The measurements associated with a king bed foundation are critical for ensuring proper support and fit for the corresponding mattress. Typically, this foundation, often constructed with wood or metal, mirrors the mattress’s size to provide a stable and level surface. An example would be a structure measuring approximately 76 inches wide and 80 inches long, designed to complement a standard king mattress. These dimensions are essential for compatibility and optimal sleep quality.
Accurate bed foundation measurements are vital for several reasons. They contribute to the longevity of the mattress by distributing weight evenly, preventing premature sagging or wear. Furthermore, these dimensions are essential for aesthetic harmony within the bedroom, ensuring that the bed frame, mattress, and foundation align seamlessly. Historically, standardized sizes have simplified the manufacturing and purchasing processes, allowing consumers to readily find compatible components.
Understanding these measurements is the first step in selecting the appropriate foundation for a king mattress. The following sections will delve into the nuances of different foundation types, their specific height profiles, and how to choose the best option for individual needs and preferences.
Considerations for King Size Mattress Foundation Measurements
Properly understanding bed foundation measurements is crucial for a comfortable and supportive sleep experience. The following tips address key aspects to consider when selecting a compatible foundation for a king mattress.
Tip 1: Verify Compatibility: Prior to purchase, confirm the foundation’s dimensions align precisely with the king mattress. Discrepancies can lead to instability and reduced mattress lifespan. For example, a foundation that is even slightly undersized may cause the mattress to overhang, creating uneven support.
Tip 2: Assess Foundation Height: Foundation height affects the overall bed height, influencing ease of entry and exit. Standard profiles range from low-profile (approximately 5 inches) to standard (approximately 9 inches). A taller foundation may be beneficial for individuals with mobility concerns, while a lower profile can create a more modern aesthetic.
Tip 3: Account for Bed Frame Compatibility: Ensure the chosen foundation is compatible with the existing bed frame. Some frames require specific foundation types or brackets for secure attachment. A platform bed, for instance, might eliminate the need for a traditional foundation altogether.
Tip 4: Evaluate Support Structure: The internal support structure of the foundation is critical for weight distribution. Look for foundations with robust wood or metal frames and closely spaced slats. This is especially important for heavier mattresses or for couples who share the bed.
Tip 5: Consider Edge Support: Edge support prevents mattress sagging along the perimeter, maximizing the usable sleep surface. Foundations with reinforced edges offer enhanced stability and prevent roll-off. This feature is particularly beneficial for individuals who sleep near the edge of the bed.
Tip 6: Review Warranty Information: Examine the foundation’s warranty for coverage against defects and premature wear. A comprehensive warranty indicates the manufacturer’s confidence in the product’s durability. Note the warrantys specific terms and conditions.
Tip 7: Factor in Storage Needs: If additional storage is required, explore foundations with built-in drawers or under-bed clearance. These options maximize space utilization, particularly in smaller bedrooms. Consider the weight capacity of the storage features.
Adhering to these guidelines ensures the selection of a bed foundation that not only complements the king mattress but also contributes to optimal sleep quality and long-term value. Proper selection of foundation can result in a long-lasting quality of sleep.
With a firm grasp of the foundation dimensions and associated considerations, the article will continue to explore the selection process, offering insights into various foundation types and their suitability for different sleep preferences and needs.
1. Standard Width
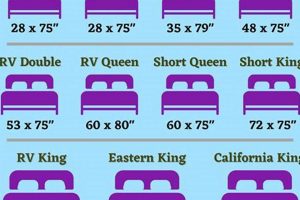
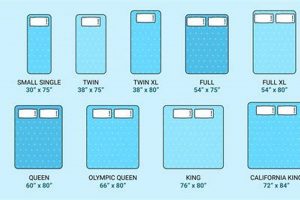
The standard width of a king foundation is a critical component of its overall dimensions, directly impacting mattress support and bed frame compatibility. This measurement, typically 76 inches, is meticulously engineered to match the corresponding king mattress. A deviation from this standard can lead to several adverse effects, including uneven weight distribution, premature mattress wear, and an unstable sleep surface. For instance, if the foundation is narrower than the mattress, the edges of the mattress may lack support, resulting in sagging and discomfort over time. A precise match in width ensures that the mattress is fully supported across its entire surface, maximizing its lifespan and promoting proper spinal alignment during sleep.
In practical terms, the standard width dimension simplifies the purchasing process for consumers. Knowing the specific width allows for confident selection of compatible bed frames and bedding accessories. Bed frame manufacturers design their products to accommodate these standard foundation widths, ensuring a secure and aesthetically pleasing fit. Furthermore, variations in foundation width are rare, minimizing the risk of compatibility issues. This standardization promotes efficiency in manufacturing and distribution, ultimately benefiting consumers through lower costs and readily available options. Improper width of king size mattress box spring dimensions can make the whole system collapse.
