattress directly correlates with its impact on the supporting foundation. The term “foundation impact” encompasses the stress and strain exerted upon the bed frame, box spring (if applicable), and underlying flooring by the static mass of the mattress. A heavier queen-size mattress, especially those constructed with dense materials such as memory foam or latex, transmits a greater force to the foundation than lighter innerspring models. This increased force can accelerate wear and tear, potentially leading to structural damage or reduced lifespan of the support system. Failure to account for this component poses risks to the foundation’s integrity and, by extension, the sleeper’s comfort and safety.
Consider, for example, an older bed frame designed for a lightweight innerspring mattress. If this frame is subsequently used to support a significantly heavier memory foam queen-size mattress, the added stress could cause the frame’s joints to weaken, slats to bend or break, and legs to buckle. Similarly, flooring beneath the bed, particularly in older homes with less robust construction, may experience increased deflection or even structural issues over time due to the concentrated mass. Regular inspection of the bed frame, box spring, and surrounding flooring is essential to identify signs of stress, such as cracks, creaks, or uneven settling. Proper distribution of the mattress’s mass through the use of a suitable foundation is crucial for mitigating these effects.
In conclusion, the relationship between queen-size mattress mass and its impact on the foundation is significant and demands careful consideration. Selection of an appropriately rated bed frame and regular assessment of the support system’s condition are paramount to ensuring structural stability, longevity, and safe operation. While manufacturers provide statistics, proper evaluation during usage remains important. By understanding and addressing this component, one can avoid potentially costly repairs and maintain the overall integrity of both the sleeping platform and the surrounding environment.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Queen Size Mattress Weight
The following section addresses common inquiries concerning the heaviness of queen-size mattresses, providing concise and informative answers.
Question 1: What is the typical range of measurement for a queen-size mattress?
The measurement generally falls between 50 and 150 pounds. Variations arise due to differences in materials and construction techniques.
Question 2: Which material contributes most significantly to the figure?
High-density materials, such as memory foam and latex, tend to contribute more than traditional innerspring systems.
Question 3: How does the core construction influence its value?
The core, whether innerspring or foam, forms the primary support and represents a substantial portion of the overall measurement.
Question 4: Does the presence of a pillow top add to the total?
Yes, pillow tops, especially those with thick layers of foam or fiber, increase the total value.
Question 5: How does this factor impact bed frame selection?
Bed frames must possess adequate support capacity to accommodate the mattress’s measurement to prevent damage or failure.
Question 6: What precautions should be taken when moving a heavy queen-size mattress?
Employ proper lifting techniques, seek assistance, and consider using furniture dollies to minimize the risk of injury.
In summary, awareness of factors influencing the measurement is essential for safe handling, proper support, and informed purchasing decisions.
The subsequent section will delve into strategies for minimizing the impact of this variable on structural integrity and ease of use.
Queen Size Mattress Weight
This exposition has traversed the complexities of queen size mattress weight, emphasizing its dependency on materials, construction methods, and support systems. The analysis has demonstrated the variable’s influence on transportation, bed frame selection, and structural integrity. Recognition of these factors provides a foundation for informed consumer choices and responsible handling practices.
The implications of queen size mattress weight extend beyond mere convenience. This variable fundamentally impacts the lifespan of supporting structures and the overall comfort and safety of the sleeping environment. Prudent evaluation and proactive management of this critical attribute are paramount for ensuring long-term satisfaction and preventing potential structural compromises.



![[Guide] What Size Mattress Do I Need? Find Your Fit! Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions [Guide] What Size Mattress Do I Need? Find Your Fit! | Organic & Natural Mattress Buyer’s Guide: Non-Toxic Sleep Solutions](https://mattressworldpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/th-2304-300x200.jpg)