In summary, the standard width measurement is not merely a number; it is a foundational element for ensuring the proper function and longevity of a king-size bed. Adherence to this standard guarantees optimal mattress support, seamless bed frame integration, and overall sleep comfort. While other aspects, such as length and height, also contribute to the overall dimensions, the standard width serves as a critical anchor point, dictating the compatibility and performance of the entire sleep system.
2. Standard Length
Standard length constitutes a vital aspect of bed foundation specifications, particularly within the context of king mattress dimensions. This measurement dictates the overall sleeping surface area and profoundly influences comfort, support, and compatibility with bed frames and mattresses. Adherence to a standardized length ensures a consistent and reliable sleep experience.
- Dimensional Harmony
The prescribed length, typically 80 inches for a king foundation, is designed to precisely accommodate a standard king mattress. Deviations from this measurement, even minor ones, can result in overhang, compression, or inadequate support along the length of the mattress. This mismatch can lead to uneven weight distribution, accelerated wear and tear, and a compromised sleep surface.
- Frame Integration
Bed frame manufacturers adhere to established length standards when designing king-size frames. A foundation conforming to the standard 80-inch length will integrate seamlessly with these frames, ensuring a secure and stable platform. Non-standard lengths may necessitate custom frame modifications or result in an unstable and potentially hazardous setup.
- Ergonomic Considerations
The standard length accommodates the average height of adult sleepers, providing ample space for comfortable extension. Shorter lengths may restrict movement and lead to discomfort, particularly for taller individuals. Conversely, excessively long foundations may create unnecessary gaps between the headboard or footboard and the mattress.
- Support Optimization
Consistent length is crucial for maintaining uniform support across the entire mattress surface. Variations in length can disrupt the internal support structure of the foundation, leading to localized sagging or unevenness. This can negatively impact spinal alignment and sleep quality over time.
In summary, the standard length of a king foundation is not an arbitrary measurement but a carefully calibrated dimension that ensures optimal mattress support, frame compatibility, ergonomic comfort, and long-term durability. Deviations from this standard can compromise the integrity of the entire sleep system, ultimately affecting sleep quality and overall well-being.
3. Foundation Height
Foundation height, as a component of bed dimensions, directly influences the overall profile and functionality of a king-size bed. The vertical measurement between the floor and the top surface of the foundation affects ease of access, aesthetic appeal, and compatibility with various bed frames. The interplay between foundation height and total bed height is critical for ergonomic considerations, especially for individuals with mobility limitations. For example, a low-profile foundation paired with a thick mattress may result in a comfortable bed height for some, while others might require a taller foundation for easier ingress and egress. Improper foundation height can lead to discomfort, difficulty in getting in and out of bed, and an unappealing visual balance within the bedroom.
Different types of foundations offer varying height options to accommodate diverse needs and preferences. Standard foundations typically range from 8 to 9 inches in height, providing a balanced profile suitable for most bed frames. Low-profile foundations, measuring around 5 inches, offer a minimalist aesthetic and are often used with platform beds or thicker mattresses. Conversely, high-profile foundations can elevate the bed significantly, providing under-bed storage space and a more traditional appearance. The choice of foundation height should consider both practical and aesthetic factors, ensuring a comfortable and visually harmonious sleep environment. A foundation that is too tall can make the bed appear disproportionate, while one that is too short can limit storage options and accessibility.
In summary, foundation height is an important dimension to consider when selecting a bed foundation. Its influence extends beyond mere aesthetics, impacting ergonomic comfort and overall bed functionality. Selecting the proper foundation height is essential for optimizing the sleep experience and ensuring compatibility with the existing bedroom decor. The relationship between foundation height and the dimensions of the king mattress is thus a significant factor in creating a comfortable and aesthetically pleasing sleep environment.
4. Frame Compatibility
Frame compatibility, when considered in relation to bed dimensions, specifically for king mattresses, refers to the precise dimensional alignment between a bed frame and the foundation designed to support the mattress. The dimensions of the frame must correspond accurately with the dimensions of the foundation to ensure stability, prevent damage, and maintain the intended aesthetic. A mismatch can result in inadequate support, causing the mattress to sag prematurely or even fall off the frame. For example, a king bed frame designed for a standard 76-inch by 80-inch foundation will not properly accommodate a foundation that is even an inch or two smaller or larger in either dimension. The effect of such a discrepancy can range from annoying instability to significant structural damage over time. Frame compatibility is therefore a crucial component of overall bed stability and mattress longevity.
Several factors contribute to frame compatibility challenges. Variations in manufacturing tolerances, particularly in older or less expensive frames, can introduce slight dimensional inconsistencies. Additionally, different styles of bed frames, such as platform beds or sleigh beds, may have specific requirements for foundation height or overall dimensions. A platform bed, for example, may eliminate the need for a traditional foundation altogether, requiring only a mattress. Furthermore, the use of non-standard or custom-made frames necessitates careful measurement and precise matching of foundation dimensions to ensure proper fit. Failure to account for these factors can result in an unstable and unsatisfactory sleeping experience. For instance, a foundation that overhangs the bed frame presents a tripping hazard and detracts from the overall appearance.
In conclusion, frame compatibility is not merely a matter of convenience but a fundamental aspect of ensuring the structural integrity and longevity of a king-size bed. Adherence to standard dimensions and careful consideration of frame-specific requirements are essential for achieving a stable, supportive, and aesthetically pleasing sleep environment. Neglecting this aspect can lead to premature mattress wear, frame damage, and an overall compromised sleeping experience. A thorough understanding of frame compatibility and associated measurements is therefore indispensable for any informed consumer.
5. Support Structure
The support structure inherent within the dimensions of a king-size foundation is critical for maintaining mattress integrity and ensuring proper weight distribution. A king mattress, due to its significant surface area and potential weight load, requires a robust foundation to prevent sagging and premature wear. The internal framework, typically constructed of wood or metal, must be designed to evenly distribute weight across its surface. Inadequate support within the defined dimensions can lead to localized stress points, resulting in mattress deformation and reduced sleep quality. For example, if the central portion of the foundation lacks sufficient reinforcement, the mattress may sag in the middle, causing discomfort and potential back problems for the sleeper. The dimensions, therefore, dictate the necessary strength and configuration of the internal supports.
The practical implications of a properly designed support structure are considerable. A well-supported mattress maintains its shape and resilience over time, extending its lifespan and ensuring consistent comfort. This support also contributes to proper spinal alignment, reducing the risk of aches and pains associated with inadequate sleep surfaces. The dimensional aspects of the foundation also influence the type of support structure that can be effectively implemented. A low-profile foundation, for instance, may necessitate a different support configuration than a standard-height foundation to achieve comparable levels of support. Understanding this relationship allows consumers to make informed decisions when selecting a foundation that meets their specific needs and preferences. Selecting a foundation with great support structure can mean saving money in the long run and can help with quality of sleep.
In summary, the support structure and the dimensions of a king-size foundation are inextricably linked. The dimensions establish the parameters within which the support structure must operate, while the support structure itself determines the foundation’s ability to effectively support the mattress and maintain its integrity over time. Challenges arise when attempting to optimize support within dimensional constraints, requiring careful engineering and material selection. A thorough understanding of this connection is essential for ensuring a comfortable, supportive, and long-lasting sleep environment.
6. Edge Reinforcement
Edge reinforcement, as it relates to king foundation measurements, constitutes a critical design element influencing sleep surface stability and longevity. The perimeter of a foundation, particularly at its edges, is inherently susceptible to compression and wear due to concentrated weight and pressure from individuals sitting or sleeping near the sides. Without reinforcement, the edges of the foundation can degrade, leading to mattress sagging and reduced usable sleep area. For example, a couple sharing a king bed may inadvertently roll towards the center if the edge support is inadequate, diminishing individual comfort. Therefore, edge reinforcement acts as a preventative measure against structural failure within the defined foundation dimensions.
Practical applications of effective edge reinforcement are evident in the construction materials and design techniques employed. High-density foam encasements, strategically placed metal supports, or reinforced wood frames along the foundation’s edges are common methods used to enhance stability. The dimensions of these reinforcements are carefully calculated to withstand anticipated loads and stresses. For instance, a foundation with reinforced edges might exhibit a more rigid and uniform surface compared to one lacking such reinforcement, resulting in a more supportive and consistent sleep experience across the entire mattress surface. Furthermore, appropriate edge support extends the usable lifespan of the mattress by preventing uneven wear patterns, thereby protecting the investment.
In summary, edge reinforcement within the defined foundation dimensions is essential for optimizing sleep surface stability, preventing mattress sagging, and maximizing usable sleep area. Overcoming challenges associated with cost and design complexity, effective edge reinforcement is paramount for delivering a comfortable and durable sleep experience. A clear understanding of the connection helps with properly supporting sleep system which involves mattress and foundation. The consequences of neglecting this aspect can compromise the integrity of the bed and diminishes sleep quality.
7. Weight Capacity
Weight capacity is a critical consideration when examining foundation dimensions, specifically within the context of king-size mattresses. The foundation’s dimensions dictate the structural requirements necessary to support a defined weight load without compromising integrity. A foundation engineered with insufficient weight capacity for its dimensions can exhibit premature sagging, structural failure, and a diminished lifespan. For example, a king mattress, often paired with two adult sleepers, may exert considerable pressure on the foundation. If the foundation lacks the requisite weight capacity, the internal support system can buckle, leading to uneven weight distribution and potential discomfort. Therefore, weight capacity is not merely a specification but an integral component of the foundation’s structural design, directly influenced by its dimensions.
Practical implications of understanding weight capacity are significant. Consumers should select a foundation with a weight rating that exceeds the combined weight of the mattress and its intended occupants. Failure to do so can invalidate warranties and result in costly replacements. A king-size memory foam mattress, known for its density and weight, requires a foundation with a higher weight capacity than a lighter innerspring mattress. Retailers often provide weight capacity information, and consumers should verify this information before purchase. Neglecting this aspect can result in premature wear and tear, reducing the overall value and performance of the sleep system. Also, it could result in a compromised and unsanitary sleep setting.
In summary, weight capacity and foundation dimensions are intrinsically linked. The dimensions define the physical space within which the support structure must operate, while the weight capacity dictates the strength and resilience required of that structure. Challenges arise in balancing weight capacity with other factors, such as cost and profile height, requiring careful consideration during the design and manufacturing processes. Awareness and a clear understanding of weight capacity are essential for ensuring a comfortable, supportive, and durable sleep environment.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding King Size Mattress Box Spring Dimensions
The following questions address common inquiries and misconceptions surrounding the dimensions of king-size mattress foundations. These answers aim to provide clarity and ensure informed decision-making during the purchase process.
Question 1: Are all king-size mattress foundations truly the same dimensions?
While a “standard” king mattress foundation nominally measures 76 inches wide by 80 inches long, slight variations may exist due to manufacturing tolerances or design differences. It is always advisable to verify actual dimensions before purchasing to ensure compatibility with the mattress and bed frame.
Question 2: How does foundation height impact the overall bed height and is there a standard height?
Foundation height directly influences the overall bed height. There is no single “standard,” but typical heights range from low-profile (approximately 5 inches) to standard (approximately 9 inches). The choice depends on personal preference, mattress thickness, and ease of access.
Question 3: What role does edge support play within the established foundation dimensions?
Edge support is crucial for preventing mattress sagging along the perimeter and maximizing the usable sleep surface. Reinforced edges enhance stability and prevent roll-off, particularly for those who sleep near the edge of the bed. The edge support structure is built into the dimensions.
Question 4: How important is the weight capacity of a king mattress foundation relative to its dimensions?
Weight capacity is paramount. The foundation must be able to support the combined weight of the mattress and occupants without compromising structural integrity. Selecting a foundation with an inadequate weight capacity can lead to premature wear and potential failure.
Question 5: Can a split king foundation, with its differing dimensions of each split, adequately support a standard king mattress?
A split king foundation (two twin XL foundations) can support a standard king mattress, provided that the combined dimensions of the two foundations match the standard king size (76 inches x 80 inches) and the support structure is robust. The split design facilitates easier transport and setup.
Question 6: How do the internal support structures relate to the king size mattress box spring dimensions?
The internal support system must be optimized within the defined dimensions to provide even weight distribution and prevent sagging. Wood or metal frames with closely spaced slats are common and should be selected depending on the type and weight of your mattress. In this case, it relates because a small mistake could affect the quality of sleep.
Understanding these dimensions and their implications is essential for selecting a king mattress foundation that provides adequate support, enhances comfort, and promotes long-term mattress durability.
The following section will provide advice on making informed decisions regarding king mattress foundation selection, including key factors to consider before making a purchase.
King Size Mattress Box Spring Dimensions
The preceding exploration of king size mattress box spring dimensions underscores their critical influence on sleep system performance. Proper consideration of width, length, height, support structure, edge reinforcement, and weight capacity is essential for ensuring mattress longevity, structural integrity, and user comfort. Deviations from standard dimensions or inadequate attention to support elements can compromise the sleep experience and lead to premature wear.
Therefore, diligent assessment of king size mattress box spring dimensions is not a trivial matter but a necessary step toward optimizing sleep quality and maximizing the value of the bedding investment. Consumers are encouraged to approach this selection process with informed discernment, prioritizing compatibility and long-term performance over superficial considerations. Failure to do so may result in a diminished sleep experience and avoidable financial burden.